Vai trò trung gian của nhận thức tính hữu ích lên mối quan hệ giữa chất lượng hệ thống thông tin kế toán và sử dụng hệ thống thông tin kế toán
Nghiên cứu được thực hiện nhằm xem xét vai trò trung gian của nhận thức tính hữu ích
của hệ thống thông tin kế toán đối với mối quan hệ giữa chất lượng hệ thống thông tin kế toán
(AIS) và sử dụng Hệ thống thông tin kế toán trong môi trường ứng dụng hệ thống hoạch định
nguồn lực doanh nghiệp (ERP) tại các doanh nghiệp tại Việt Nam. Mẫu nghiên cứu chính thức
gồm 104 đối tượng, bao gồm cả nhân viên kế toán và nhà quản lý tham gia vào việc sử dụng AIS.
Dữ liệu nghiên cứu được thu thập chủ yếu thông qua khảo sát bảng câu hỏi (từ tháng 7 năm
2019 đến tháng 9 năm 2019) và sau đó được sử dụng để phân tích thống kê mô tả và thực hiện
kiểm định giả thuyết. Kết quả cho thấy nhận thức tính hữu ích không đóng vai trò trung gian
trong mối quan hệ giữa chất lượng hệ thống thông tin kế toán và sử dụng hệ thống thông tin kế
toán. Có sự ảnh hưởng trực tiếp đáng kể nhưng sự ảnh hưởng gián tiếp là không đáng kể.

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5
Trang 6
Trang 7
Trang 8
Trang 9

Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Vai trò trung gian của nhận thức tính hữu ích lên mối quan hệ giữa chất lượng hệ thống thông tin kế toán và sử dụng hệ thống thông tin kế toán

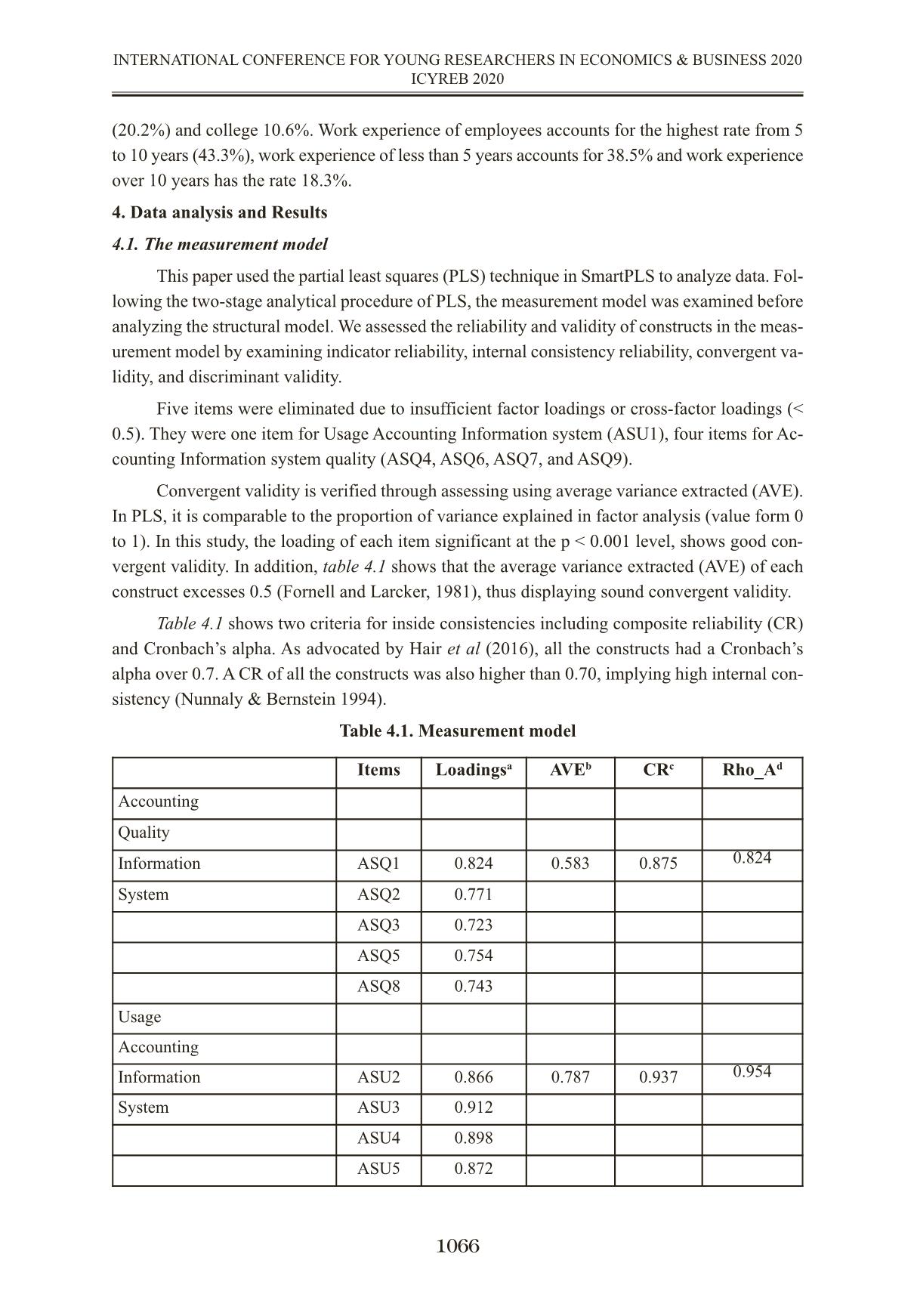
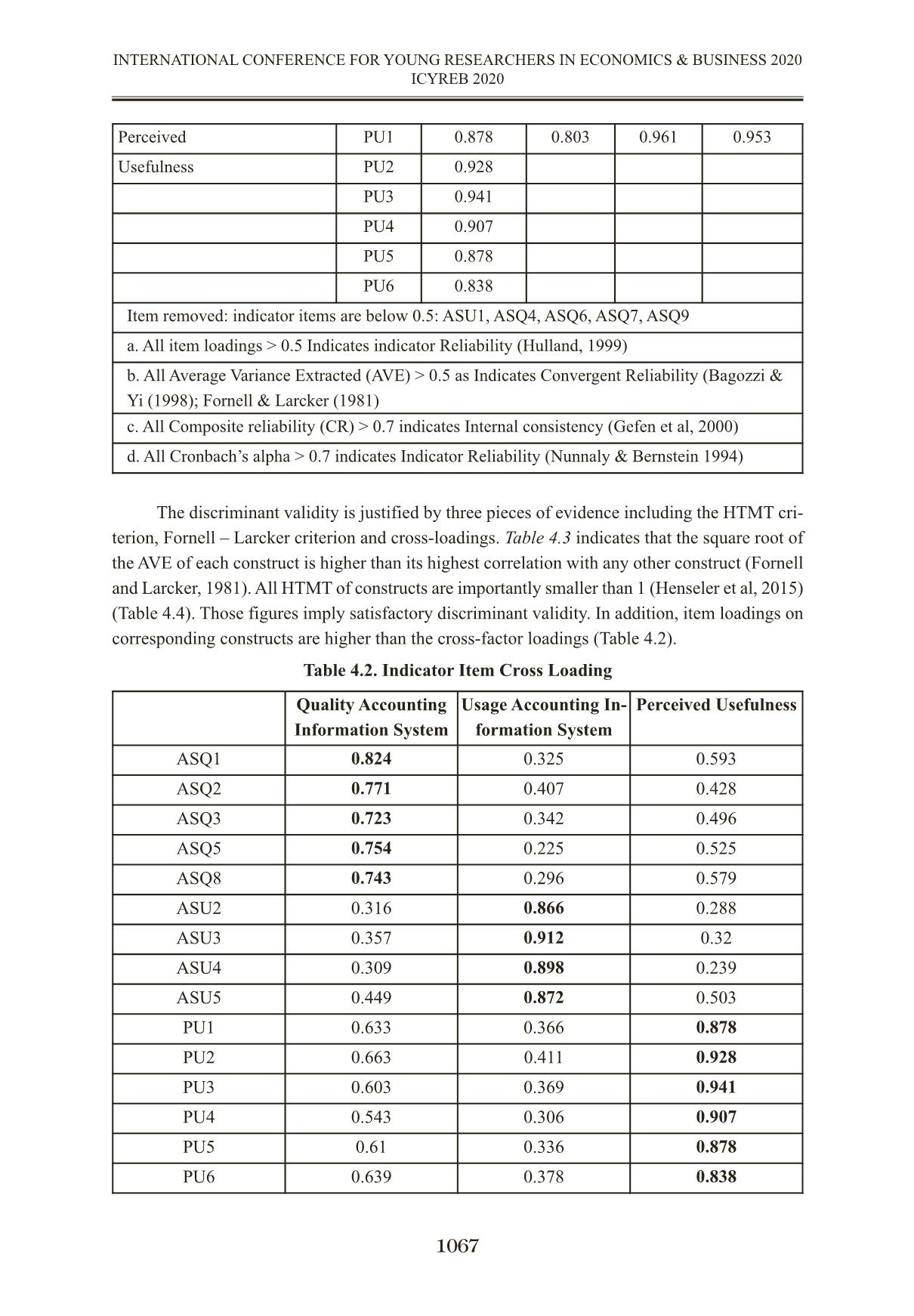
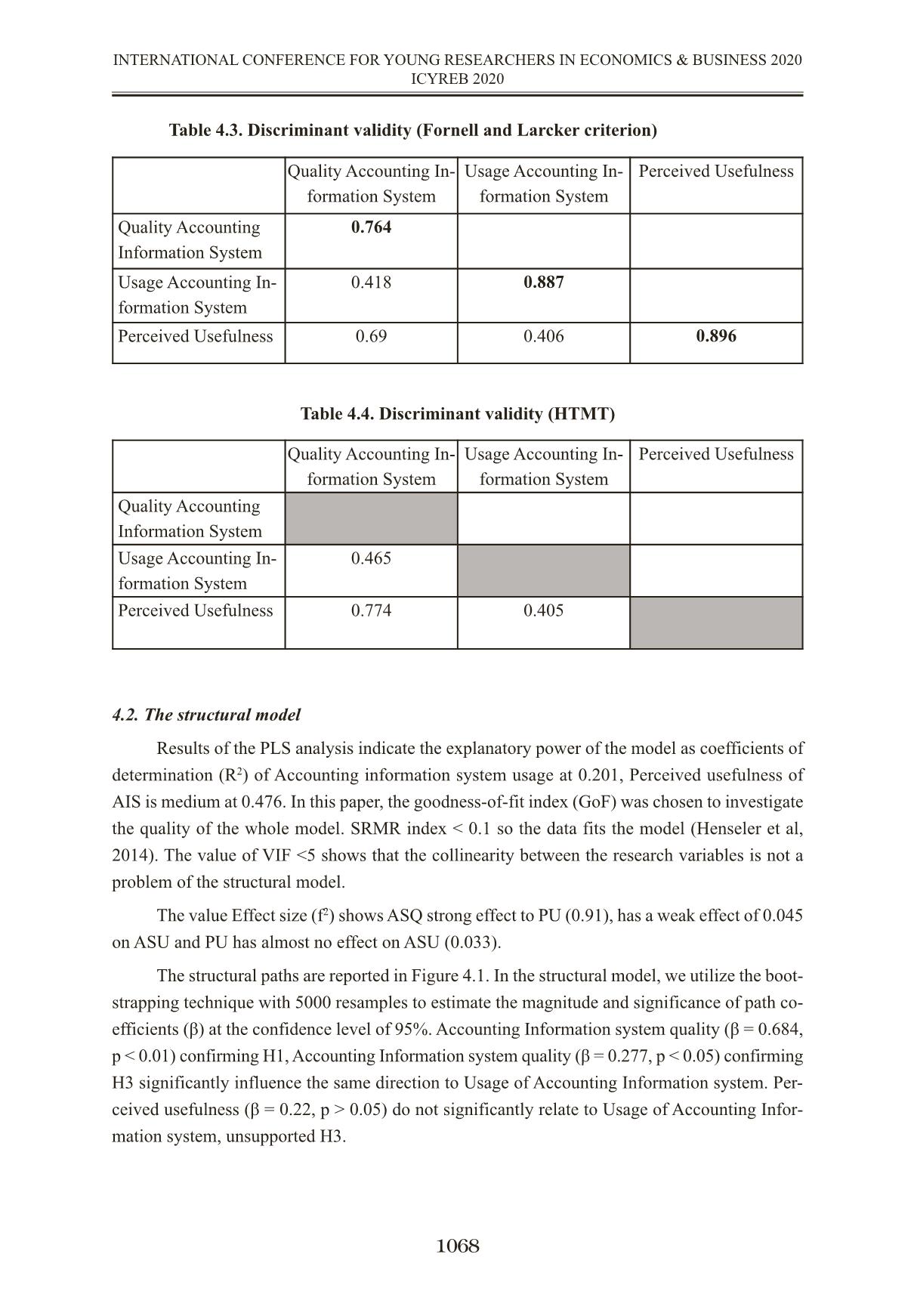
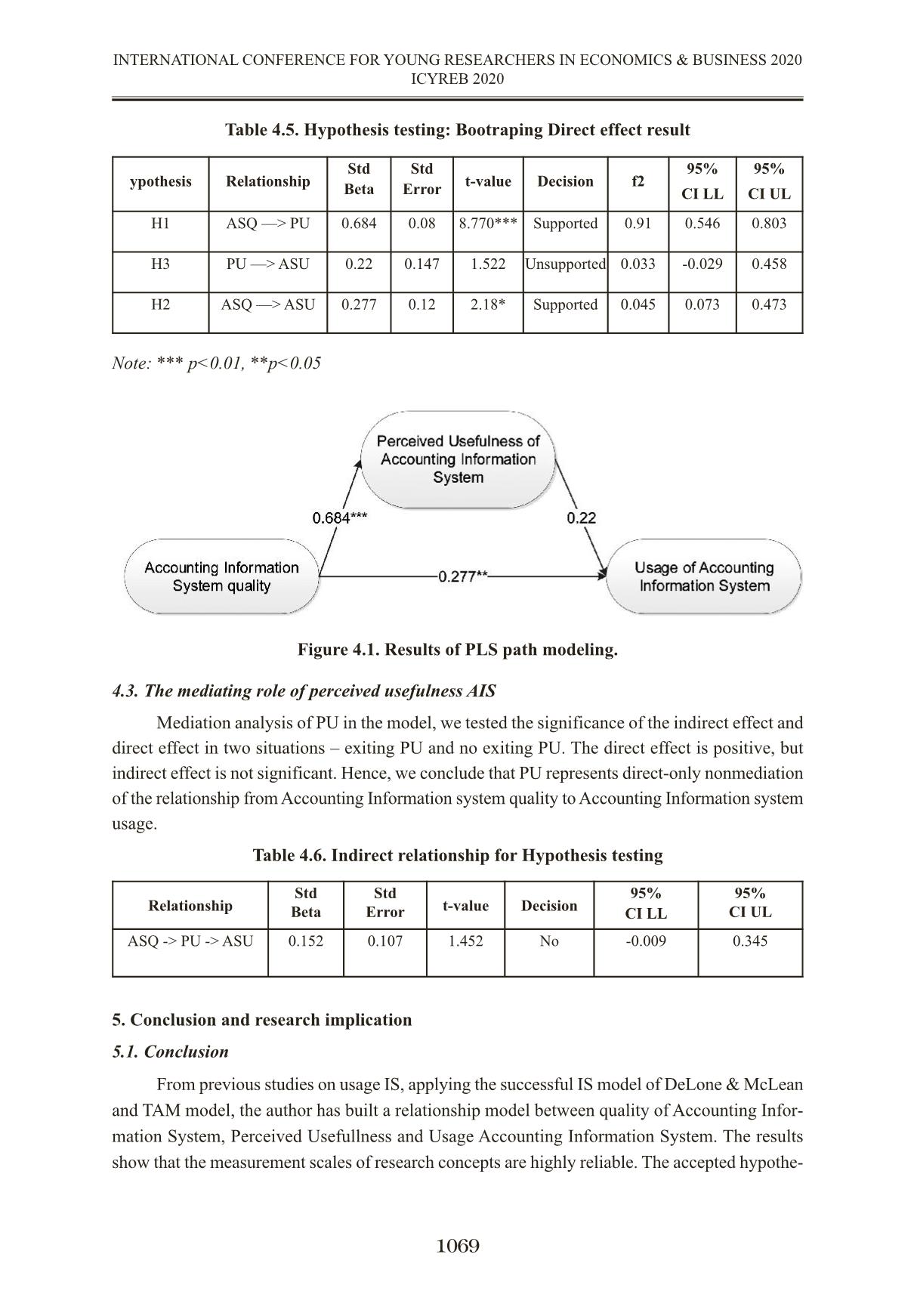
