Morphometric and meristic variability in butis koilomatodon (gobiiformes: eleotridae) in estuarine and coastal areas of the Mekong delta
The study aimed to investigate morphometric and meristic variability
in the mud sleeper Butis koilomatodon (Bleeker, 1849) in the Mekong
Delta. This species is a commercial fish species with a small-size and
is mainly distributed in some coastal areas from Tra Vinh to Ca Mau
provinces. In the present research, the parameters of morphometry
and measurement, including the head length, body depth, eye
diameter, distance of the two eyes, and the interrelationships among
the morphometric variables, were determined. The results revealed
that the total length and weight of the fish changed by sex, season,
habitat, and the interaction between the seasons and habitats.
Likewise, the meristic criteria were different between males and
females, and the dry and wet seasons, but not by their interactions.
The growth rate of males was faster than females. The outcomes also
showed that the body size of this species was larger in the dry season
and the largest fish were found in Duyen Hai and Tra Vinh provinces.
The Findings would be useful not only for further effects of
environmental factors on morphology but also for comparisons
between congeners Butis morphologically.

Trang 1

Trang 2
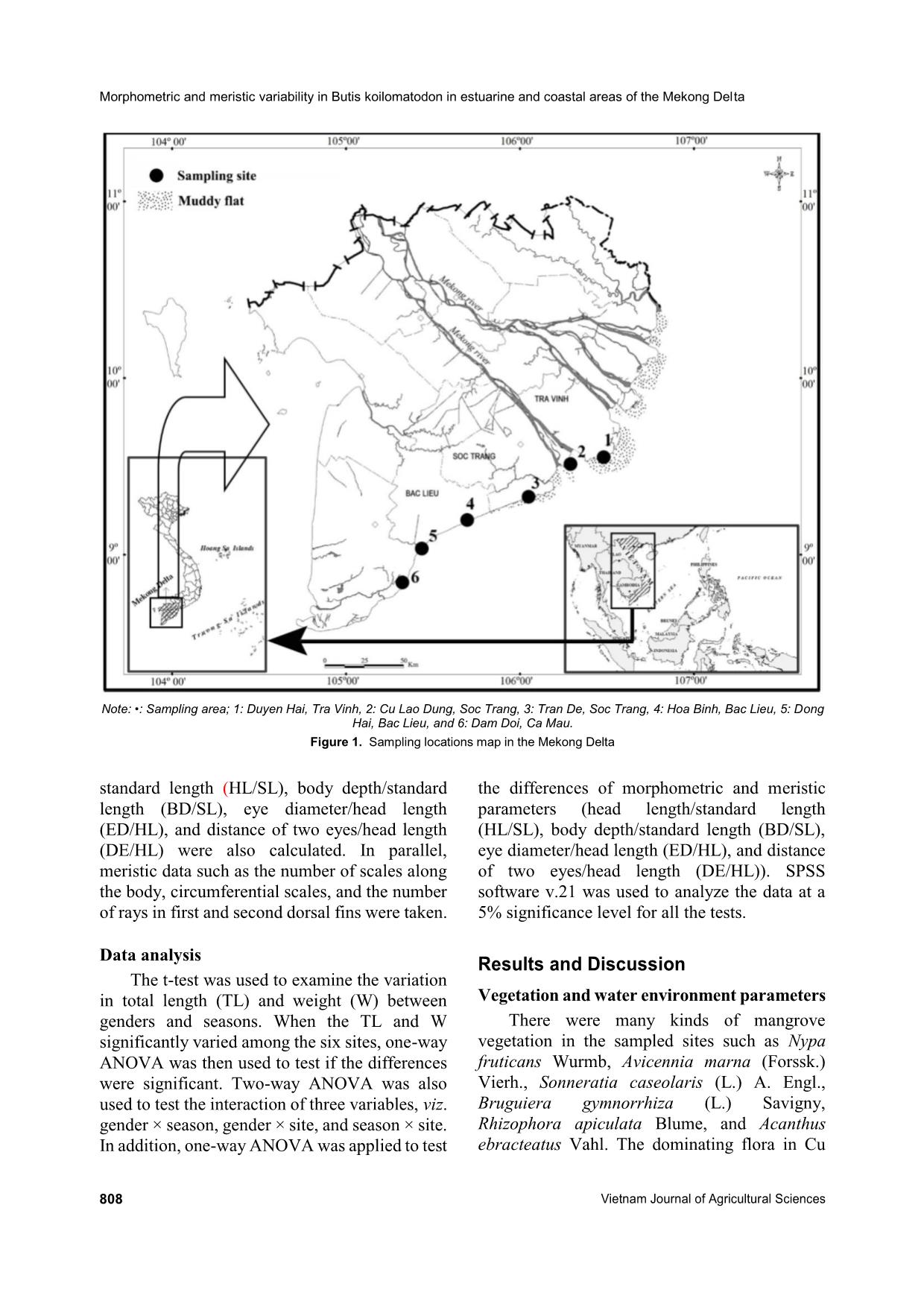
Trang 3
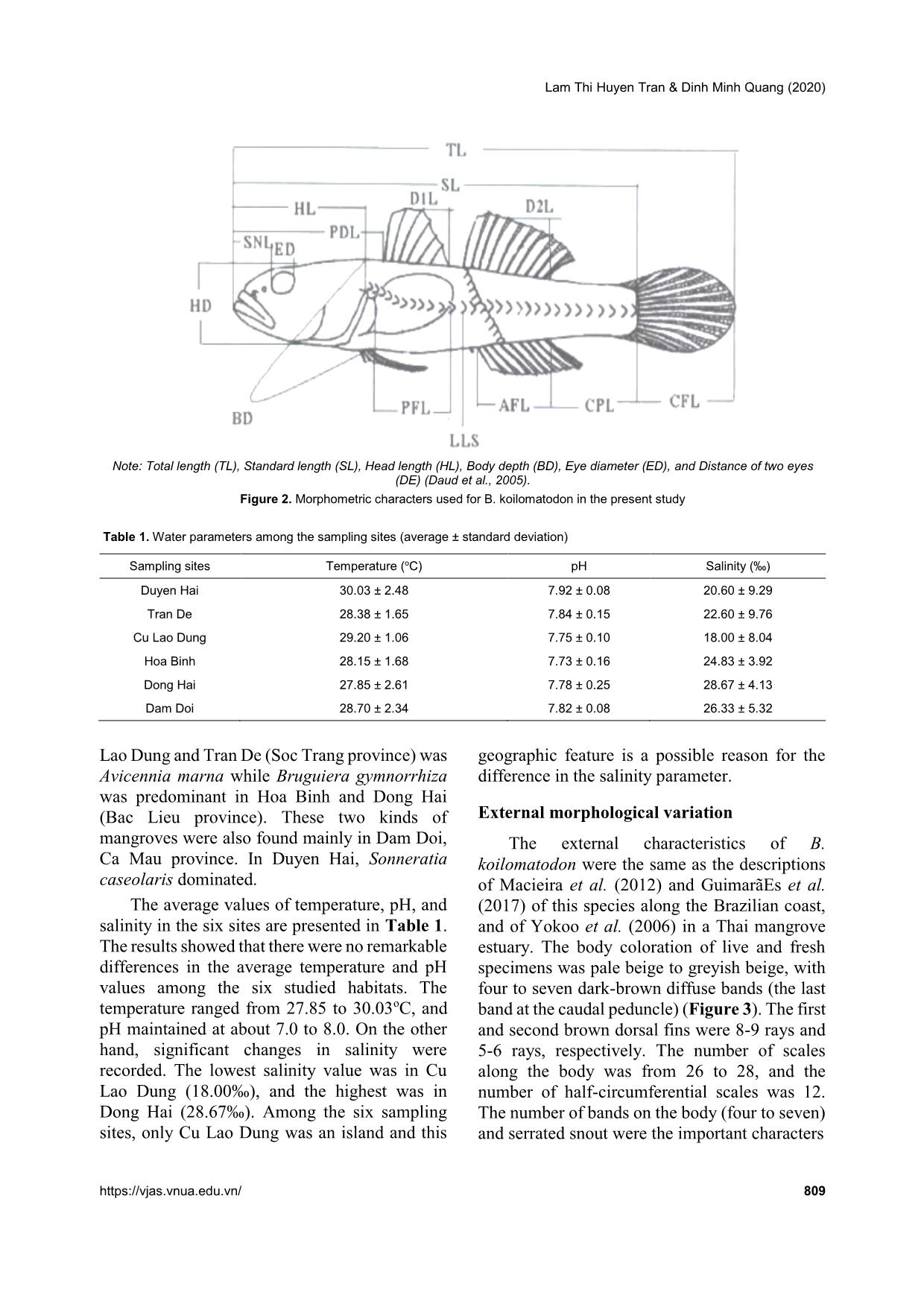
Trang 4

Trang 5
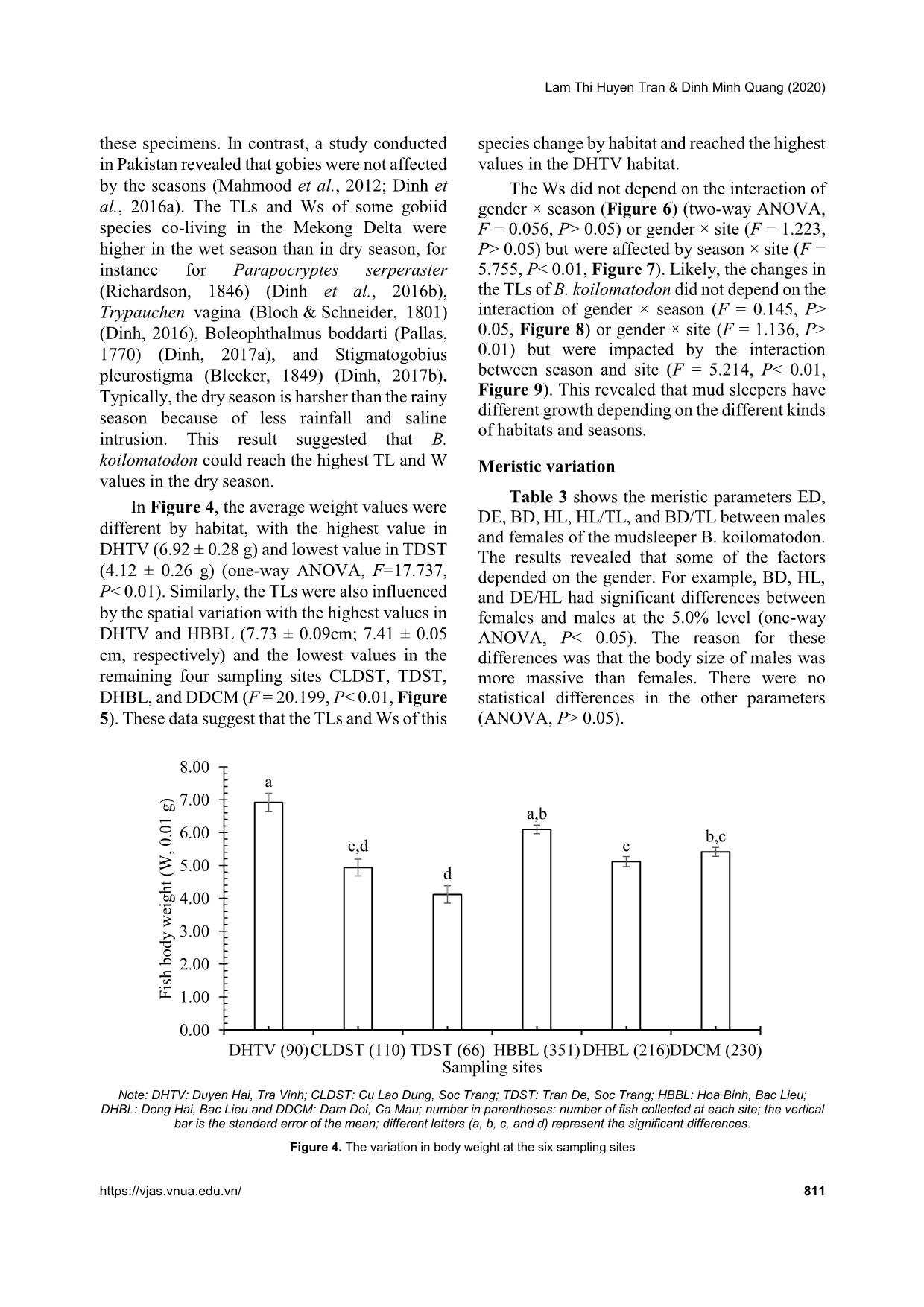
Trang 6
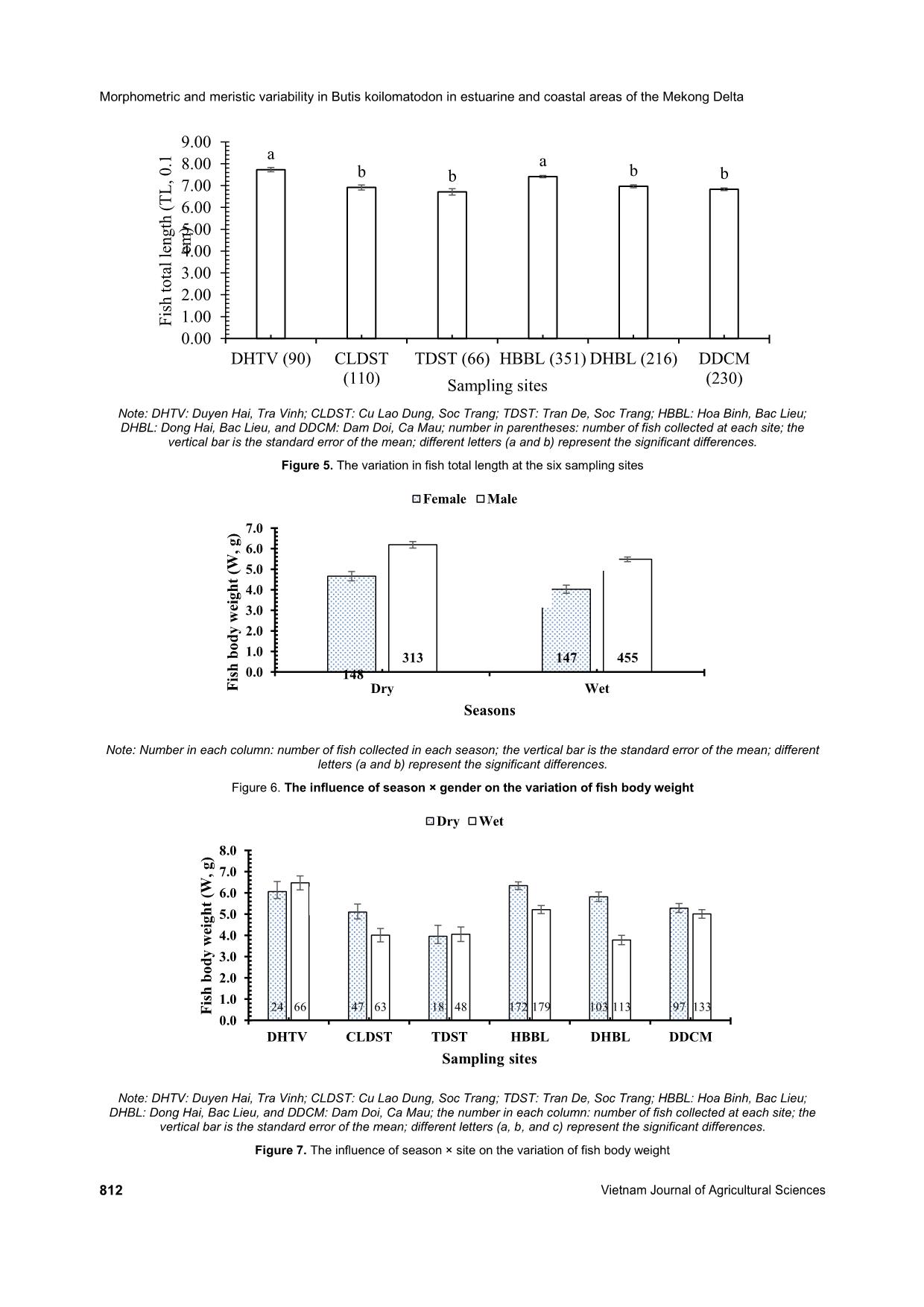
Trang 7
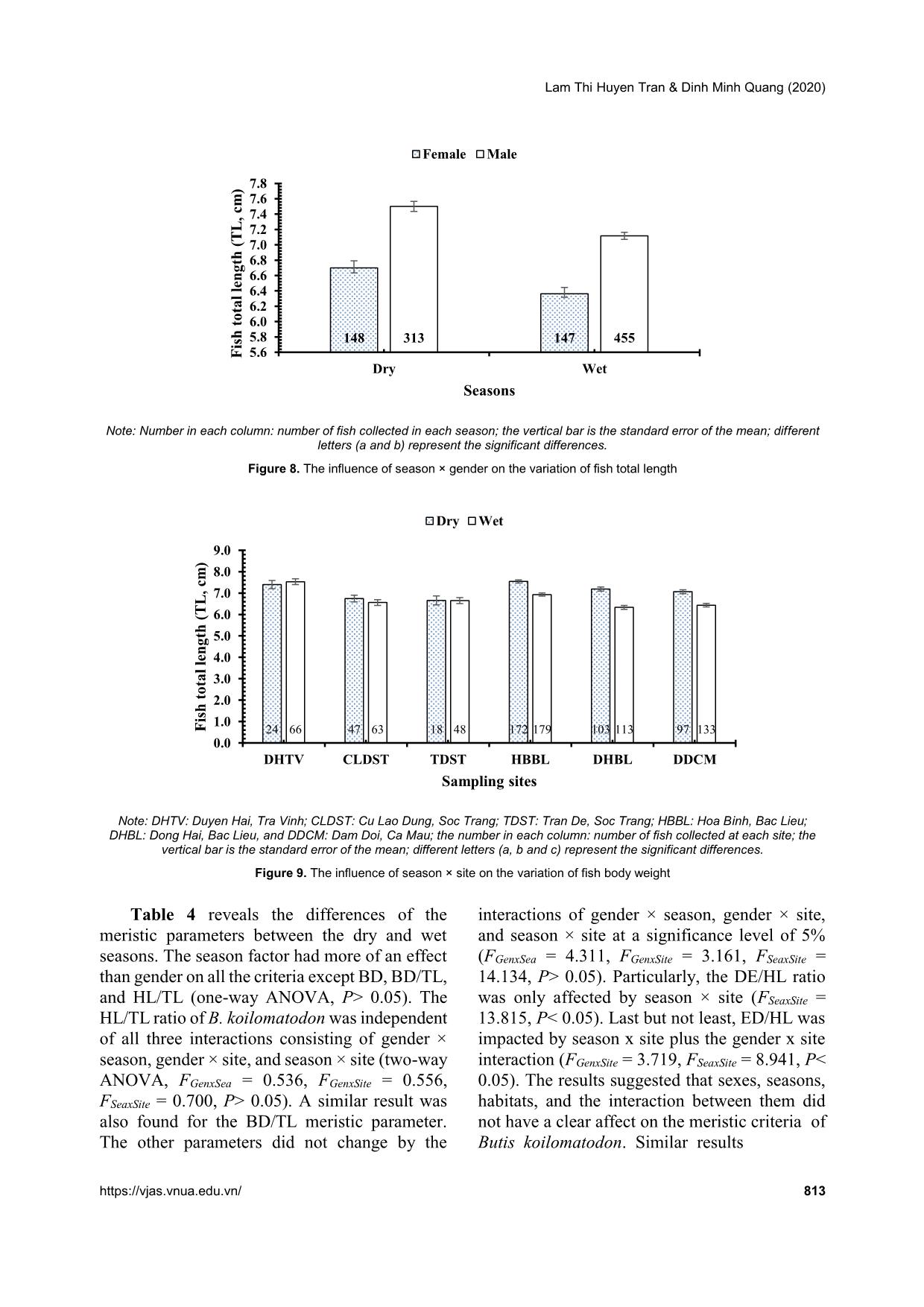
Trang 8
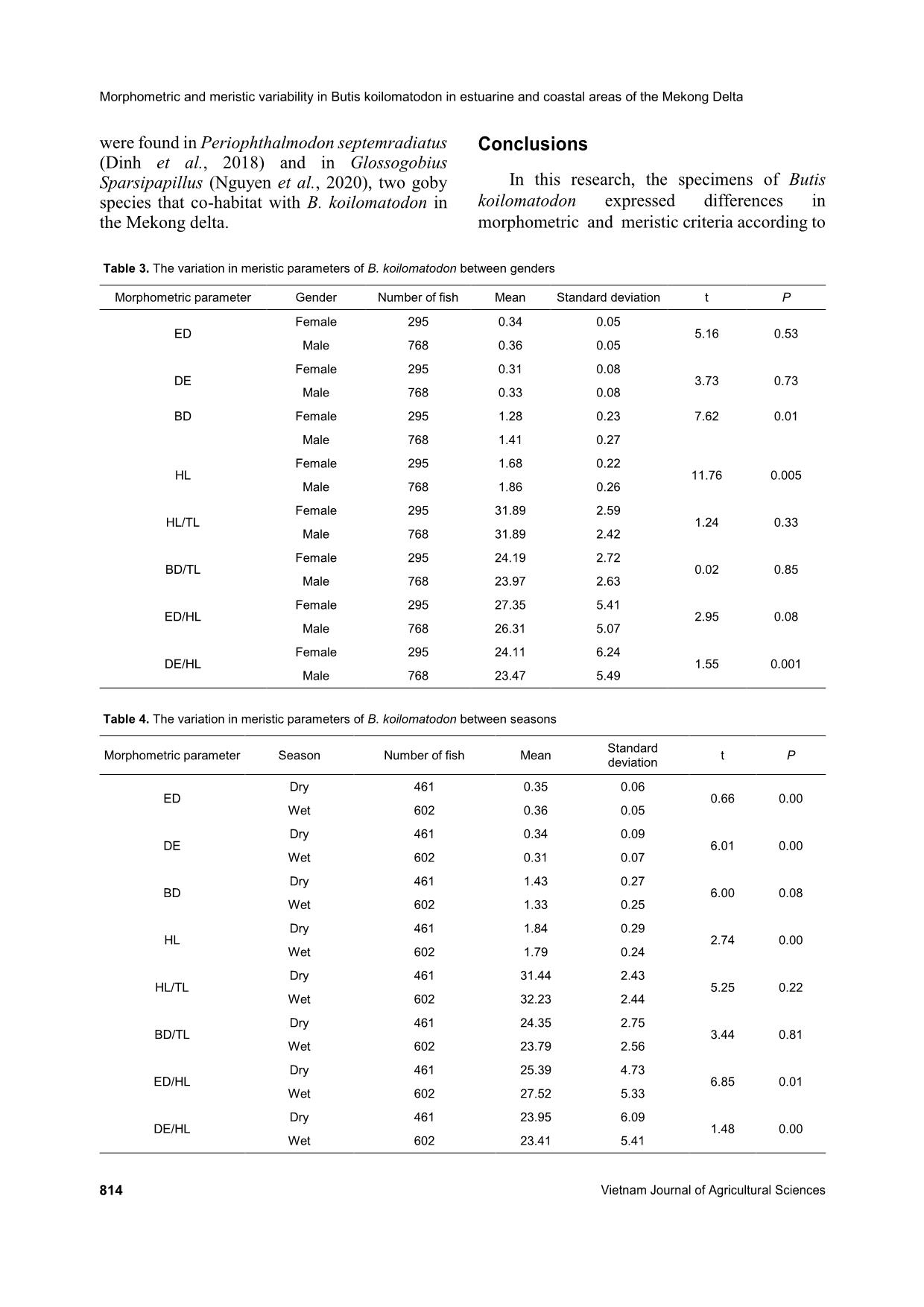
Trang 9

Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Morphometric and meristic variability in butis koilomatodon (gobiiformes: eleotridae) in estuarine and coastal areas of the Mekong delta

Vietnam Journal of Agricultural Sciences ISSN 2588-1299 VJAS 2020; 3(4): 806-816 https://doi.org/10.31817/vjas.2020.3.4.04 806 Vietnam Journal of Agricultural Sciences Received: June 8, 2020 Accepted: October 28, 2020 Correspondence to dmquang@mku.edu.vn Morphometric and Meristic Variability in Butis koilomatodon (Gobiiformes: Eleotridae) in Estuarine and Coastal Areas of the Mekong Delta Lam Thi Huyen Tran1,2 & Dinh Minh Quang3 1Biotechnology Research and Development Institute, Can Tho University, Can Tho 900000, Vietnam 2Faculty of Agriculture and Fishery, University of Cuu Long, Vinh Long 890000, Vietnam 3Department of Biology, School of Education, Can Tho University, Can Tho 900000, Vietnam Abstract The study aimed to investigate morphometric and meristic variability in the mud sleeper Butis