Biochemical compositions, antioxidant activity, and in vitro antibacterial activity of extract from wild bitter melon (momordica charantia var. abbreviata ser.)
Wild bitter melon (Momordica charantia var. abbreviata Ser.) is a type of vine that grows
wildly in the mountains and plains in Vietnam. The main use parts of the tree are fruit, stem,
and leaf that can be eaten as vegetables. This study aims to (1) identify several bioactive chemical
compounds in the stems and leaves of bitter melon trees in the forests in the district of Mang Yang,
Gia Lai province; (2) evaluate the nutrient composition, antioxidant activity, and antimicrobial
ability of fresh juice and extract with ethanol 70°. The results indicated that fresh juice and ethanol
70° extract currently inhibited the growth of experimental strains of microorganisms, in which
ethanol 70o extract gives the highest antimicrobial effect. The qualitative results determined
that the chemical components of wide bitter melon consist of flavonoids, saponins, tannins,
free reducing sugar, organic acids, starch, and fatty acids as the basis for the standardization of
exploitation of medicinal resources this material.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4
Trang 5

Trang 6
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Biochemical compositions, antioxidant activity, and in vitro antibacterial activity of extract from wild bitter melon (momordica charantia var. abbreviata ser.)

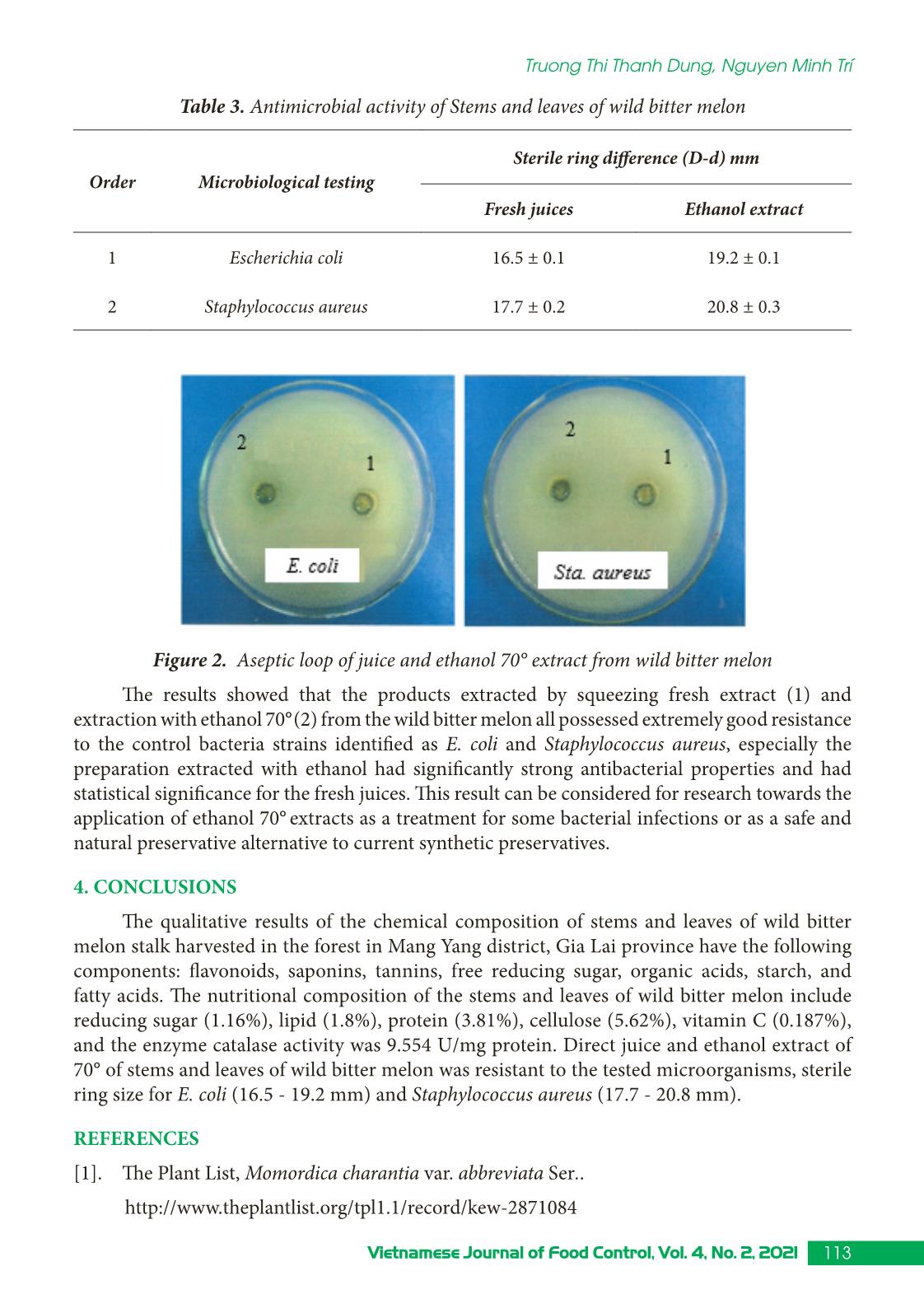
Research Article 109Vietnamese Journal of Food Control, Vol. 4, No. 2, 2021 Biochemical compositions, antioxidant activity, and in vitro antibacterial activity of extract from wild bitter melon (Momordica charantia var. abbreviata Ser.) Truong Thi Thanh Dung1, Nguyen Minh Trí2* 1Pleiku High School, Gia Lai, Vietnam 2University of Sciences, Hue University, Thua Thien Hue, Vietnam (Received: 10/04/2021; Accepted: 25/05/2021) Abstract Wild bitter melon (Momordica charantia var. abbreviata Ser.) is a type of vine that grows wildly in the mountains and plains in Vietnam. The main use parts of the tree are fruit, stem, and leaf that can be eaten as vegetables. This study aims to (1) identify several bioactive chemical compounds in the stems and leaves of bitter melon trees in the forests in the district of Mang Yang, Gia Lai province; (2) evaluate the nutrient composition, antioxidant activity, and antimicrobial ability of fresh juice and extract with ethanol 70°. The results indicated that fresh juice and ethanol 70° extract currently inhibited the growth of experimental strains of microorganisms, in which ethanol 70o extract gives the highest antimicrobial effect. The qualitative results determined that the chemical components of wide bitter melon consist of flavonoids, saponins, tannins, free reducing sugar, organic acids, starch, and fatty acids as the basis for the standardization of exploitation of medicinal resources this material. Keywords: momordica charantia, antioxidant activity, antimicrobial ability. 