THE MEDIATING ROLE OF PERCEIVED USEFULNESS ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN QUALITY OF ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM AND USAGE ACCOUNTING INFORMATION SYSTEM VAI TRÒ TRUNG GIAN CỦA NHẬN THỨC TÍNH HỮU ÍCH LÊN MỐI QUAN HỆ GIỮA CHẤT LƯỢNG HỆ THỐNG THÔNG TIN KẾ TOÁN VÀ SỬ DỤNG HỆ THỐNG THÔNG TIN KẾ TOÁN TS. Lương Đức Thuận; ThS. Trương Thị Thu Hương Trường Đại học Kinh tế TP.HCM thuanluongktkt@ueh.edu.vn Abstract The study was conducted to examine the mediating role of perceived usefulness of Ac- counting Information System on relationship between quality of accounting information system (AIS) and usage of Accounting Information System in application enterprise resource planning (ERP) in enterprises in Viet Nam. Formal research samples of 104 subjects, including account- ants and managers involved in the use AIS in the ERP. Research data were collected primarily through questionnaire survey (July, 2019 – September, 2019) and then it is used to analyze de- scriptive statistics and perform hypothesis tests. The result shows that perceived usefulness do not plays a mediating role in the relationship between quality of accounting information system and the usage of accounting information system. There is significant direct effect but not signif- icant indirect effect. Keywords: Quality of Accounting Information System, Perceived usefulness of Accounting Information System, Usage of Accounting Information System. Tóm tắt Nghiên cứu được thực hiện nhằm xem xét vai trò trung gian của nhận thức tính hữu ích của hệ thống thông tin kế toán đối với mối quan hệ giữa chất lượng hệ thống thông tin kế toán (AIS) và sử dụng Hệ thống thông tin kế toán trong môi trường ứng dụng hệ thống hoạch định nguồn lực doanh nghiệp (ERP) tại các doanh nghiệp