koilomatodon (Bleeker, 1849) in the Mekong Delta. This species is a commercial fish species with a small-size and is mainly distributed in some coastal areas from Tra Vinh to Ca Mau provinces. In the present research, the parameters of morphometry and measurement, including the head length, body depth, eye diameter, distance of the two eyes, and the interrelationships among the morphometric variables, were determined. The results revealed that the total length and weight of the fish changed by sex, season, habitat, and the interaction between the seasons and habitats. Likewise, the meristic criteria were different between males and females, and the dry and wet seasons, but not by their interactions. The growth rate of males was faster than females. The outcomes also showed that the body size of this species was larger in the dry season and the largest fish were found in Duyen Hai and Tra Vinh provinces. The Findings would be useful not only for further effects of environmental factors on morphology but also for comparisons between congeners Butis morphologically. Keywords Measurement, meristic criteria, morphometry, the growth rate, the mud sleeper Introduction Morphometric and meristic characters have played a crucial role in identifying fish stocks and establishing the evolutionary linkages between ancient and modern fish fauna (Turan, 2004). In fisheries biology, morphometric characteristics have been used to estimate the percentage of fish harvested from length-weight data, determine the effects of environmental improvement, and regulate fisheries Lam Thi Huyen Tran & Dinh Minh Quang (2020) https://vjas.vnua.edu.vn/ 807 (Ibáñez-Aguirre et al., 2006). In classification, this information has been useful to classify fish (Nelson et al., 2016) and measure differences and relationships among congeners (Turan et al., 2006). Besides, they have also been used to study variations due to environmental factors (Hossain et al., 2009). Sandlund et al. (1992) noted that the morphological characteristics of fish populations like body coloration, meristic characteristics, growth, size, and age at sexual maturity could differ in different habitats. Morphological characteristics may be the result of evolution over time to adapt to natural selective pressures, genetic modifications, food availability, habitat competition, or even simple coincidence (Burns & Sidlauskas, 2019; Thacker & Gkenas, 2019). Butis koilomatodon (Bleeker, 1849) belongs to the family Eleotridae, order Gobiiformes, and is found along the Indo-Western Pacific region as a native species (Dawson, 1973). However, it is considered an invasive