Bài giảng Ndustrial hygiene
What is Industrial Hygiene?
Industrial hygiene : the science of protecting
and enhancing the health and safety of
pepeole at work and in their communities.
The American Board of Inductrial Hygiene
Key factors:
- Employee exposure to hazards
- Control for hazards to protect workers
Basic principles of Industrial Hygiene
1. Anticipation of potential risks
2. Recognition of existing health hazards at the
workplace
3. Evaluation of health risks
4. Contol of unacceptable risks

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3
Trang 4
Trang 5

Trang 6

Trang 7
Trang 8

Trang 9

Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Bạn đang xem 10 trang mẫu của tài liệu "Bài giảng Ndustrial hygiene", để tải tài liệu gốc về máy hãy click vào nút Download ở trên
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Bài giảng Ndustrial hygiene

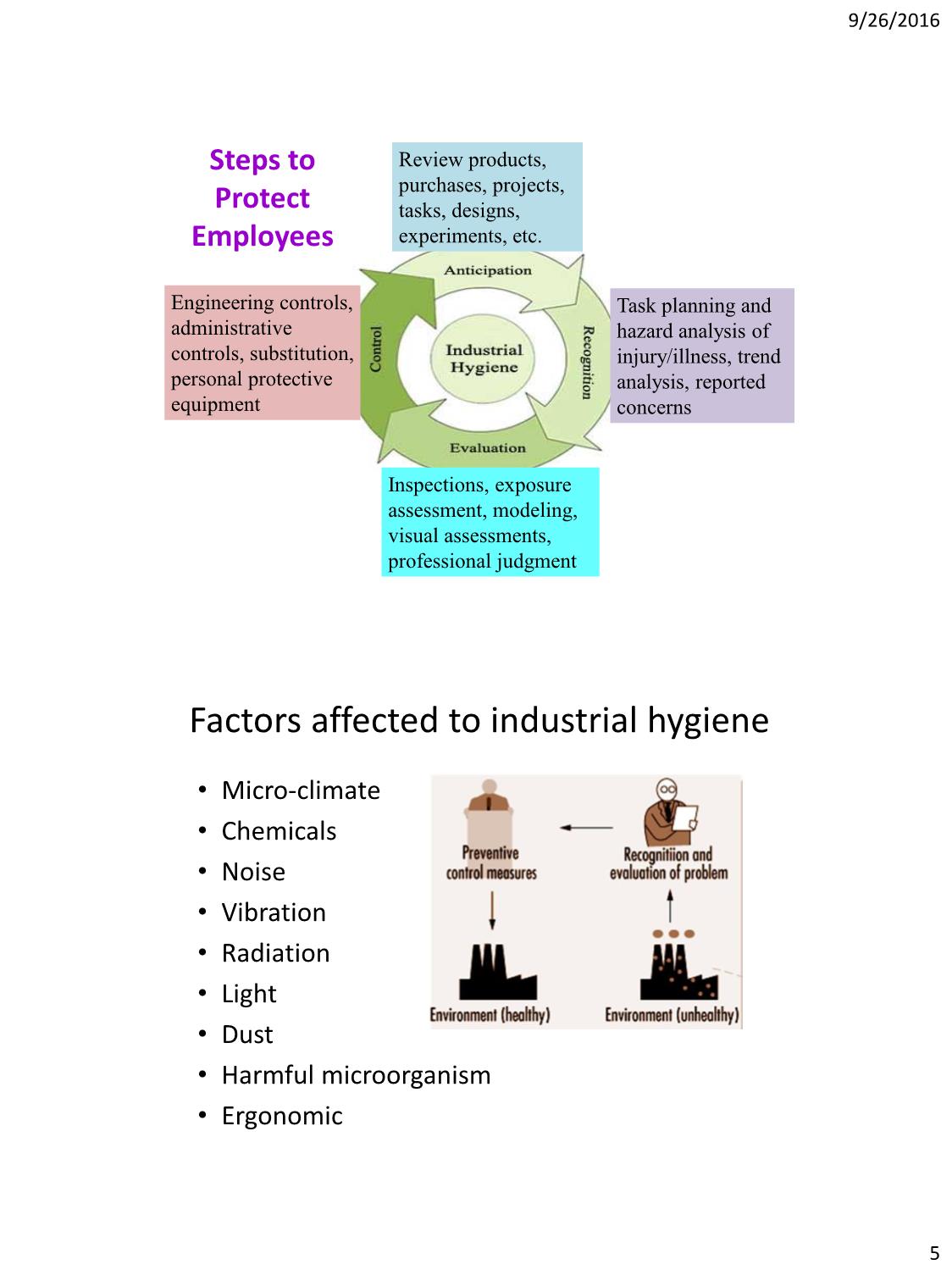
9/26/2016 1 Chapter 2: INDUSTRIAL HYGIENE Vietnam National University – HCMC Ho Chi Minh City University of Technology Faculty of Resource & Environment Lecturer: Dr. TRAN BICH CHAU Email: tbchau@hcmus.edu.vn 02/2016 1. What is Occupational/Industrial Hygiene? 2. Four steps to create healthy working place (A.R.E.C): – Anticipation – Recognition – Evaluation – Control 3. Factors affecting to industrial hygiene: – Chemical hazards – Physical agents – Biological hazards – Ergonomic hazards OUTLINE: INDUSTRIAL HYGIENE 9/26/2016 2 Industrial/Occupational Hygiene? Interactions between people and the environment 9/26/2016 3 INDUSTRIAL HYGIENE OCCUPATIONAL HYGIENE = 0r ≠ What is the diferrence between industrial hygiene and occupational hygiene ??? Industrial hygiene is the science of anticipating, recognizing, evaluating, and controlling workplace conditions that may cause workers' injury or illness. Berenice I. Ferrari Goelzer What is Industrial Hygiene? 9/26/2016 4 What is Industrial Hygiene? Industrial hygiene : the science of protecting and enhancing the health and safety of pepeole at work and in their communities. The American Board of Inductrial Hygiene Key factors: - Employee exposure to hazards - Control for hazards to protect workers Basic principles of Industrial Hygiene 1. Anticipation of potential risks 2. Recognition of existing health hazards at the workplace 3. Evaluation of health risks 4. Contol of unacceptable risks Remember the acronym: A.R.E.C 9/26/2016 5 Task planning and hazard analysis of injury/illness, trend analysis, reported concerns Inspections, exposure assessment, modeling, visual assessments, professional judgment Engineering controls, administrative controls, substitution, personal protective equipment Review products, purchases, projects, tasks, designs, experiments, etc. Steps to Protect Employees Factors affected to industrial hygiene • Micro-climate • Chemicals • Noise • Vibration • Radiation • Light • Dust • Harmful microorganism • Ergonomic 9/26/2016 6 • Chemical hazards • Physical hazards • Biological hazards • Ergonomic hazards Factors affected to industrial hygiene Environmental Factors or Stresses • gases, vapors, dusts, fumes, mists, and smoke Chemical hazards Physical hazards: radiation, noise, vibration, extreme temperatures and pressures 12 9/26/2016 7 Environmental Factors or Stresses Hazards 13 Chemical hazards • Dusts, fumes, gases, mists • Skin contact with oils, paints etc. 9/26/2016 8 Physical agents • Noise, • Vibration • Heat • UV Biological hazards • Legionella • Zoonoses • Anthrax Ex: Wastes from hospitals and research facilities containing disease-causing organism s that could infect site personnel 9/26/2016 9 Ergonomic hazards • Manual handling • Repetitive work • Display screen equipment An ergonomic hazard is a physical factor within the environment that harms the musculoskeletal system Factors affected to industrial hygiene • Micro-climate • Chemicals • Noise • Vibration • Radiation • Light • Dust • Harmful microorganism • Ergonomic 9/26/2016 10 Meteorology: A microclimate is the distinctive climate of a small- scale area, such as a garden, park, valley or part of a city. The weather variables in a microclimate, such as temperature, rainfall, wind or humidity, may be subtly different to the condition prevailing over the area as a whole and from those that might be reasonably expected under certain types of pressure or cloud cover What is microclimate? Occupational Hygiene: Microclimate is the physical state of the atmosphere in the narrow space of the workplace including the factors temperature, humidity, radiant heat and speed of air transport. These factors must be guaranteed in certain limit, consistent with human physiology What is microclimate? 9/26/2016 11 Classify of microclimate Microclimate of working environment can be classified into the following areas: Cold area; Thermally neutral microclimat, comfortalble, endurable areas; Warm or hot areas Parameters of microclimate Four basic parametere of thermal effect: Air temperature; Relative humidity; Air flow velocity ; Thermal radiation Distinguising levels of climate sensation: Comfortable levels Endurable level Unbearable level 9/26/2016 12 Temperature: Temperature is the basic factor that acts on the metabolism and human health. Temperature may act directly or indirectly on human body Temperature always transmits from hotter to colder place by conduction, convection and radiation. Humidity: - Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. - Higher humidity reduces the effectiveness of sweating in cooling the body by reducing the rate of evaporation of moisture from the skin. Vietnam Hygiene standard (TCVS 3733:2002): relative humidiy from 75 – 85 % 9/26/2016 13 Air flow : - Flow of air into and out of a working area, ex: an office space, - It helps to dilute any contaminants by adding some fresh air - This can be provided by natural ventilation or forced ventilation Thermal radiation: Thermal radiation is energy transfer by the emission of electromagnetic waves which carry energy away from the emitting object. Examples of thermal radiation include the visible light and infrared light emitted by an incandescent light bulb. Infrared radiation - <760 nm (heat) 9/26/2016 14 Relationship of temperature, humidity and work performance: The effects of microclimate factors to workers List the effects of temperature and humidity to workers? Factors Effects T0 high T0 low Humidity low Humidity high 9/26/2016 15 Improvements of microclimate conditions 1. Technical measures - Mechanization - Manufacturing automation - Ventilation - Air condition - Thermal insulation 2. Administration and Medical Measures - Set up reasonable schedules - Provide enough PPEs - Recruit/arrange suitable labors for each sector - Supply enough nutritional food - Perform periodic medical examinations Improvements of microclimate conditions 9/26/2016 16 ERGONOMICS WHAT IS ERGONOMICS”?? Ergos = work Nomos = laws