Applicability of ifrs in Viet Nam stock exchange listed companies: Perspective from theory of planned behavior
The research, based upon data collected from 273 enterprises,
uses the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) to identify and estimate
the degree to which factors the ability to apply IFRS in listed nonfinancial enterprises has been affected. Through Exploratory Factor
Analysis (EFA) and multivariate linear regression approach, the
research proves that there are four factors placing impacts on IFRS
adoption in listed companies in Vietnam. Those are management’s
attitude, costs, economic integration, accounting staff’s knowledge
and skills. The research results are the foundation for businesses to
be fully prepared for the favorable and successful application of
IFRS. In addition, the results of this study are also useful references
for policy-making agencies and professional associations in
promoting IFRS application in Vietnam the next time.

Trang 1
Trang 2

Trang 3
Trang 4
Trang 5
Trang 6
Trang 7
Trang 8
Trang 9
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Applicability of ifrs in Viet Nam stock exchange listed companies: Perspective from theory of planned behavior

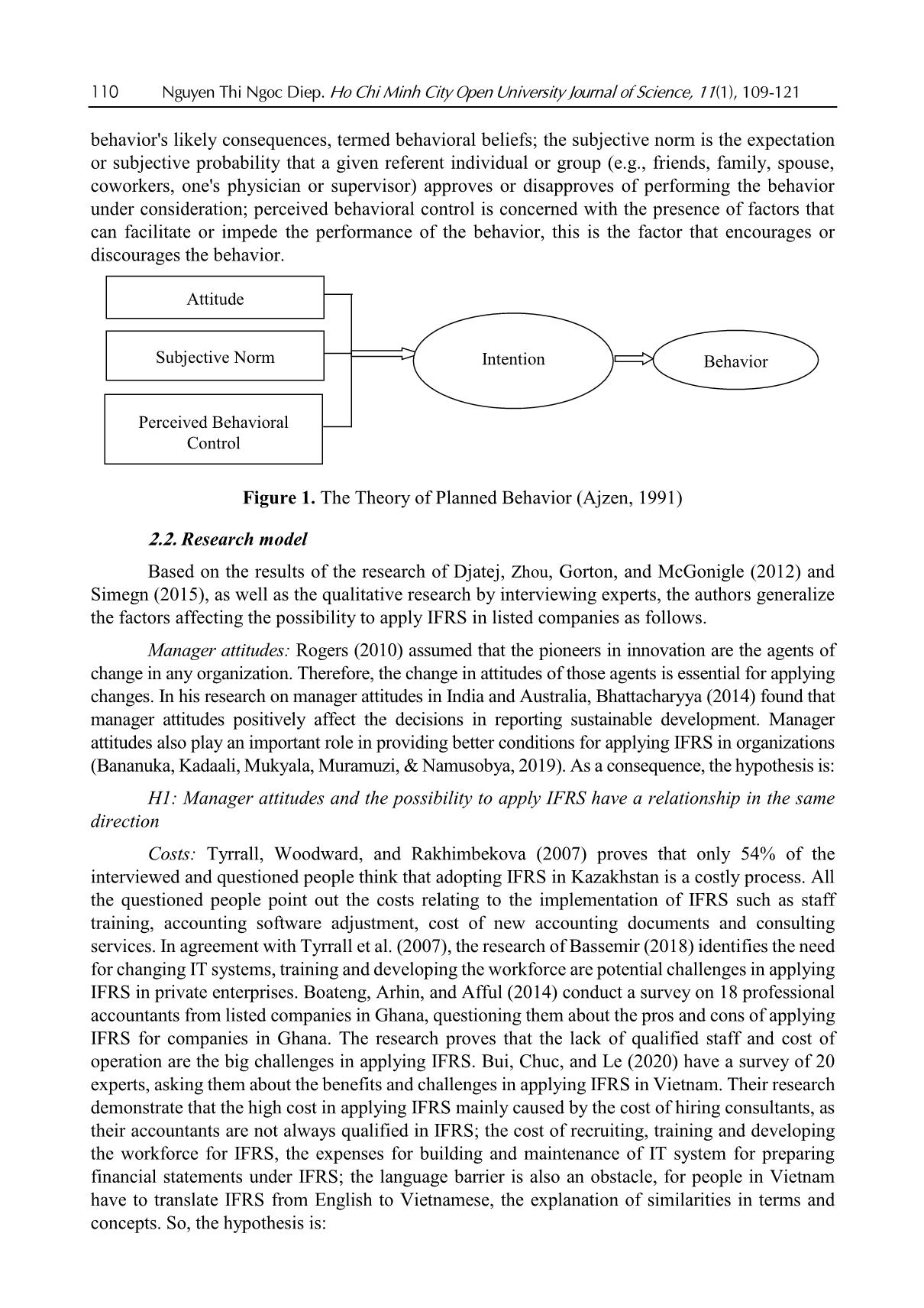
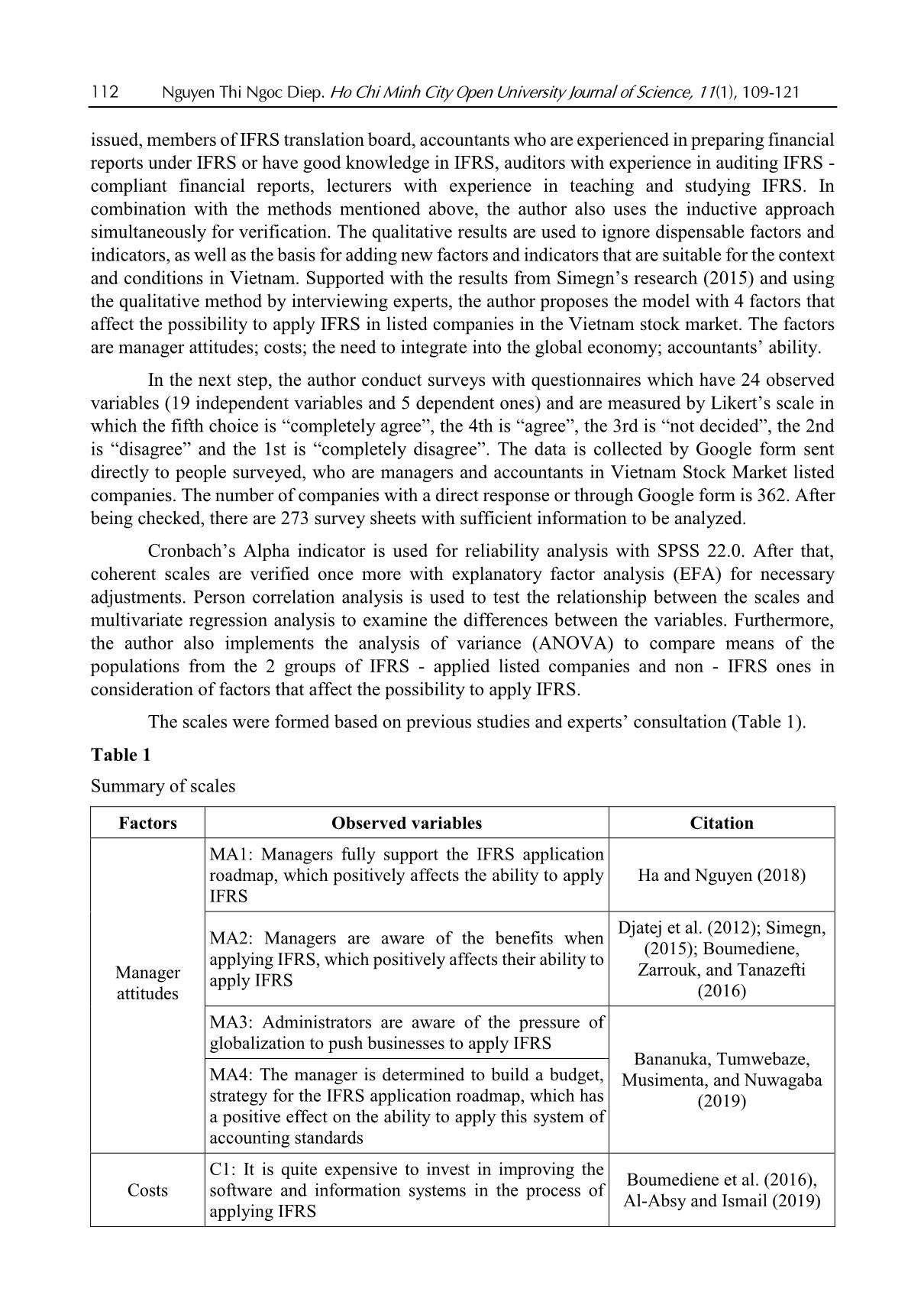
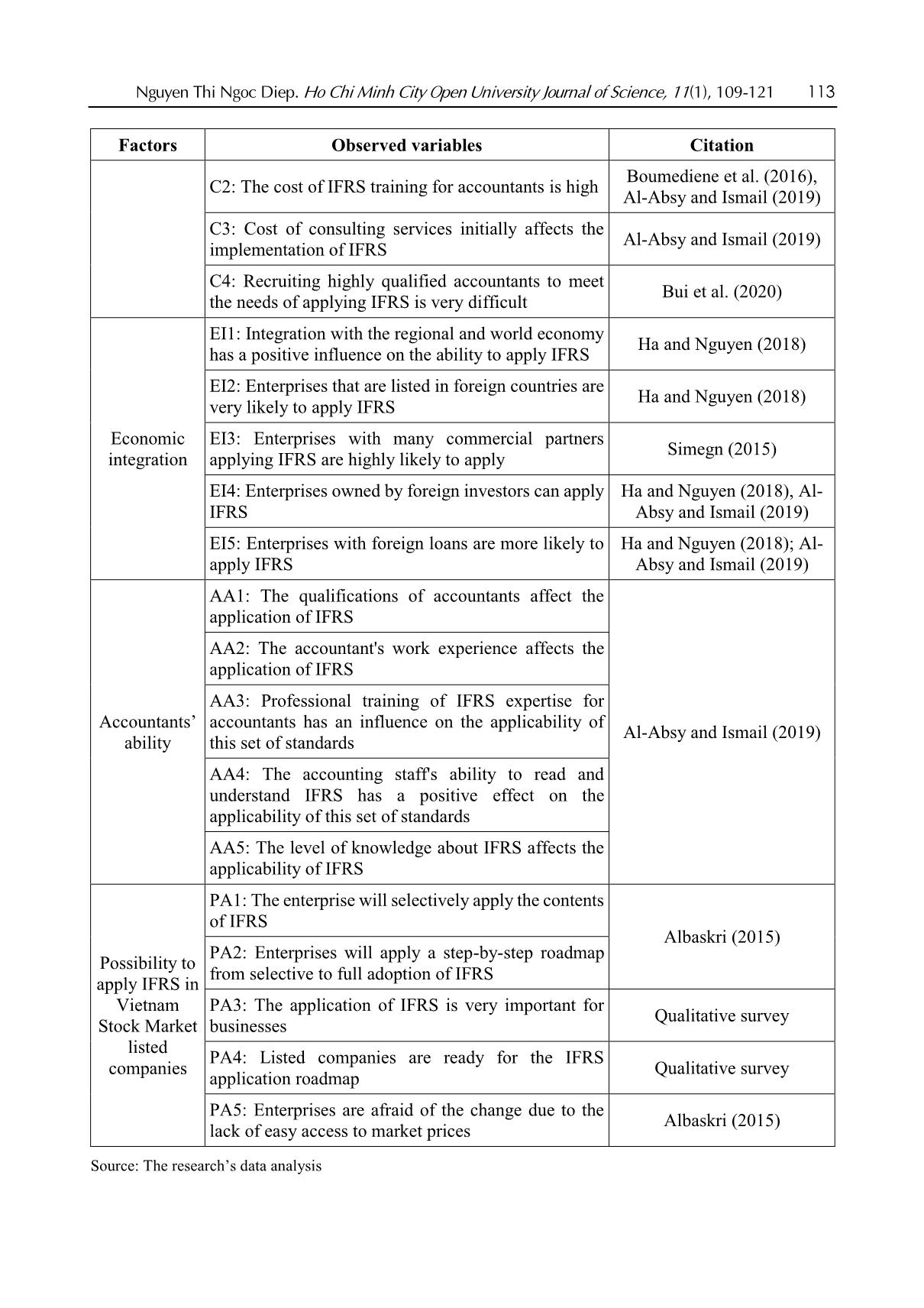
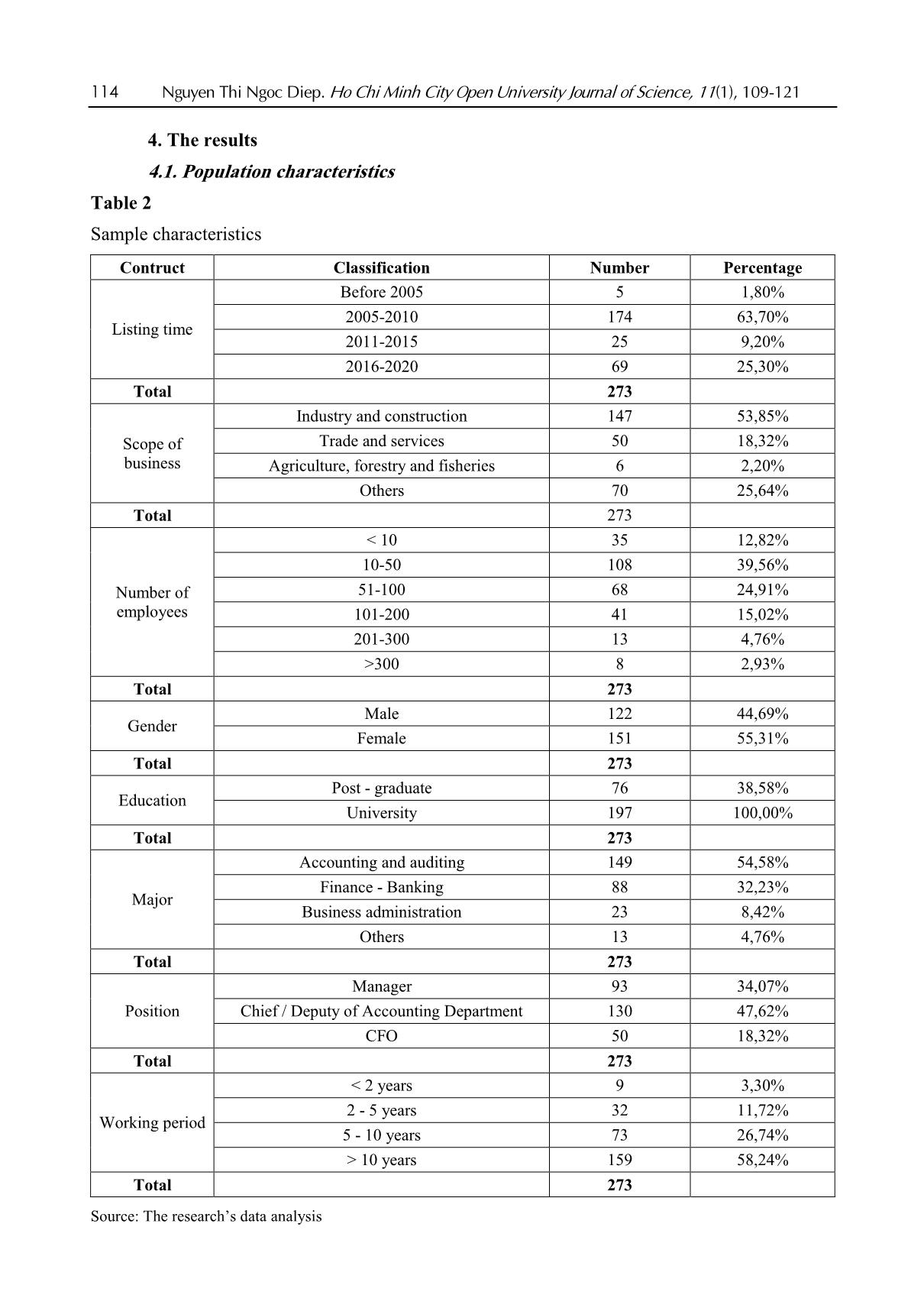
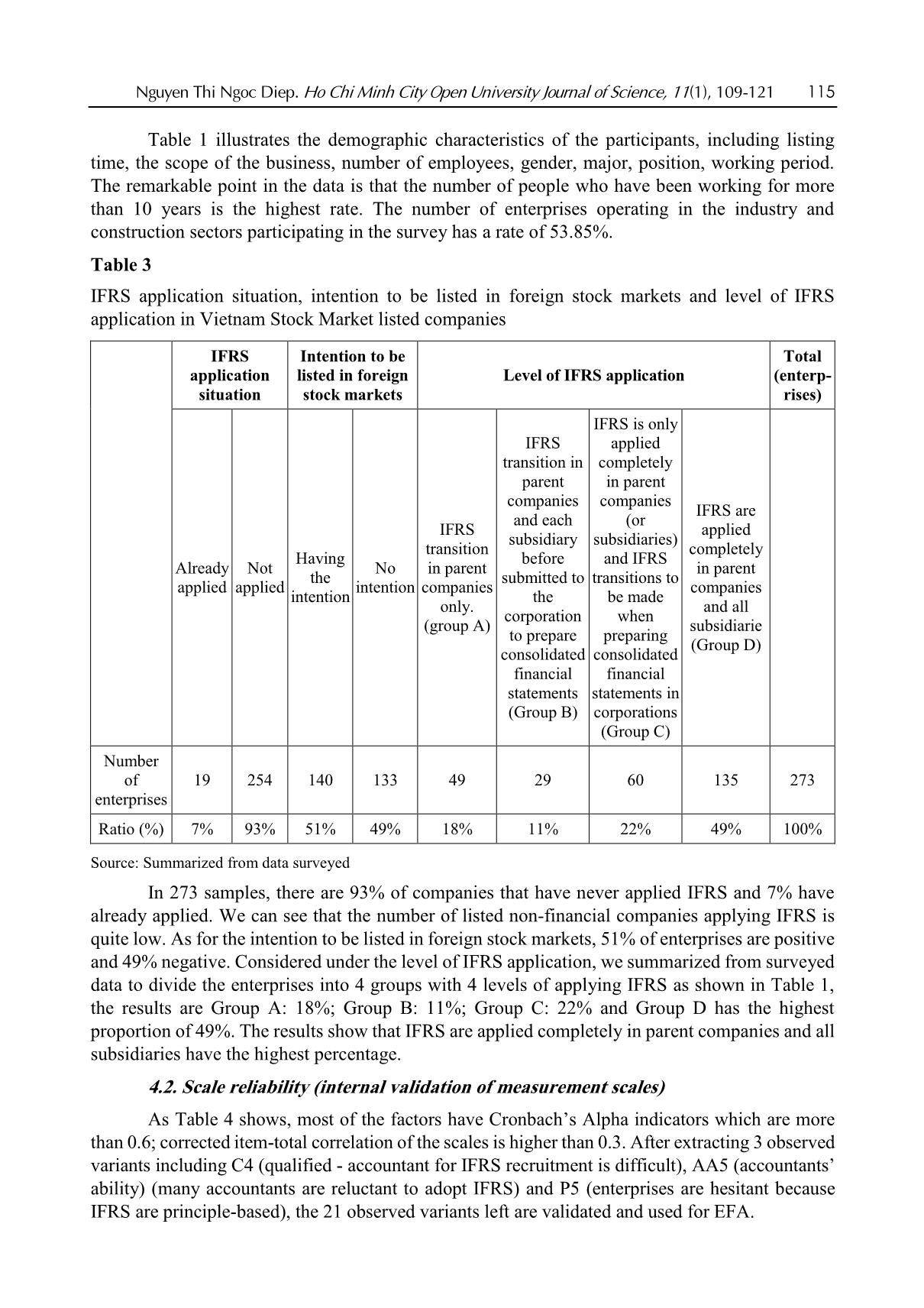
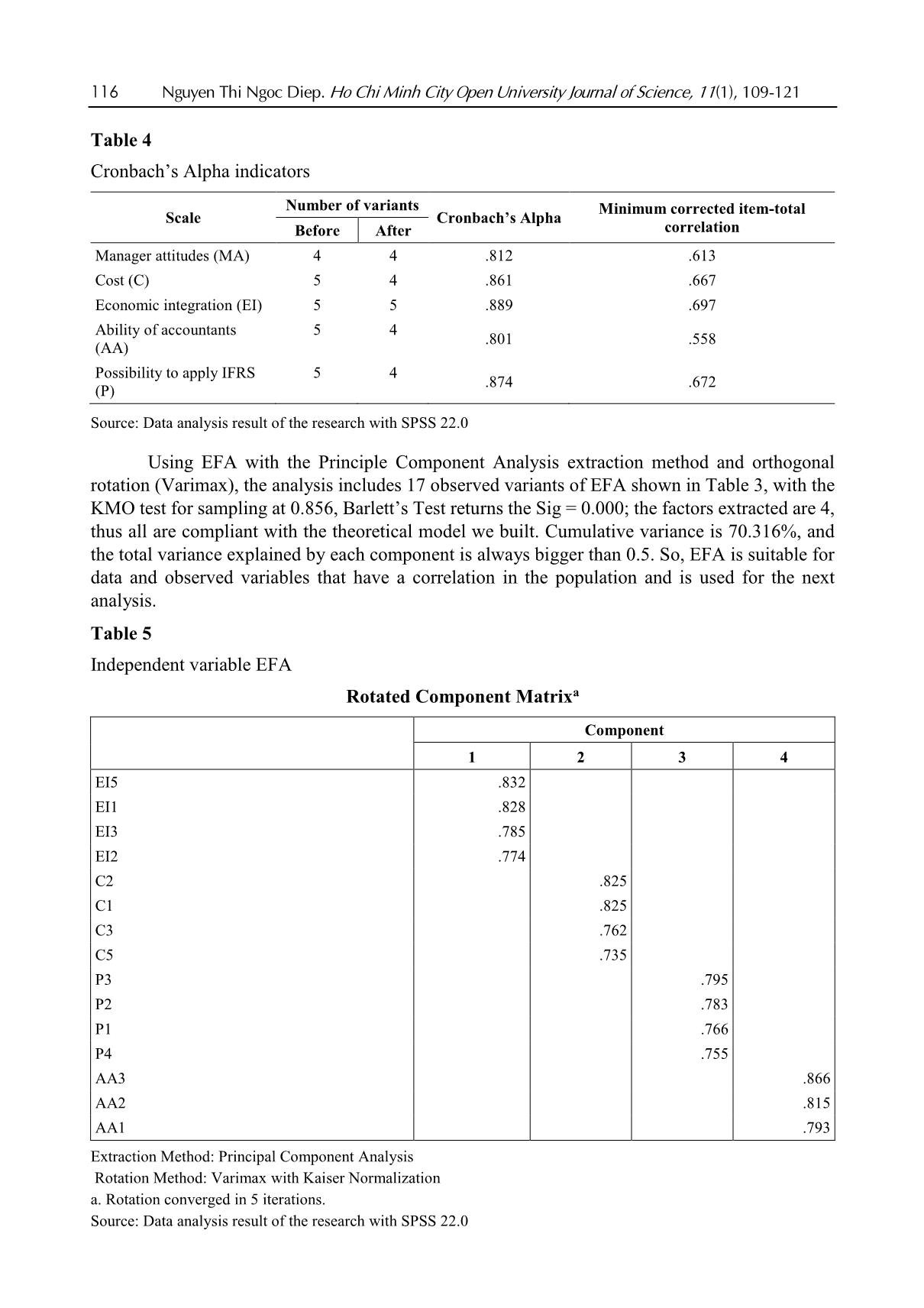
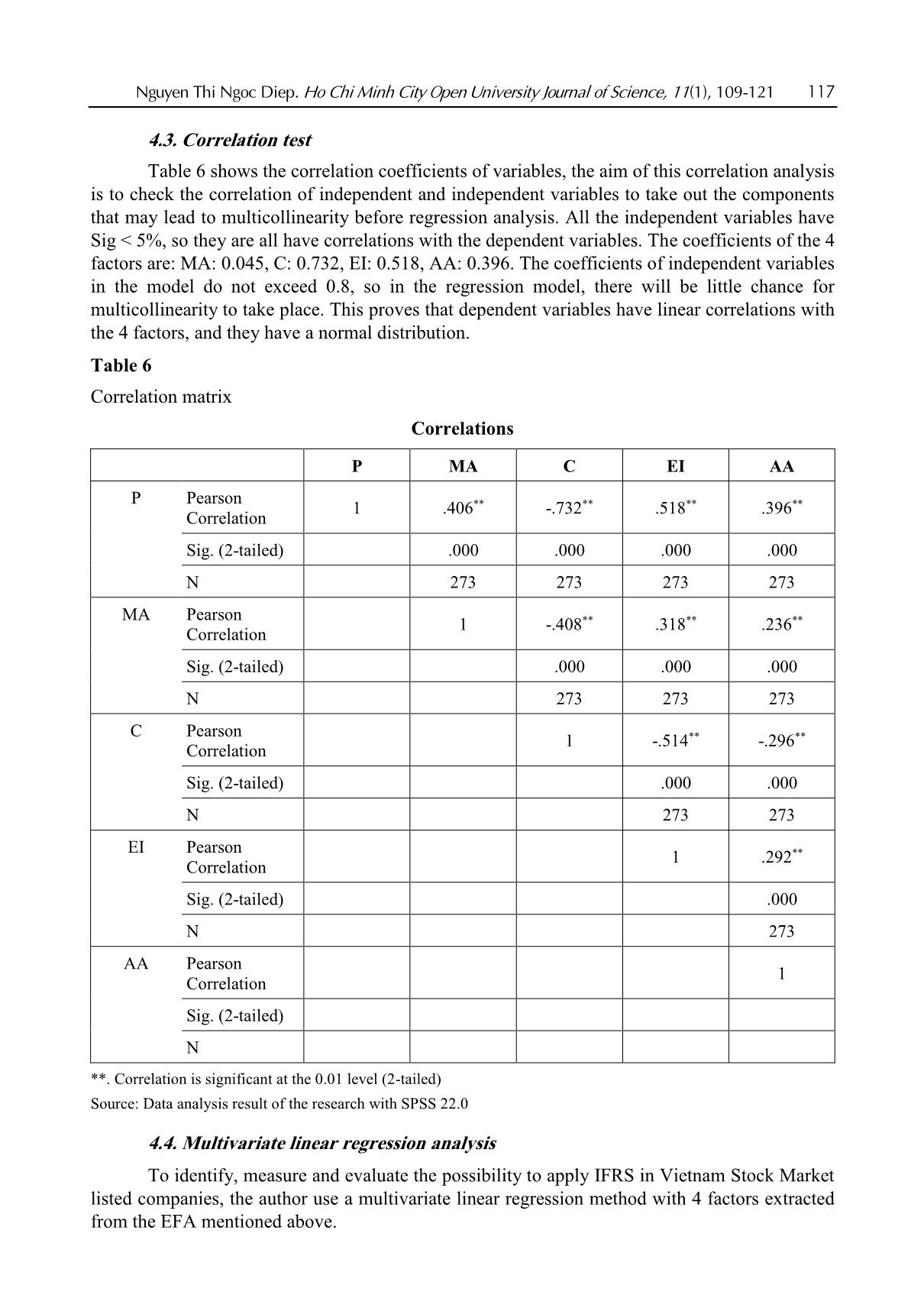
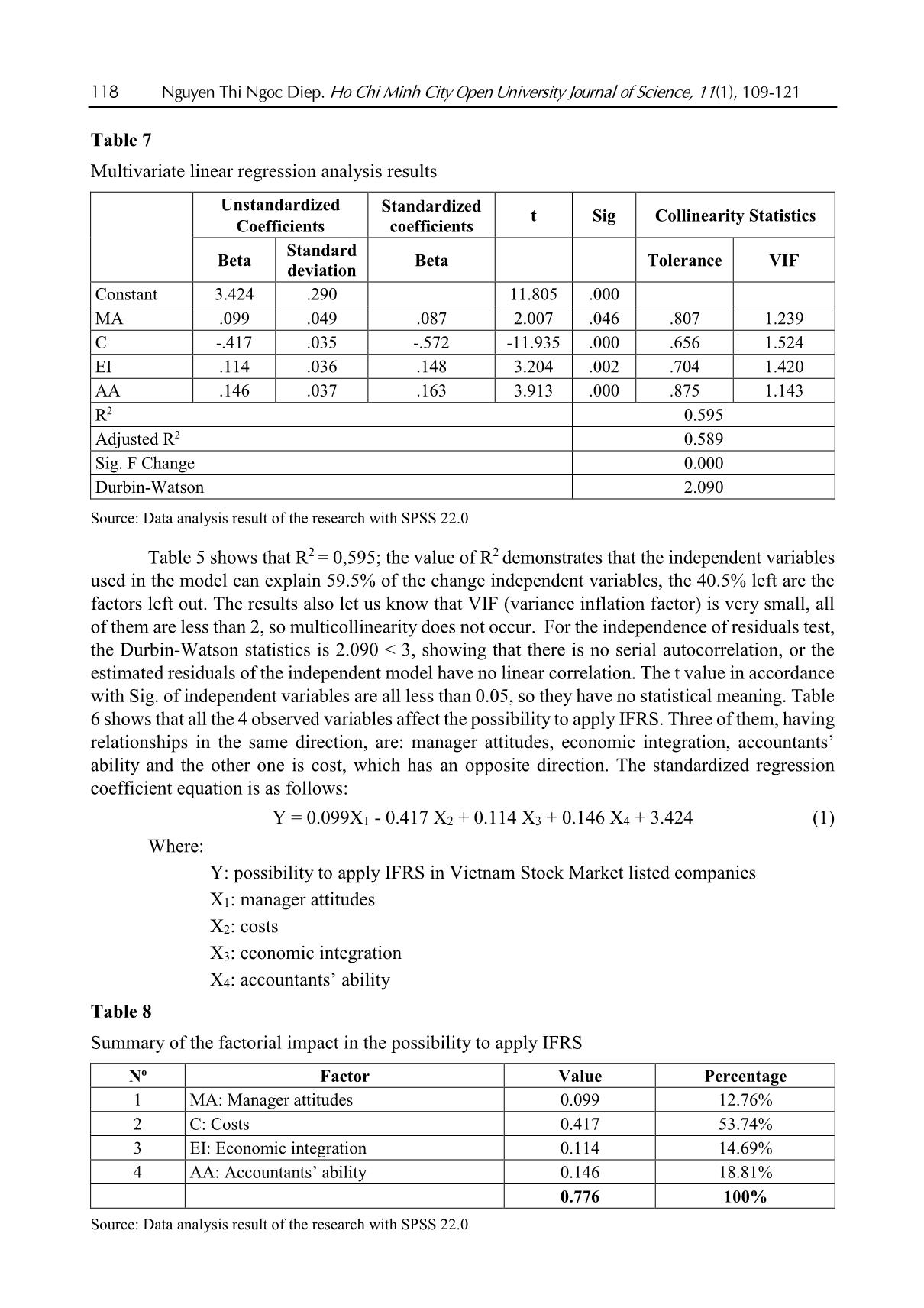
Nguyen Thi Ngoc Diep. Ho Chi Minh City Open University Journal of Science, 11(1), 109-121 109 Applicability of IFRS in Vietnam stock exchange listed companies: Perspective from Theory of Planned Behavior Nguyen Thi Ngoc Diep1* 1Ho Chi Minh City Open University, Vietnam *Corresponding author: diep.ntn@ou.edu.vn ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT DOI:10.46223/HCMCOUJS. econ.en.11.1.1237.2021 Received: October 27th, 2020 Revised: January 6th, 2021 Accepted: January 18th, 2021 Keywords: IFRS, ability of IFRS adoption The research, based upon data collected from 273 enterprises, uses the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) to identify and estimate the degree to which factors the ability to apply IFRS in listed non- financial enterprises has been affected. Through Exploratory Factor Analysis (EFA) and multivariate linear regression approach, the research proves that there are four factors placing impacts on IFRS adoption in listed companies in Vietnam. Those are management’s attitude, costs, economic integration, accounting