Characteristics of immunologic markers in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia with genetic mutation at national institute of hematology and blood transfusion from 2016 to 2018
ABSTRACT
diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of pediatric ALL.
Objective:
National institute of Hematology and Blood transfusion from 2016-2018.
Methods: Cross-sectional descriptive on 189 pediatric patients aged 1-15 years old with newly
diagnosis ALL.
Results. Frequency of fusion genes was 26.9% (fusion gene TEL-AML1 13.2%, BCR-ABL 8.5%, E2APBX1 2.6%, MLL-AF4 2.6%). B - ALL was prevalent with 82.0%; T - ALL accounted for 16.4%. 97,8% of
the patients with genetic mutation were in group of B-ALL. CD45 showed strong positive expression in
of CD34 patients was highest in the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene group. The E2A-PBX1 gene mutation group
was negative for CD34. The presence of CD19, CD79a markers was high in pediatric patients. CD10 (+)
was low in the MLL-AF4 group. The incidence of CD20 was low in the groups. The incidence of myeloid CD
was highest in BCR-ABL1 (37.5% positive for CD33), without the presence of myeloid CD in the pediatric
patients with the E2A- PBX1 and MLL-AF4 fusion gene.

Trang 1
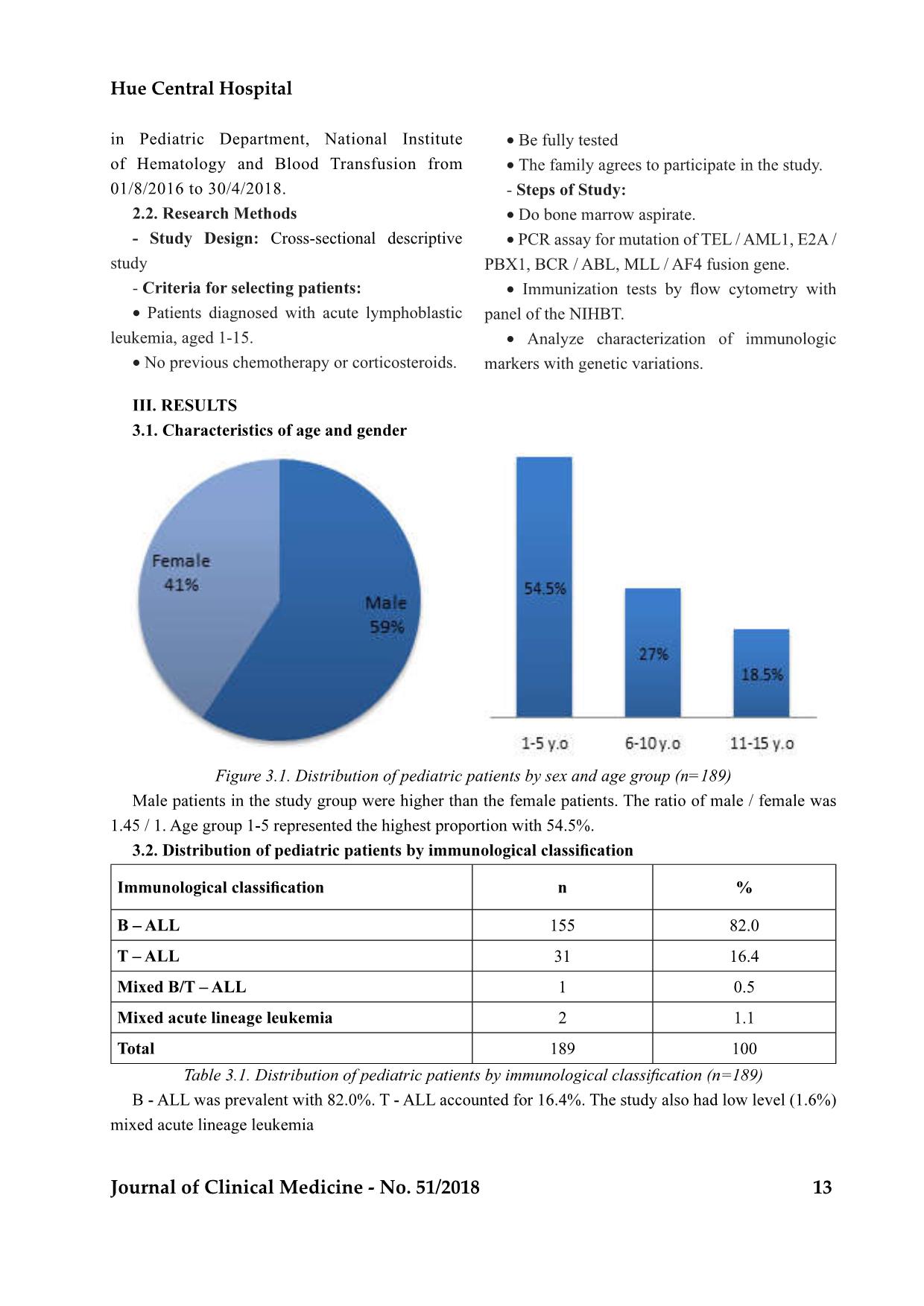
Trang 2
Trang 3
Trang 4
Trang 5

Trang 6

Trang 7
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Characteristics of immunologic markers in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia with genetic mutation at national institute of hematology and blood transfusion from 2016 to 2018

T12 Journal of Clinical Medicine - No. 51/2018 CHARACTERISTICS OF IMMUNOLOGIC MARKERS IN PEDIATRIC ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA WITH GENETIC MUTATION AT NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HEMATOLOGY AND BLOOD TRANSFUSION FROM 2016 TO 2018 Hoang Thi Hong1, Mai Lan1, Nguyen Quang Tung1, Nguyen Trieu Van1, Bach Quoc Khanh1 ABSTRACT diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of pediatric ALL. Objective: National institute of Hematology and Blood transfusion from 2016-2018. Methods: Cross-sectional descriptive on 189 pediatric patients aged 1-15 years old with newly diagnosis ALL. Results. Frequency of fusion genes was 26.9% (fusion gene TEL-AML1 13.2%, BCR-ABL 8.5%, E2A- PBX1 2.6%, MLL-AF4 2.6%). B - ALL was prevalent with 82.0%; T - ALL accounted for 16.4%. 97,8% of the patients with genetic mutation were in group of B-ALL. CD45 showed strong positive expression in of CD34 patients was highest in the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene group. The E2A-PBX1 gene mutation group was negative for CD34. The presence of CD19, CD79a markers was high in pediatric patients. CD10 (+) was low in the MLL-AF4 group. The incidence of CD20 was low in the groups. The incidence of myeloid