Ergonomics = the laws of work ERGONOMICS What Does Ergonomics Mean? Designing jobs, equipments, and work tasks to fit human physical characteristics and energy limitations It considers body dimensions, mobility, and the body’s stress behaviors “Make the work fit the person, not the person fit the work” 9/26/2016 17 Benefits of Ergonomics – safer jobs with fewer injuries – increased efficiency and productivity – improved quality and fewer errors – improved morales Ergonomic Goals Reduce muscle and joint injuries -- and get the job done safely and quickly Keeping young/mature bodies from being worn out prematurely/early 9/26/2016 18 1. What’s he doing wrong ? 2. What are the wrong ergonomics that people usually have?? Wrong working postures 9/26/2016 19 Wrong working postures 9/26/2016 20 GUIDELINE ABOUT WEIGHTS • Chemical hazards • Physical hazards • Biological hazards • Ergonomic hazards Factors affected to industrial hygiene 9/26/2016 21 • Microclimate • Argonomics • Poisoning • Noise • Dust Factors affected to industrial hygiene • A poison is any substance that can cause injury, illness or death when introduced into the body. • poisons are substances that cause disturbances in organisms, usually by chemical reaction or other activity on the molecular scale, when an organism absorbs a sufficient quantity • Poisoning is considered a sudden illness • The limit between non-toxic and toxic depends on doses. Poisoning prevention in industries 9/26/2016 22 Poisoning prevention in industries Classify of toxic substance in industries • Non-dangerous in contact and no health effect • Harmful to health, but able to recovery • Cause diseases and able to recovery • Cause chronic diseases or death. Poisoning prevention in industries • Factors causing harmful of a toxic - Chemical characteristic - Physical characteristic - Exposure level/concentration and time - Body condition, age, gender, biophysiology of the receivors - Environmental factors such as high humidity, high temperature, etc. 9/26/2016 23 How poisons enter the body: Injection Inhalation Ingestion Absorption respiratory tract skin or eyes. skin digestive tract Types of Hazards Toxicity • Acute poisoning is characterized by rapid absorption of the substance sudden & severe exposure. • Normally, a single large dose/exposure is involved. 9/26/2016 24 Types of Hazards Toxicity • Chronic poisoning is characterized by prolonged or repeated exposures of a duration measured in days, months or years. • Symptoms may not be immediately apparent, but tend to build up in the body. The effects are not seen until a critical body burden is reached. • Normally, several small/little exposures are involved. Symptoms of Poisoning Nausea or vomiting. Diarrhea. Chest or abdominal pain. Trouble breathing. Sweating. Changes in consciousness. Seizures. Headache. Dizziness. Weakness. Irregular pupil size. Burning or tearing eyes. Abnormal skin color. Burn injuries around the lips or tongue. 