1. INTRODUCTION It was reported that the wild bitter melon (Momordica charantia var. abbreviata Ser.) grows wildly in all mountainous regions in Vietnam [1], it has a life cycle of 3 - 4 months. Fruits are mainly used for vegetable consumption, whereas stalks, leaves, and seeds are mostly discarded. Wild bitter melon fruit has been widely used in folk medicine to treat diabetes [2]. Although many studies have been demonstrated that bitter melon contains many groups of natural compounds including saponins; the chemical composition and antibacterial properties of the medicinal plant remain unclear. This article introduces the nutritional and qualitative composition of chemical compounds and antibacterial properties of bitter leaf stalks through the forest as a scientific basis for the use of this raw material in medical application, such as drugs, functional foods, and so on, which contribute to the conservation and development of medicinal plant resources. 2. MATERIALS AND METHODS 2.1. Research subjects Stems and leaves of wild bitter melon trees with a size of 15 - 20 cm from the tops were collected in Mang Yang district, Gia Lai province from December 2020 to March 2021 (Figure 1). *Corresponding author: Tel: 0914031085 Email: trihatrangthi@gmail.com 110 Vietnamese Journal of Food Control, Vol. 4, No. 2, 2021 Biochemical compositions, antioxidant activity, and in vitro antibacterial... Figure 1. Stems and leaves of wild bitter melon The collected samples were washed, dried, and ground for the experiments. 2.2. Research methods The quality of chemical components in raw materials was estimated through the following criteria: flavonoids, alkaloids, saponins, tannins, reducing sugar, organic acids, etc. according to Nguyen Van Dan [3]. - Determination of protein content using the Bradford method [4]. - Quantification of fiber by hydrolysis with acid [4]. - Quantification of reducing sugar using DNS method [4]. - Quantification of vitamin C using iodometric titration method [4]. - Determination of enzyme catalase activity according to Nguyen Van Mui [4]. - Determination of the total polyphenol content according to the Folin-Ciocalteu method [5]. - Determination of the antibacterial activity of the extract by diffusion method on agar plates. Accordingly, the tested antimicrobial activity was assessed by measuring the radius of the inhibitory ring (BK) by the formula BK (mm) = D - d where D was the diameter of the sterile ring and d was the hole diameter [6]. The sensitivity of bacteria to extracts was classified according to the antibacterial ring diameter: + Antimicrobial ring diameter < 8 mm: not good + Diameter of an antibacterial ring from 9 - 14 mm: good + Diameter of antibacterial ring 15 - 19 mm: very good + Antimicrobial ring diameter > 20 mm: extremely good [7]. Data processing the results of the measured antibacterial loop were analyzed from the mean of the replications, expressed in terms of mean ± SD. ANOVA and LSD were used to examine differences between the treatment groups. 