CD was highest in BCR-ABL1 (37.5% positive for CD33), without the presence of myeloid CD in the pediatric patients with the E2A- PBX1 and MLL-AF4 fusion gene. 1. National Institute of Hematology and Blood transfusion - Received: 8/8/2018; Revised: 16/8/2018 - Accepted: 27/8/2018 - Corresponding author: Hoang Thi Hong - Email: hoanghong.nihbt@gmail.com. Tel: 0983885350 I. INTRODUCTION Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) accounts for about 25% of childhood cancers and about 1% of adult cancers. About 60-70% of ALL have genetic changes. The presence of genetic alterations and characteristics of immunologic markers are important in prognosis, evaluating the therapeutic response for ALL [1], [2], [ 3]. In Vietnam, the relationship between genetic variation and immunological traits has not been studied extensively. So we conducted this research with the aim: - Research characteristics of immunologic markersin pediatric all with genetic mutation in national institute of hematology and blood transfusion from 2016 to 2018. II. SUBJECTS AND METHODS 2.1. Subjects of Study 189 pediatric patients who were diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia newly according to the WHO 2008 standard, treated Hue Central Hospital Journal of Clinical Medicine - No. 51/2018 13 in Pediatric Department, National Institute of Hematology and Blood Transfusion from 01/8/2016 to 30/4/2018. Cross-sectional descriptive study - leukemia, aged 1-15. No previous chemotherapy or corticosteroids. Be fully tested The family agrees to participate in the study. - PCR assay for mutation of TEL / AML1, E2A / PBX1, BCR / ABL, MLL / AF4 fusion gene. panel of the NIHBT. Analyze characterization of immunologic Figure 3.1. Distribution of pediatric patients by sex and age group (n=189) % 155 82.0 31 16.4 1 0.5 2 1.1 189 100 mixed acute lineage leukemia 14 Journal of Clinical Medicine - No. 51/2018 Research characteristics of immunologic markers... Table 3.2. Rate of genetic variations in the study (n=189) % No gene mutations detected 138 73.1 Fusion genes detected (n=46, 26.9%) TEL-AML1 25 13.2 BCR-ABL1 16 8.5 E2A-PBX1 5 2.6 MLL-AF4 5 2.6 189 100 the TEL-AML1 fusion gene accounted for the highest rate of 13.2%. 8.5% of pediatric patients had the proportion (2.6%). Immune phenotype Fusion gene B-ALL T-ALL Total TEL-AML1 25 (100%) 0 (0%) 25 (100%) BCR-ABL1 15 (93,8%) 1 (6,2%) 16 (100%) E2A-PBX1 5 (100%) 0 (0%) 5 (100%) MLL-AF4 5 (100%) 0 (0%) 5 (100%) Total 45 (97,8%) 1 (2,2%) 46 (100%) (2.2%) had BCR-ABL1 fusion gene in the T-ALL group. Figure 3.2. Characteristic of CD45 expression in fusion gene groups (n=189) Hue Central Hospital Journal of Clinical Medicine - No. 51/2018 15 Table 3.4. Characteristic of CD34 and HLA-DR expression in fusion gene groups (n=189) CD Fusion genes HLA-DR CD34 Negative Positive Negative Positive No