staff’s knowledge and skills. The research results are the foundation for businesses to be fully prepared for the favorable and successful application of IFRS. In addition, the results of this study are also useful references for policy-making agencies and professional associations in promoting IFRS application in Vietnam the next time. 1. Introduction International accounting integration is always a challenging process (Christopher & Parker, 2016). The implementation of IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards) in Vietnam has been constrained due to economic, educational, political and legal conditions (Tran, 2016). Furthermore, the IFRS are basically built on Anglo - Saxon model (Anglo-Saxon model of corporate governance) and are principle-based, and as a consequence, the standards are, culturally and practically, not easily adapted in Vietnam. The project on application of financial reporting standards in Vietnam (Decision No. 345/QD-BTC on March 16, 2020 - Ministry of Finance) confirms the determination to apply these standards in financial reporting in Vietnam. The main business entities which are considered to have the abilities and conditions and to be encouraged to apply IFRS voluntarily in the period of 2022 to 2025 are listed companies. Can those companies apply IFRS? To what degree should they be involved? 2. Theoretical and hypothetical basis 2.1. Theory of Planned Behavior - TPB The Theory of Planned Behavior (Ajzen, 1991) supposes that any behavior is affected directly by behavioral intentions. The more salient the intentions are the more possibility for according behaviors we have. The main purpose of TPB is to explain human behaviors, not for predictions only, so according to the TPB, behavioral intentions are determined by three factors: attitude toward the behavior, subjective norm concerning the behavior, and perceived behavioral control. Attitude toward the behavior is assumed to be a function of readily accessible beliefs regarding the 110 Nguyen Thi Ngoc Diep. Ho Chi Minh City Open University Journal of Science, 11(1), 109-121 behavior's likely consequences, termed behavioral beliefs; the subjective norm is the expectation or subjective probability that a given referent individual or group (e.g., friends, family, spouse, coworkers, one's physician or supervisor) approves or disapproves of performing the behavior under consideration; perceived behavioral control is concerned with the presence of factors that can facilitate or impede the performance of the behavior, this is the factor that encourages or discourages the behavior. Figure 1. The