9/26/2016 25 Care for Poisoning The severity of a poisoning depends on: The type and amount of poison. How and where the poison entered the body. The time elapsed since the poisoning. The victim’s size, weight, medical condition and age. Call 113, 114, 115 in Vietnam or the local emergency number for life-threatening emergencies first. Reasons for Poisoning in industries The reasons of toxic contamination in productions - Lack of knowledge about poisons - Non-compliance procedures of poison uses and management - Not use equipment for poisoning prevention - Worker’s health is not good and workers have deseases that make their bodies increase susceptibility to poison 9/26/2016 26 Reasons for Poisoning in industries The reasons of toxic contamination in productions - Old and out-of-date technologies applied in production cause toxic emission and contaminate the working environment - Poor ventilation - Physical propeties of a poison * lower evaporation abitity higher toxicity * higher solubility in water and solvents higher toxicity Technical solutions - Eliminating toxins - Isolation and shielding - Ventilation - PPEs - Fire fighting and protection - Up-to-date technology Poisoning prevention in industries 9/26/2016 27 Medical hygiene solutions - Treating waste before disposal - Perform periodic health examinations - Personal hygiene Poisoning prevention in industries • Microclimate • Argonomics • Poisoning • Dust • Noise Factors affected to industrial hygiene 9/26/2016 28 Dust prevention in industries Dust is the physical element with diffuse small size in air environment. When in the air with toxic substances accounted for a large proportion, it will have an impact on human health: affect the respiratory system, vision and quality of life. On human health: affect the respiratory system, vision and quality of life. Especially for inhalation, as small dust particles greater their impact, with a particle size of 0.5 - 10μm they can penetrate deep into the respiratory tract so called respiratory dust. Harm level of each substance depending on the nature of the dust, its concentrations in air, duration of human exposure, health status, size of dust particles Effects of Dust 9/26/2016 29 Dust prevention in industries The smaller the size the more harmful. Large dust particles, the easier removal capabilities so little effects on humans. Types of dust: organic inorganic (more harmful) Dust prevention in industries Technical solutions - Mechanization and automation of the production process dust to workers not exposed to dust and dirt less spread out. - Changes in technology measures such as pneumatic transport, use a vacuum, clean with water instead of cleaning by sand blasting ... - Sealed devices and production lines when needed. - Change the dust generating materials with materials with little or no dust ... - Use ventilation, vacuum in the dusty workshop 9/26/2016 30 Medical hygiene solutions - Perform periodic health examinations - Use PPEs : mask, protection cloths, glass, ect. - Have a healthy eating plan: the rations for workers who work in dusty place need more vitamins, especially vitamin C. Provide plenty of vegetables and fresh fruits. Dust prevention in industries • Microclimate • Argonomics • Poisoning • Dust • Noise Factors affected to industrial hygiene 9/26/2016 31 Effects of Noise - On human health: body collapse, diseases such as stress, anxiety, other indirect disorders, nervous system - Lack of concentration on work, discomfort - Low quality of work. What is the solution to prevent workers from noise???? 9/26/2016 32 Summary: 1. What is Occupational/Industrial Hygiene? 2. Four steps to create healthy working place (A.R.E.C): – Anticipation – Recognition – Evaluation – Control 3. Factors affecting to industrial hygiene: – Chemical hazards – Physical agents – Biological hazards – Ergonomic hazards
File đính kèm:
 bai_giang_ndustrial_hygiene.pdf
bai_giang_ndustrial_hygiene.pdf