species in northeastern Brazil, competing with other native gobies for food and habitat (Macieira et al., 2012; GuimarãEs et al., 2017). This goby is a carnivore, and its main food items are crustaceans and small fish (Froese and Pauly, 2000). This mud goby usually dwells in estuaries and mangrove creeks with salinity from 3.8‰ to 37.0‰ (Contente et al., 2016). In Vietnam, B. koilomatodon is found in the Mekong Delta (Rainboth, 1996; Tran et al., 2013), especially in coastal areas. Because of its nutritional value, good flavor, and firm texture, the economic value of this fish is relatively high. Nevertheless, recent studies on the morphological characters of B. koilomatodon have been fragmented and insufficient (Soares et al., 2012; Contente et al., 2016; GuimarãEs et al., 2017). Hence, this research aims to fill the knowledge gaps about the morphometric and meristic parameters of this species according to gender, season, and regions of several Vietnamese provinces, namely Duyen Hai (Tra Vinh); Cu Lao Dung and Tran De (Soc Trang); Hoa Binh and Dong Hai (Bac Lieu); and Dam Doi (Ca Mau). Materials and Methods Study sites Fish samples were collected from 04/2019 to 03/2020 in six different sites along estuarine regions, namely Duyen Hai, Tra Vinh (DHTV, 9°41'18.6"N 106°30'35.8"E); Cu Lao Dung (CLDST, 9°33'20.1"N 106°16'57.9"E); ... oilomatodon did not depend on the interaction of gender × season (F = 0.145, P> 0.05, Figure 8) or gender × site (F = 1.136, P> 0.01) but were impacted by the interaction between season and site (F = 5.214, P< 0.01, Figure 9). This revealed that mud sleepers have different growth depending on the different kinds of habitats and seasons. Meristic variation Table 3 shows the meristic parameters ED, DE, BD, HL, HL/TL, and BD/TL between males and females of the mudsleeper B. koilomatodon. The results revealed that some of the factors depended on the gender. For example, BD, HL, and DE/HL had significant differences between females and males at the 5.0% level (one-way ANOVA, P< 0.05). The reason for these differences was that the body size of males was more massive than females. There were no statistical differences in the other parameters (ANOVA, P> 0.05). Note: DHTV: Duyen Hai, Tra Vinh; CLDST: Cu Lao Dung, Soc Trang; TDST: Tran De, Soc Trang; HBBL: Hoa Binh, Bac Lieu; DHBL: Dong Hai, Bac Lieu and DDCM: Dam Doi, Ca Mau; number in parentheses: number of fish collected at each site; the vertical bar is the standard error of the mean; different letters (a, b, c, and d) represent the significant differences. Figure 4. The variation in body weight at the six sampling sites a