Theory of Planned Behavior (Ajzen, 1991) 2.2. Research model Based on the results of the research of Djatej, Zhou, Gorton, and McGonigle (2012) and Simegn (2015), as well as the qualitative research by interviewing experts, the authors generalize the factors affecting the possibility to apply IFRS in listed companies as follows. Manager attitudes: Rogers (2010) assumed that the pioneers in innovation are the agents of change in any organization. Therefore, the change in attitudes of those agents is essential for applying changes. In his research on manager attitudes in India and Australia, Bhattacharyya (2014) found that manager attitudes positively affect the decisions in reporting sustainable development. Manager attitudes also play an important role in providing better conditions for applying IFRS in organizations (Bananuka, Kadaali, Mukyala, Muramuzi, & Namusobya, 2019). As a consequence, the hypothesis is: H1: Manager attitudes and the possibility to apply IFRS have a relationship in the same direction Costs: Tyrrall, Woodward, and Rakhimbekova (2007) proves that only 54% of the interviewed and questioned people think that adopting IFRS in Kazakhstan is a costly process. All the questioned people po ... ts (Group B) IFRS is only applied completely in parent companies (or subsidiaries) and IFRS transitions to be made when preparing consolidated financial statements in corporations (Group C) IFRS are applied completely in parent companies and all subsidiarie (Group D) Number of enterprises 19 254 140 133 49 29 60 135 273 Ratio (%) 7% 93% 51% 49% 18% 11% 22% 49% 100% Source: Summarized from data surveyed In 273 samples, there are 93% of companies that have never applied IFRS and 7% have already applied. We can see that the number of listed non-financial companies applying IFRS is quite low. As for the intention to be listed in foreign stock markets, 51% of enterprises are positive and 49% negative. Considered under the level of IFRS application, we summarized from surveyed data to divide the enterprises into 4 groups with 4 levels of applying IFRS as shown in Table 1, the results are Group A: 18%; Group B: 11%; Group C: 22% and Group D has the highest proportion of 49%. The results show that IFRS are applied completely in parent companies and all subsidiaries have the highest percentage. 