fusion genes detected 31.2% 68.8% 38.4% 61.6% TEL-AML1 4.0% 96.0% 24% 76% BCR-ABL1 18.8% 81.2% 6.2% 93.8% E2A-PBX1 0% 100% 100% 0% MLL-AF4 0% 100% 20% 80% Table 3.5. Characteristic features of B- cell phenotype in fusion gene groups (n=46) TEL-AML1 BCR-ABL1 E2A-PBX1 MLL-AF4 CD10 (+) 100% 93.8% 100% 20% CD19 (+) 100% 87.5% 100% 100% CD20 (+) 12.0% 25.0% 0% 20% CD79a (+) 100% 93,8% 100% 100% and did not appear in the E2A-PBX1 fusion gene group. Table 3.6. Characteristics of abnormalities immune marker in fusion gene groups TEL-AML1 BCR-ABL1 E2A-PBX1 MLL-AF4 CD13 (+) 4.0% 0 % 0 % 0 % CD33 (+) 4.0% 37.5% 0% 0% CD56 (+) 4.0% 6.2% 0% 0% Our research is similar to that of Mai Lan (2015), higher than female, the age group 1-5 represented the highest proportion in pediatric ALL patients of NIHBT. . The proportion of B-cell ALL patients is T-cell ALL patients is 16,4% and the rest is the level 16 Journal of Clinical Medicine - No. 51/2018 Research characteristics of immunologic markers... various domestic and international researches. The ALL is about 15%. The study of author Hoang Chi the percentage of the mixed acute lineage leukemia (4,3%). The mixed acute lineage leukemia is rare in the genetic expression and got the results that the PBX1 2.6%, MLL / AF4 2.6% (Table 3.2). Table 4.1. Comparing the rate of mutated gene detection with some domestic and international studies. Yanming Zhang- Michelle M Le Beau 5 25 5 5-7 Terzah M Horton- C Philip Steuber 3-4 20-25 5 5 Karen Rabin- 3 25 6 8 C.H.Pui 2-3 20-25 4 2 Cheryl L. Willman 2 28 6 4 P.T.D. An 3 25 5 8 10 14 4 2 Our study (n=189) 8.5 13.2 2.6 2.6 Consequently, our proportion of mutated gene studies. This may be due to the fact that many of Hematology and Blood Transfusion in high risk groups, so the frequency of fusion gene detection is higher than in other studies. Table 3.3 illustrates that 97.8% pediatric patients B-cell ALL group. Because majority of ALL is B-cell the B- cell ALL. Especially, the study encountered The literature also reported several instances of The research on the characteristics of several - In terms of the level of CD45 expression, the study found that the CD45-high positive rate (over in most groups, especially in the BCR-ABL1 and E2A-PBX1 fusion gene group. According to the study of author Hoang Chi Cuong, CD45 expres- - cytes (95.7%). In our study, the majority of patients group, therefore the overall result of strong positive the at normal risk population (TEL-AML1) than in Hue Central Hospital Journal of Clinical Medicine - No. 51/2018 17 the high risk g - - - Our results present that blast cells in the TEL- AML1, BCR-ABL1 and MLL-AF4 genetic complex HLA-DR and CD34 markers. This result is similar (57/57 patients), CD34 positive proportion is 58% HLA-DR (+) in all subtypes of B-cell ALL (100%), and CD34 positive in 70% of patients [8]. Pediatric - erally positive for CD19, CD10, CD79a, HLA-DR but negative for CD34 [10]. - Among the examined hallmarks of B lym- phocytes, the CD19, CD79a markers had a high than other B-type imprints because these mutated in less than 6 months of age and older infants, - on there surface [9]. - Occurrence of myeloid markers in ALL may be observed at rates ranging from 13 to 28% in some studies. In our research, the incidence of myeloid incidence of myeloid markers is highest in BCR- cases. Several studies have also found that the inci- dence of myeloid imprints may be as high as 30% in cases of BCR-ABL1 [9]. some conclusions: - B-cell ALL accounted for the majority (82%); B-cell ALL group. - A rare case of BCR-ABL1 fusion gene belonged to T-cell ALL. - The CD34-negative count in the E2A-PBX1 the groups. ABL1 (37.5% positive for CD33). 1. Ching-Hon Pui, William L. Carroll, Soheil Biolo- Acute Leukemias: An Update, Oncology, Vol 29, 2011. Rede- risk ALL and implementing precision medicine, Blood, 25 june 2015 , volume 125, number 26, p 3977-3987. 3. Hoang Chi Cuong (2014), Study on immunosup- pressive markers in pediatric acute lymphoblas- Institute of Hematology and Blood Transfusion, Master of Medicine thesis, Hanoi Medical Uni- versity. 4. Mai Lan (2016), Research distribution of pediat- ric blood disease in National Institute of Hema- 18 Journal of Clinical Medicine - No. 51/2018 tology and Blood Transfusion from 2013-2015, Specialist doctor level II, NIHBT. Study on clinical char- acteristics, laboratory and response to induction treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in chil- dren with genetic mutation at the National Insti- tute of Hematology and Blood Transfusion, Mas- ter of Medicine thesis, Hanoi Medical University. 6. Phan Thi Duy An, (2011), Survey on character- istics of cytogenetic and molecular biology in lymphoblastic leukemia in children in pediatric department of BTH from March 2010 to March 2011, Master of Medicine thesis, HCM Univer- sity of Medicine and Pharmacy. 7. Patrizia Comoli et al (2017), T-cell therapy in Ph+ ALL patients on tyrosine- kinase inhibitors, Blood, 2017, 129:582-586. Clini- cal and biologic relevance of immunologic marker studies in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia, blood 1993, Blood, Vol 82,1993: pp 343-362. 9. Sanam Loghavi, et al (2015), B-Acute Lympho- blastic Leukemia/Lymphoblastic Lymphoma, Predictabil- ity of the t(1;19)(q23;p13) from surface antigen phenotype: implication for screening cases of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia for mo- lecular analysis: a Pediatric Oncology Group Study. Blood. 1993;83:1086–91. Research characteristics of immunologic markers...
File đính kèm:
 characteristics_of_immunologic_markers_in_pediatric_acute_ly.pdf
characteristics_of_immunologic_markers_in_pediatric_acute_ly.pdf