c,d d a,b c b,c 0.00 1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00 6.00 7.00 8.00 DHTV (90)CLDST (110) TDST (66) HBBL (351) DHBL (216)DDCM (230) F is h b o d y w ei g h t (W , 0 .0 1 g ) Sampling sites Morphometric and meristic variability in Butis koilomatodon in estuarine and coastal areas of the Mekong Delta 812 Vietnam Journal of Agricultural Sciences Note: DHTV: Duyen Hai, Tra Vinh; CLDST: Cu Lao Dung, Soc Trang; TDST: Tran De, Soc Trang; HBBL: Hoa Binh, Bac Lieu; DHBL: Dong Hai, Bac Lieu, and DDCM: Dam Doi, Ca Mau; number in parentheses: number of fish collected at each site; the vertical bar is the standard error of the mean; different letters (a and b) represent the significant differences. Figure 5. The variation in fish total length at the six sampling sites Note: Number in each column: number of fish collected in each season; the vertical bar is the standard error of the mean; different letters (a and b) represent the significant differences. Figure 6. The influence of season × gender on the variation of fish body weight Note: DHTV: Duyen Hai, Tra Vinh; CLDST: Cu Lao Dung, Soc Trang; TDST: Tran De, Soc Trang; HBBL: Hoa Binh, Bac Lieu; DHBL: Dong Hai, Bac Lieu, and DDCM: Dam Doi, Ca Mau; the number in each column: number of fish collected at each site; the vertical bar is the standard error of the mean; different letters (a, b, and c) represent the significant differences. Figure 7. The influence of season × site on the variation of fish body weight a b b a b b 0.00 1.00 2.00 3.00 4.00 5.00 6.00 7.00 8.00 9.00 DHTV (90) CLDST (110) TDST (66) HBBL (351) DHBL (216) DDCM (230) F is h t o ta l le n g th ( T L , 0 .1 cm ) Sampling sites 148 147313 455 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 Dry WetF is h b o d y w ei g h t (W , g ) Seasons Female Male 24 47 18 172 103 9766 63 48 179 113 133 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 DHTV CLDST TDST HBBL DHBL DDCM F is h b o d y w ei g h t (W , g ) Sampling sites Dry Wet a a b b Lam Thi Huyen Tran & Dinh Minh Quang (2020) https://vjas.vnua.edu.vn/ 813 Note: Number in each column: number of fish collected in each season; the vertical bar is the standard error of the mean; different letters (a and b) represent the significant differences. Figure 8. The influence of season × gender on the variation of fish total length Note: DHTV: Duyen Hai, Tra Vinh; CLDST: Cu Lao Dung, Soc Trang; TDST: Tran De, Soc Trang; HBBL: Hoa Binh, Bac Lieu; DHBL: Dong Hai, Bac Lieu, and DDCM: Dam Doi, Ca Mau; the number in each column: number of fish collected at each site; the vertical bar is the standard error of the mean; different