tại Việt Nam. Mẫu nghiên cứu chính thức gồm 104 đối tượng, bao gồm cả nhân viên kế toán và nhà quản lý tham gia vào việc sử dụng AIS. Dữ liệu nghiên cứu được thu thập chủ yếu thông qua khảo sát bảng câu hỏi (từ tháng 7 năm 2019 đến tháng 9 năm 2019) và sau đó được sử dụng để phân tích thống kê mô tả và thực hiện kiểm định giả thuyết. Kết quả cho thấy nhận thức tính hữu ích không đóng vai trò trung gian trong mối quan hệ giữa chất lượng hệ thống thông tin kế toán và sử dụng hệ thống thông tin kế toán. Có sự ảnh hưởng trực tiếp đáng kể nhưng sự ảnh hưởng gián tiếp là không đáng kể. Từ khóa: Chất lượng Hệ thống thông tin kế toán, Nhận thức tính hữu ích của hệ thống thông tin kế toán, Sử dụng hệ thống thông tin kế toán. 1061 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE FOR YOUNG RESEARCHERS IN ECONOMICS & BUSINESS 2020 ICYREB 2020 1. Introduction In the field of AIS research, the use of AIS is considered a new issue attracting the research interest of researchers. According to the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) of Davis (1989), information system usage (IS) behavior is understood as the usage process of the system users when they realize the usefulness and the ease of use of a new system or technology. In addition, in DeLone & McLean’s successful IS model, the use of the system is mentioned, which is the extent and way in which employees use the IS capabilities and to engage in behavior of usage IS need a quality IS. The usage AIS played a crucial role which enhance company’s value added by providing internally generated financial statements that would help the company to make better and