4.2. Scale reliability (internal validation of measurement scales) As Table 4 shows, most of the factors have Cronbach’s Alpha indicators which are more than 0.6; corrected item-total correlation of the scales is higher than 0.3. After extracting 3 observed variants including C4 (qualified - accountant for IFRS recruitment is difficult), AA5 (accountants’ ability) (many accountants are reluctant to adopt IFRS) and P5 (enterprises are hesitant because IFRS are principle-based), the 21 observed variants left are validated and used for EFA. 116 Nguyen Thi Ngoc Diep. Ho Chi Minh City Open University Journal of Science, 11(1), 109-121 Table 4 Cronbach’s Alpha indicators Scale Number of variants Cronbach’s Alpha Minimum corrected item-total correlation Before After Manager attitudes (MA) 4 4 .812 .613 Cost (C) 5 4 .861 .667 Economic integration (EI) 5 5 .889 .697 Ability of accountants (AA) 5 4 .801 .558 Possibility to apply IFRS (P) 5 4 .874 .672 Source: Data analysis result of the research with SPSS 22.0 Using EFA with the Principle Component Analysis extraction method and orthogonal rotation (Varimax), the analysis includes 17 observed variants of EFA shown in Table 3, with the KMO test for sampling at 0.856, Barlett’s Test returns the Sig = 0.000; the factors extracted are 4, thus all are compliant with the theoretical model we built. Cumulative variance is 70.316%, and the total variance explained by each component is always bigger than 0.5. So, EFA is suitable for data and observed variables that have a correlation in the population and is used for the next analysis. Table 5 Independent variable EFA Rotated Component Matrixa Component 1 2 3 4 EI5 .832 EI1 .828 EI3 .785 EI2 .774 C2 .825 C1 .825 C3 .762 C5 .735 P3 .795 P2 .783 P1 .766 P4 .755 AA3 .866 AA2 .815 AA1 .793 Extraction Method: Principal Component Analysis Rotation Method: Varimax with Kaiser Normalization a. Rotation converged in 5 iterations. Source: Data analysis result of the research with SPSS 22.0 Nguyen Thi Ngoc Diep. Ho Chi Minh City Open University Journal of Science, 11(1), 109-121 117 4.3. Correlation test Table 6 shows the correlation coefficients of variables, the aim of this correlation analysis is to check the correlation of independent and independent variables to take out the components that may lead to multicollinearity before regression analysis. All the independent variables have Sig < 5%, so they are all have correlations with the dependent variables. The coefficients of the 4 factors are: MA: 0.045, C: 0.732, EI: 0.518, AA: 0.396. The coefficients of independent variables in the model do not exceed 0.8, so in the regression model, there will be little chance for multicollinearity to take place. This proves that dependent variables have linear correlations with the 4 factors, and they have a normal distribution. Table 6 Correlation matrix Correlations P MA C EI AA P Pearson Correlation 1 .406** -.732** .518** .396** Sig. (2-tailed) .000 .000 .000 .000 N 273 273 273 273 MA Pearson Correlation 1 -.408** .318** .236** Sig. (2-tailed) .000 .000 .000 N 273 273 273 C Pearson Correlation 1 -.514** -.296** Sig. (2-tailed) .000 .000 N 273 273 EI Pearson Correlation 1 .292** Sig. (2-tailed) .000 N 273 AA Pearson Correlation 1 Sig. (2-tailed) N **. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed) Source: Data analysis result of the research with SPSS 22.0 4.4. Multivariate linear regression analysis To identify, measure and evaluate the possibility to apply IFRS in Vietnam Stock Market listed companies, the author use a multivariate linear regression method with 4 factors extracted from the EFA mentioned above. 118 Nguyen Thi Ngoc Diep. Ho Chi Minh City Open University Journal of Science, 11(1), 109-121 Table 7 Multivariate linear regression analysis results Unstandardized Coefficients Standardized coefficients t Sig Collinearity Statistics Beta Standard deviation Beta Tolerance VIF Constant 3.424 .290 11.805 .000 MA .099 .049 .087 2.007 .046 .807 1.239 C -.417 .035 -.572 -11.935 .000 .656 1.524 EI .114 .036 .148 3.204 .002 .704 1.420 AA .146 .037 .163 3.913 .000 .875 1.143 R2 0.595 Adjusted R2 0.589 Sig. F Change 0.000 Durbin-Watson 2.090 Source: Data analysis result of the research with SPSS 22.0 Table 5 shows that R2 = 0,595; the value of R2 demonstrates that the independent variables used in the model can explain 59.5% of the change independent variables, the 40.5% left are the factors left out. The results also let us know that VIF (variance inflation factor) is very small, all of them are less than 2, so multicollinearity does not occur. For the independence of residuals test, the Durbin-Watson statistics is 2.090 < 3, showing that there is no serial autocorrelation, or the estimated residuals of the independent model have no linear correlation. The t value in accordance with Sig. of independent variables are all less than 0.05, so they have no statistical meaning. Table 6 shows that all the 4 observed variables affect the possibility to apply IFRS. Three of them, having relationships in the same direction, are: manager attitudes, economic integration, accountants’ ability and the other one is cost, which has an opposite direction. The standardized regression coefficient equation is as follows: Y = 0.099X1 - 0.417 X2 + 0.114 X3 + 0.146 X4 + 3.424 (1) Where: Y: possibility to apply IFRS in Vietnam Stock Market listed companies X1: manager attitudes X2: costs X3: economic integration X4: accountants’ ability Table 8 Summary of the factorial impact in the