letters (a, b and c) represent the significant differences. Figure 9. The influence of season × site on the variation of fish body weight Table 4 reveals the differences of the meristic parameters between the dry and wet seasons. The season factor had more of an effect than gender on all the criteria except BD, BD/TL, and HL/TL (one-way ANOVA, P> 0.05). The HL/TL ratio of B. koilomatodon was independent of all three interactions consisting of gender × season, gender × site, and season × site (two-way ANOVA, FGenxSea = 0.536, FGenxSite = 0.556, FSeaxSite = 0.700, P> 0.05). A similar result was also found for the BD/TL meristic parameter. The other parameters did not change by the interactions of gender × season, gender × site, and season × site at a significance level of 5% (FGenxSea = 4.311, FGenxSite = 3.161, FSeaxSite = 14.134, P> 0.05). Particularly, the DE/HL ratio was only affected by season × site (FSeaxSite = 13.815, P< 0.05). Last but not least, ED/HL was impacted by season x site plus the gender x site interaction (FGenxSite = 3.719, FSeaxSite = 8.941, P< 0.05). The results suggested that sexes, seasons, habitats, and the interaction between them did not have a clear affect on the meristic criteria of Butis koilomatodon. Similar results 148 147313 455 5.6 5.8 6.0 6.2 6.4 6.6 6.8 7.0 7.2 7.4 7.6 7.8 Dry Wet F is h t o ta l le n g th ( T L , cm ) Seasons Female Male 24 47 18 172 103 9766 63 48 179 113 133 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 DHTV CLDST TDST HBBL DHBL DDCM F is h t o ta l le n g th ( T L , cm ) Sampling sites Dry Wet a a a b b b c c c c c c b a b a Morphometric and meristic variability in Butis koilomatodon in estuarine and coastal areas of the Mekong Delta 814 Vietnam Journal of Agricultural Sciences were found in Periophthalmodon septemradiatus (Dinh et al., 2018) and in Glossogobius Sparsipapillus (Nguyen et al., 2020), two goby species that co-habitat with B. koilomatodon in the Mekong delta. Conclusions In this research, the specimens of Butis koilomatodon expressed differences in morphometric and meristic criteria according to Table 3. The variation in meristic parameters of B. koilomatodon between genders Morphometric parameter Gender Number of fish Mean Standard deviation t P ED Female 295 0.34 0.05 5.16 0.53 Male 768 0.36 0.05 DE Female 295 0.31 0.08 3.73 0.73 Male 768 0.33 0.08 BD Female 295 1.28 0.23 7.62 0.01 Male 768 1.41 0.27 HL Female 295 1.68 0.22 11.76 0.005 Male 768 1.86 0.26 HL/TL Female 295 31.89 2.59 1.24 0.33 Male 768 31.89 2.42 BD/TL Female 295 24.19 2.72 0.02 0.85 Male 768 23.97 2.63 ED/HL Female 295 27.35 5.41 2.95 0.08 