efficient strategic plan. Regarding the research on decisions or behaviors using IS, using enterprise resource plan- ning system (ERP), a lot of research has been done and mainly based on the Technology Accept- ance Model TAM. The TAM model was first introduced by Davis in 1989, up to now there are many different versions of the TAM model to reinforce and further improve the applicability of this model in the assessment of attitudes and behavior of usage information technology, usage IS. Researches in the world and in the country have used successful IS theory and TAM model to measure and evaluate the factors affecting the behavior of using IS. Thus, the combination of successful IS theory and TAM model will help to see the inter- action between AIS quality and the behavior of using AIS through users’ perception in the system about the usefulness of AIS. In this study, applies a combination of successful IS theory and TAM model in explaining the mediating role of perceived usefulness of AIS in the relationship between AIS quality and usage AIS. 2. Literature review and research model 2.1. Literature review 2.1.1. Quality of Accounting Information System The views on the quality of AIS are mainly based on the view of the quality of IS imple- mented in previous studies and analyzed from the quality point of view of the information systems model by DeLone & McLean. According to DeLone & McLean, 2003, system quality is associ- ated with success and they use a scale of quality of information system consistent with the de- veloped model, including: ease of use, sys ... ariance Extracted (AVE) > 0.5 as Indicates Convergent Reliability (Bagozzi & Yi (1998); Fornell & Larcker (1981) c. All Composite reliability (CR) > 0.7 indicates Internal consistency (Gefen et al, 2000) d. All Cronbach’s alpha > 0.7 indicates Indicator Reliability (Nunnaly & Bernstein 1994) Quality Accounting Information System Usage Accounting In- formation System Perceived Usefulness ASQ1 0.824 0.325 0.593 ASQ2 0.771 0.407 0.428 ASQ3 0.723 0.342 0.496 ASQ5 0.754 0.225 0.525 ASQ8 0.743 0.296 0.579 ASU2 0.316 0.866 0.288 ASU3 0.357 0.912 0.32 ASU4 0.309 0.898 0.239 ASU5 0.449 0.872 0.503 PU1 0.633 0.366 0.878 PU2 0.663 0.411 0.928 PU3 0.603 0.369 0.941 PU4 0.543 0.306 0.907 PU5 0.61 0.336 0.878 PU6 0.639 0.378 0.838 Table 4.3. Discriminant validity (Fornell and Larcker criterion) Table 4.4. Discriminant validity (HTMT) 4.2. The structural model Results of the PLS analysis indicate the explanatory power of the model as coefficients of determination (R2) of Accounting information system usage at 0.201, Perceived usefulness of AIS is medium at 0.476. In this paper, the goodness-of-fit index (GoF) was chosen to investigate the quality of the whole model. SRMR index < 0.1 so the data fits the model (Henseler et al, 2014). The value of VIF <5 shows that the collinearity between the research variables is not a problem of the structural model. The value Effect size (f2) shows ASQ strong effect to PU (0.91), has a weak effect of 0.045 on ASU and PU has almost no effect on ASU (0.033). The structural paths are reported in Figure 4.1. In the structural model, we utilize the boot- strapping technique with 5000 resamples to estimate the magnitude and significance of path co- efficients (β) at the