possibility to apply IFRS No Factor Value Percentage 1 MA: Manager attitudes 0.099 12.76% 2 C: Costs 0.417 53.74% 3 EI: Economic integration 0.114 14.69% 4 AA: Accountants’ ability 0.146 18.81% 0.776 100% Source: Data analysis result of the research with SPSS 22.0 Nguyen Thi Ngoc Diep. Ho Chi Minh City Open University Journal of Science, 11(1), 109-121 119 In Table 8, among the influencing factors, the cost has the strongest effect and the opposite direction on the ability to apply IFRS, specifically: C: cost, takes 53.74%; second: Accountants’ ability, takes 18.81%, third comes economic integration factor, takes 14.69% to the possibility to apply IFRS and last comes manager attitude factor, with 12.76%. 5. Conclusion 5.1. Conclusion The article analyzes and identifies 3 positive factors and one negative that place impacts on the possibility of applying IFRS in non-financial enterprises listed in the Vietnam Stock Market. They are manager attitudes, costs, economic integration and accountants’ ability. With this paper, the author hope to help administrators and policy planners have more specific concepts about the above issues and have better solutions in the coming time, giving better conditions for enterprises to apply IFRS more swiftly and successfully. 5.2. Policy implication Costs, the factor that places the most important impact on the possibility of the application of IFRS, can be easily identified. The higher the initial cost of investment, the bigger the obstacles for enterprises to adapt to IFRS implementation. To cut costs for companies, experts from professional organizations must be involved, they can give good help on IFRS implementation, ensuring the “do right the first time” for enterprises in meeting IFRS requirements. Furthermore, accountants’ knowledge of IFRS is another factor determining the success of IFRS application. If the knowledge in IFRS is widely updated among those staff, the IFRS implementation will no more give difficulties for enterprises. Additionally, the economic integration also pushes the possibility to apply IFRS. Graceful governmental policies to encourage international business activities also give benefits to the implementation of IFRS in Vietnamese enterprises. Lastly, the manager's attitude should be changed and updated towards IFRS adaptation. The more positive the attitude they have, the better chance for IFRS to be applied. So, it is important for policymakers to make business managers understand their benefits and responsibilities in IFRS implementation. References Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 50(2), 