Male 768 26.31 5.07 DE/HL Female 295 24.11 6.24 1.55 0.001 Male 768 23.47 5.49 Table 4. The variation in meristic parameters of B. koilomatodon between seasons Morphometric parameter Season Number of fish Mean Standard deviation t P ED Dry 461 0.35 0.06 0.66 0.00 Wet 602 0.36 0.05 DE Dry 461 0.34 0.09 6.01 0.00 Wet 602 0.31 0.07 BD Dry 461 1.43 0.27 6.00 0.08 Wet 602 1.33 0.25 HL Dry 461 1.84 0.29 2.74 0.00 Wet 602 1.79 0.24 HL/TL Dry 461 31.44 2.43 5.25 0.22 Wet 602 32.23 2.44 BD/TL Dry 461 24.35 2.75 3.44 0.81 Wet 602 23.79 2.56 ED/HL Dry 461 25.39 4.73 6.85 0.01 Wet 602 27.52 5.33 DE/HL Dry 461 23.95 6.09 1.48 0.00 Wet 602 23.41 5.41 Lam Thi Huyen Tran & Dinh Minh Quang (2020) https://vjas.vnua.edu.vn/ 815 genders, sites, and seasons as well as the interactions between them. The data indicated that this species reached the highest values of body size in the dry season. In addition, the highest values of its body size were recorded in DHTV. These results would provide useful information for further studies about the influence of food availability and geographical environment on the morphological characteristics of this mud sleeper. Acknowledgements We are grateful to the Ministry of Education and Training for funding support (Project No.: B2019-TCT-02), and Nguyen Thi Nha Y, Nguyen Huu Duc Ton, Nguyen Thi Thuy Hien, Tran Chi Canh, and Dang Hoa Thao for assisting in fish collection and data analysis. References Burns M. D. & Sidlauskas B. L. (2019). Ancient and contingent body shape diversification in a hyperdiverse continental fish radiation. Evolution. 73: 569-587. Contente R. F., Brenha-Nunes M. R., Siliprandi C. C., Lamas R. A. & Conversani V. R. (2016). A new record of the non-native fish species Butis koilomatodon (Bleeker 1849) (Teleostei: Eleotridae) for southeastern Brazil. Biotemas. 29: 113-118. Daud S. K., Mohammadi M., Siraj S. S. & Zakaria M. P. (2005). Morphometric analysis of Malaysian oxudercine goby, Boleophthalmus boddarti (Pallas, 1770). Pertanika Journal of Tropical Agricultural Science. 28: 121-134. Dawson C. (1973). Occurrence of an exotic eleotrid fish in Panama with discussion of probable origin and mode of introduction. Copeia. 1973(1): 141-144. Dinh M. Q., Tran T. L. & Nguyen T. Y. N. (2018). The flexibility of morphometric and meristic measurements of Periophthalmodon septemradiatus (Hamilton, 1822) in Hau river. Journal of Science and Technology. 187: 81-90. Dinh Q. M. (2016). Growth pattern and body condition of Trypauchen vagina in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. The Journal of Animal and Plant Sciences. 