111Vietnamese Journal of Food Control, Vol. 4, No. 2, 2021 Truong Thi Thanh Dung, Nguyen Minh Trí 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS 3.1. Qualitative chemical components in stems and leaves of wild bitter melon Stems and leaves of wild bitter melon were dried and ground into a paste. Qualitative analysis was then performed with specific chemical reagents. The results were shown in Table 1. Table 1. The qualitative results of organic matter in stems and leaves of wild bitter melon No. Chemical substance Characteristic response Results Conclusion 1 Flavonoid React with alkali ++ Containing flavonoid React with FeCl3 5% ++ 2 Alkaloid Reaction Mayer ++ Containing alkaloid Bouchard reaction ++ 3 Glycoside Baljet reaction ++ Containing glycoside Kell – Kiliani reaction + 5 Saponin Foaming phenomenon +++ Containing saponinDistinguish between steroid sa- ponins and triterpenoid saponins +++ 6 Anthropoid Bonrntrager reaction ++ Containing anthracoid 7 Reducing sugar Fehling reaction ++ Containing reducing sugar 8 Organic acid React with Na2CO3 ++ Containing organic acid 9 Tannin React with FeCl3 5% ++ Containing tannin React with (CH3COO)2Pb 20% ++ 10 Fatty acid Blur on filter paper ++ Containing fatty 12 Starch React with Lugol’s reagent ++ Containing starch Notes: +: Positive reaction ++: Clear positive reaction -: Negative reaction +++: The positive reaction is very clear From the qualitative results of the groups of substances, it can be concluded that the stems and leaves of wild bitter melon consist of flavonoids, saponins, tannins, free reducing sugars, organic acids, starch, and fatty acids. 3.2. Nutritional composition of stems and leaves of wild bitter melon Biochemical analysis results investigated that there are full of elemental quantities and minerals in the stems and leaves of wild bitter melon: 5.81/100 g of protein, 0.98/100 g of fat; 4.75/100 g of fiber, 1.95/100 g of sugar, etc. Especially, in the leaf stem of wild bitter melon, there are many beneficial nutrients for the body such as iron, calcium, magnesium, and zinc. 112 Vietnamese Journal of Food Control, Vol. 4, No. 2, 2021 Biochemical compositions, antioxidant activity, and in vitro antibacterial... Table 2. Biochemical composition of stems and leaves of wild bitter melon calculated by dry weight Parameter Results Parameter Results 1. Moisture (%) 87.8 8. Calcium (mg/100 g) 9.24 2. Crude fiber (g/100 g) 4.75 9. Iron (mg/100 g) 1.89 3. Crude protein (g/100 g) 5.81 10. Magnesium (mg/100 g) 16.34 4. Lipid (g/100 g) 0.98 11. Zinc (mg/100 g) 0.86 5. Reducing sugar (g/100 g) 1.95 12. Catalase (U/mg protein) 9.65 6. Phosphorus (mg/100 g) 36.52 13. Vitamin C (mg/100 g) 83.04 7. Kalium (mg/100 g) 319.52 14. Polyphenol (mg GAE/100 g) 36.5 People often use fruits for food but less consider for stems and leaves. The results showed that young leaf stalks of wild bitter melon trees are also able to be used as a kind of vegetable. In addition, crushed leaves are also used for skin diseases and burns treatments. 