179-211. Al-Absy, M. S. M., & Ismail, K. N. I. K. (2019). Accountants perception on the factors affecting the adoption of international financial reporting standards in Yemen. International Journal of Financial Research, 10(4), 128-142. Albaskri, I. K. M. (2015). The perception of accountants on IFRS adoption: Evidence from Libya (Unpublished master's thesis). University Utara Malaysia, Malaysia. Bananuka, J., Kadaali, A. W., Mukyala, V., Muramuzi, B., & Namusobya, Z. (2019). Audit committee effectiveness, isomorphic forces, managerial attitude and adoption of international financial reporting standards. Journal of Accounting in Emerging Economies, 9(4), 502-526. 120 Nguyen Thi Ngoc Diep. Ho Chi Minh City Open University Journal of Science, 11(1), 109-121 Bananuka, J., Tumwebaze, Z., Musimenta, D., & Nuwagaba, P. (2019). Determinants of adoption of international financial reporting standards in Ugandan micro finance institutions. African Journal of Economic and Management Studies, 10(3), 336-355. Baruni, W., & Sentosa, I. (2014). The effect of economic factors and stock market in implementing the IAS in Libya. International Journal of Business and Management Invention, 2(10), 32-44. Bassemir, M. (2018). Why do private firms adopt IFRS? Accounting and Business Research, 48(3), 237-263. Bhattacharyya, A. (2014). Managerial attitude and support for social responsibility through the lens of legitimacy theory-a cross country comparison. Social Responsibility Journal, 10(4), 716-736. Boateng, A. A., Arhin, A. B., & Afful, V. (2014). International financial reporting standard’s (IFRS) adoption in Ghana: Rationael, benefits and challenges. Journal of Advocacy, Research and Education, 1(1), 26-32. Boumediene, S. L., Zarrouk, R., & Tanazefti, I. (2016). Obstacles to the adoption of the IAS/IFRS in Tunisia. Journal of Applied Business Research, 32(3), 621-636. Bui, N. T., Chuc, T. A., & Le, O. T. T. (2020). The implication of applying IFRS in Vietnamese enterprises from an expert perspective. Management Science Letters, 10(3), 551-564. Choi, F. D., & Meek, G. (2008). International accounting (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education Inc. Christopher, N., & Parker, R. B. (2016). Comparative international accounting (13th ed.). Edinburgh Gate, England: Pearson Education Limited. Djatej, A., Zhou, D., Gorton, D., & McGonigle, W. (2012). Critical factors of IFRS adoption in the US: An empirical study. Journal of Finance and Accountancy, 9(1), 1-14. Ha, T. X., & Nguyen, H. N. (2018). Factors affecting the transion from Vietnamese accounting standards to IFRS in financial