26: 523-531. Dinh Q. M. (2017a). Morphometric, growth and condition factor variations of Boleophthalmus boddarti in the Mekong delta, Vietnam. Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences. 16: 822-831. Dinh Q. M. (2017b). Morphometrics and condition factor dynamics of the goby Stigmatogobius pleurostigma (Bleeker 1849) during dry and wet seasons in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Asian Fisheries Sciences. 30: 17-25. Dinh Q. M., Qin J. G., Dittmann S. & Tran D. D. (2016a). Morphometric variation of Parapocryptes serperaster (Gobiidae) in dry and wet seasons in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Ichthyological Research. 63: 267-274. Dinh Q. M., Qin J. G., Dittmann S. & Tran D. D. (2016b). Reproductive biology of the burrow dwelling goby Parapocryptes serperaster. Ichthyological Research. 63: 324-332. Dinh Q. M., Tran L. T., Ngo N. C., Pham T. B. & Nguyen T. T. K. (2020). Reproductive biology of the unique mudskipper Periophthalmodon septemradiatus living from estuary to upstream of the Hau River. Acta Zoologica. 101: 206-217. Froese R. & Pauly D. (2000). FishBase a global information system on fishes. FishBase, Makati City, Philippines. GuimarãEs E. C., Brito P. & Ottoni F. P. (2017). First record of Butis koilomatodon (Bleeker, 1849)(Gobiiformes: Eleotridae) for the Maranhão state, northeastern Brazil: a case of bioinvasion. Cybium. 41: 299-300. Hossain M. Y., Ohtomi J., Ahmed Z. F., Ibrahim A. H. M. & Jasmine S. (2009). Length-weight and morphometric relationships of the Tank goby Glossogobius giuris (Hamilton, 1822) (Perciformes: Gobiidae) in the Ganges of Northwestern Bangladesh. Asian Fisheries Sciences. 22: 961-969. Houde A. E. (2001). Sex roles, ornaments, and evolutionary explanation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 98: 12857-12859. Ibáñez-Aguirre A. L., Cabral-Solís E., Gallardo-Cabello M. & Espino-Barr E. (2006). Comparative morphometrics of two populations of Mugil curema (Pisces: Mugilidae) on the Atlantic and Mexican Pacific coasts. Scientia Marina. 70: 139-145. Le Thong, Nguyen Minh Tue, Nguyen Van Phu, Nguyen Dang Chung, Pham Xuan Hau, Nguyen Thi Son, Hoang Van Chuc, Hoang Phuc Lam, Le Huynh & Dao Ngoc Canh (2006). Provinces and City in the Mekong Delta. Education Publishing House, Hanoi (in Vietnamese). Lindström K. & Hellström M. (1993). Male size and parental care in the sand goby, Pomatoschistus minutus. Ethology Ecology and Evolution. 5: 97-106. Macieira R., Giarrizzo T., Gasparini J. & Sazima I. (2012). Geographic expansion of the invasive mud sleeper Butis koilomatodon (Perciformes: Eleotridae) in the western Atlantic Ocean. Journal of Fish Biology. 