3.3. Antioxidant activity The antioxidant capacity of the plant is shown through the activity of redox enzymes such as catalase, or some substances with high antioxidant activity such as polyphenols, vitamin C, reducing sugar, etc. These important components play an important role in reducing free radicals produced during plant metabolism. Survey results of some active ingredients in bitter melon trees in Table 2 shows: - The polyphenol content extracted from leaves of wild bitter melon had the highest phenolic content (36.5 mg GAE/100g) and was higher than the phenolic content in leaves of Taiwanese wild bitter melon trees in Tsung Hsien Tsai’s studies [8]. - The activity of enzyme catalase was 9.65 U/mg protein, lower than that in the leaves of Cassia alata L. (12.06 U/mg protein) [9]. - The value of vitamin C was 83.04 mg/100 g, 0.23% lower than that of betel leaves. These active ingredients have high biosafety, with little or no side effects, thus they can be added to pharmaceuticals and functional foods to enhance the body’s immunity and treat other diseases caused by free radicals such as diabetes, impaired nervous system, premature aging, cancer, and so on. 3.4. In vitro antibacterial activity of stems and leaves of wild bitter melon Antimicrobial activity is one of the biological effects of medicinal plants, related to important compounds such as saponins, tannins, flavonoids, etc. In this experiment, we also used juice and fluids which were extracted by ethanol 70° from the stem and leaf of wild bitter melon to have antibacterial activity of microorganisms of the Gram-positive (+) and Gram- negative (-) groups. Evaluation of antibacterial ability by measuring the sterile ring diameter after 48 hours incubation, the results obtained are shown in Table 3 and Figure 2. 113Vietnamese Journal of Food Control, Vol. 4, No. 2, 2021 Truong Thi Thanh Dung, Nguyen Minh Trí Table 3. Antimicrobial activity of Stems and leaves of wild bitter melon Order Microbiological testing Sterile ring difference (D-d) mm Fresh juices Ethanol extract 1 Escherichia coli 16.5 ± 0.1 19.2 ± 0.1 2 Staphylococcus aureus 17.7 ± 0.2 20.8 ± 0.3 Figure 2. Aseptic loop of juice and ethanol 70° extract from wild bitter melon The results showed that the products extracted by squeezing fresh extract (1) and extraction with ethanol 70°(2) from the wild bitter melon all possessed extremely good resistance to the control bacteria strains identified as E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus, especially the preparation extracted with ethanol had significantly strong antibacterial properties and had statistical significance for the fresh juices. This result can be considered for research towards the application of ethanol 70° extracts as a treatment for some bacterial infections or as a safe and natural preservative alternative to current synthetic preservatives. 4. CONCLUSIONS The qualitative results of the chemical composition of stems and leaves of wild bitter melon stalk harvested in the forest in Mang Yang district, Gia Lai province have the following components: flavonoids, saponins, tannins, free reducing sugar, organic acids, starch, and fatty acids. The nutritional composition of the stems and leaves of wild bitter melon include reducing sugar (1.16%), lipid (1.8%), protein (3.81%), cellulose (5.62%), vitamin C (0.187%), and the enzyme catalase activity was 9.554 U/mg protein. Direct juice and ethanol extract of 70° of stems and leaves of wild bitter melon was resistant to the tested microorganisms, sterile