statements. Foreign Economic Magazine, 102, 1-19. Judge, W., Li, S., & Pinsker, R. (2010). National adoption of international accounting standards: An institutional perspective. Corporate Governance: An International Review, 18(3), 161-174. Kossentini, A., & Othman, H. (2014). A study of the institutional and economic determinants of IFRS adoption in emerging economies. Paper presented at the TIJA Symposium TIJA, VK Zimmerman Center for International Education & Research in Accounting, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, IL. Lasmin, R. (2011). An institutional perspective on international financial reporting standards adoption in developing countries. Academy of Accounting and Financial Studies Journal, 15(2), 61-71. Ministry of Finance. (2020). Decision 345/QD-BTC - Approving scheme for application of financial reporting standards in Vietnam. Ministry of finance. Retrieved August 20, 2020, from Mısırlıoğlu, İ. U., Tucker, J., & Yükseltürk, O. (2013). Does mandatory adoption of IFRS guarantee compliance? The International Journal of Accounting, 48(3), 327-363. Nguyen Thi Ngoc Diep. Ho Chi Minh City Open University Journal of Science, 11(1), 109-121 121 Nguyen, P. C., & Nguyen, T. D. K. (2012). International harmonization and national particularities of accounting: Recent accounting development in Vietnam. Journal of Accounting & Organizational Change, 8(3), 431-451. Oppong, C., & Aga, M. (2019). Economic growth in European Union: Does IFRS mandatory adoption matter? International Journal of Emerging Markets, 14(5), 792-808. Rogers, E. M. (2010). Diffusion of innovations (4th ed.). New York, NY: Simon and Schuster. Shima, K. M., & Yang, D. C. (2012). Factors affecting the adoption of IFRS. International Journal of Business, 17(3), 276 -298. Simegn, Y. (2015). Adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) in Ethiopia: Empirical evidence. The International Journal Research Publication’s Research Journal of Economics and Business Studies, 4(3), 1-20. Tran, T. Q. (2016). Factors that affect the application of international standards in for accounting in countries. Retrieved August 20, 2020, from doi-72/nhung-nhan-to-tac-dong-den-viec-ap-dung-chuan-muc-quoc-te-ve-ke-toan-tai-cac- quoc-gia-191.html Tyrrall, D., Woodward, D., & Rakhimbekova, A. (2007). The relevance of international financial reporting standards to a developing country: Evidence from Kazakhstan. The International Journal of Accounting, 42(1), 82-110.
File đính kèm:
 applicability_of_ifrs_in_viet_nam_stock_exchange_listed_comp.pdf
applicability_of_ifrs_in_viet_nam_stock_exchange_listed_comp.pdf