81: 308-313. Mahmood K., Ayub Z., Moazzam M. & Siddiqui G. (2012). Length-weight relationship and condition factor of Ilisha melastoma (Clupeiformes: Pristigasteridae) off Pakistan. Pakistan Journal of Zoology. 44: 71-77. Murdy E. O. (1989). A taxonomic revision and cladistic Morphometric and meristic variability in Butis koilomatodon in estuarine and coastal areas of the Mekong Delta 816 Vietnam Journal of Agricultural Sciences analysis of the oxudercine gobies (Gobiidae, Oxudercinae). Australian Museum Journal. 11: 93. Nelson J. S., Grande T. C. & Wilson M. V. (2016). Fishes of the World. John Wiley & Sons. Nguyen T. H. D., Nguyen H. T. T., Tran T. C., Nguyen Y. T. N. & Dinh Q. M. (2020). Morphometric and meristic variations of Glossogobius sparsipapillus along the coastline in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam, International Journal of Zoology and Animal Biology. 3: 1-9. Rainboth W. J. (1996). Fishes of the Cambodian Mekong. FAO, Roma. Sandlund O. T., Gunnarsson K., Jónasson P. M., Jonsson B., Lindem T., Magnússon K. P., Malmquist H. J., Sigurjónsdóttir H., Skúlason S. & Snorrason S. S. (1992). The arctic charr Salvelinus alpinus in Thingvallavatn. Oikos. 64: 305-351. Soares B. E., Ruffeil T. O. B. & Montag L. d. A. (2012). Occurrence of the non-native sleeper Butis koilomatodon (Bleeker, 1849) (Perciformes: Eleotridae) in the Amazon coastal zone, Brazil. BioInvasions Records. 1: 95-99. Thacker C. E. & Gkenas C. (2019). Morphometric convergence among European sand gobies in freshwater (Gobiiformes: Gobionellidae). Ecology and Evolution. 9: 8087-8103. Tran Dac Dinh, Shibukawa, K., Nguyen Thanh Phuong, Ha Phuoc Hung, Tran Tran Xua Loi, Mai Van Hieu, & Utsugi K. (2013). "Fishes of Mekong Delta, Vietnam," Can Tho University Publisher, Can Tho (in Vietnamese). Turan C. (2004). Stock identification of Mediterranean horse mackerel (Trachurus mediterraneus) using morphometric and meristic characters. ICES Journal of Marine Science. 61: 774-781. Turan C., Oral M., Öztürk B. & Düzgüneş E. (2006). Morphometric and meristic variation between stocks of Bluefish (Pomatomus saltatrix) in the Black, Marmara, Aegean and northeastern Mediterranean Seas. Fisheries Research. 79: 139-147. Yokoo T., Kanou K., Moteki M., Kohno H., Tongnunui P. & Kurokura H. (2006). Juvenile morphology and occurrence patterns of three Butis species (Gobioidei: Eleotridae) in a mangrove estuary, southern Thailand. Ichthyological Research. 53: 330-336.
File đính kèm:
 morphometric_and_meristic_variability_in_butis_koilomatodon.pdf
morphometric_and_meristic_variability_in_butis_koilomatodon.pdf