ring size for E. coli (16.5 - 19.2 mm) and Staphylococcus aureus (17.7 - 20.8 mm). REFERENCES [1]. The Plant List, Momordica charantia var. abbreviata Ser.. 114 Vietnamese Journal of Food Control, Vol. 4, No. 2, 2021 Biochemical compositions, antioxidant activity, and in vitro antibacterial... [2]. D. H. Bich, D.X. Chung, “Medicinal plants and medicinal animals in Vietnam”. Hanoi: Science and Technology Publisher, vol 1, 2004. [3]. N. V. Dan, N. V. Tuu, “Chemical research methods of medicinal plants”. Hanoi: Medical Publisher, 1985. [4]. N. V. Mui, “Practicing biochemistry”. Hanoi: Science and Technology Publisher, 2001. [5]. Fu, L., Xu, B.-T., Xu, X.-R., Gan, R.-Y., Zhang, Y., Xia, E.- Q. &Li, H.-B., “Antioxidant capacities and total phenolic contents of 62 fruits,” Food Chemistry, vol.129, no. 2, pp. 345- 350, 2011. [6]. M. Balouiri, M. Sadiki and S. Ibnsouda, “Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review,” Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, vol. 6, pp. 71-79, 2016. [7]. N. Celikel và G. Kavas, “Antimicrobial Properties of Some Essential Oils against Some Pathogenic Microorganisms,” Czech Journal of Food Sciences, vol. 26, no. 3, pp. 174-181. [8]. Tsung-Hsien Tsai, Ching-Jang Huang, Wen-Huey Wu, Wen-Cheng Huang, Jong-Ho Chyuan and Po-Jung Tsai, “Antioxidant, cell-protective, and anti-melanogenic activities of leaf extracts from wild bitter melon (Momordica charantia Linn. var. abbreviata Ser.) cultivars,” Botanical StudiesAn International Journal, 2014. [9]. V. T. M. Huong, “Biochemical compositions and the antibacterial activity of extract form (Cassia alata L.)”, The Journal of Science, Hue University, vol.52, pp. 45-52, 2009. Thành phần hoá sinh, hoạt tính chống oxy hoá và kháng khuẩn in vitro của cây khổ qua rừng (Momordica charantia var. abbreviata Ser.) Trương Thị Thanh Dung1, Nguyễn Minh Trí2 1Trường THPT Pleiku, Gia Lai, Việt Nam 2Trường Đại học Khoa học, Đại học Huế, Thừa Thiên Huế, Việt Nam Tóm tắt Cây khổ qua rừng (Momordica charantia var. abbreviata Ser.) là một loại dây leo mọc hoang dại ở khắp các vùng núi và đồng bằng của nước ta, bộ phận sử dụng chính của cây là quả, thân và lá có thể làm rau ăn. Mục tiêu của nghiên cứu này nhằm xác định một số hợp chất hoá học có hoạt tính sinh học trong phần thân và lá của cây khổ qua rừng tại huyện Mang Yang, tỉnh Gia Lai. Đánh giá về thành phần hoá sinh, hoạt tính chống oxy hoá, khả năng kháng khuẩn của dịch ép tươi và dịch chiết bằng ethanol 70o. Kết quả cho thấy dịch ép tươi và dịch chiết ethanol 70o từ đoạn thân lá khổ qua rừng đều thể hiện ức chế sự phát triển của các chủng vi sinh vật thử nghiệm, trong đó dịch chiết ethanol 70o cho thấy hiệu quả kháng vi sinh vật cao nhất. Kết quả định tính thành phần hóa học trong cây khổ qua rừng có các thành phần: flavonoid, saponin, tanin, đường khử tự do, acid hữu cơ, tinh bột và acid béo làm cơ sở cho việc tiêu chuẩn hóa khai thác nguồn dược liệu này. Từ khoá: cây thuốc, khổ qua rừng, dịch chiết, chống oxy hóa, kháng khuẩn.
File đính kèm:
 biochemical_compositions_antioxidant_activity_and_in_vitro_a.pdf
biochemical_compositions_antioxidant_activity_and_in_vitro_a.pdf