confidence level of 95%. Accounting Information system quality (β = 0.684, p < 0.01) confirming H1, Accounting Information system quality (β = 0.277, p < 0.05) confirming H3 significantly influence the same direction to Usage of Accounting Information system. Per- ceived usefulness (β = 0.22, p > 0.05) do not significantly relate to Usage of Accounting Infor- mation system, unsupported H3. 1068 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE FOR YOUNG RESEARCHERS IN ECONOMICS & BUSINESS 2020 ICYREB 2020 Quality Accounting In- formation System Usage Accounting In- formation System Perceived Usefulness Quality Accounting Information System 0.764 Usage Accounting In- formation System 0.418 0.887 Perceived Usefulness 0.69 0.406 0.896 Quality Accounting In- formation System Usage Accounting In- formation System Perceived Usefulness Quality Accounting Information System Usage Accounting In- formation System 0.465 Perceived Usefulness 0.774 0.405 Table 4.5. Hypothesis testing: Bootraping Direct effect result Note: *** p<0.01, **p<0.05 Figure 4.1. Results of PLS path modeling. 4.3. The mediating role of perceived usefulness AIS Mediation analysis of PU in the model, we tested the significance of the indirect effect and direct effect in two situations – exiting PU and no exiting PU. The direct effect is positive, but indirect effect is not significant. Hence, we conclude that PU represents direct-only nonmediation of the relationship from Accounting Information system quality to Accounting Information system usage. Table 4.6. Indirect relationship for Hypothesis testing 5. Conclusion and research implication 5.1. Conclusion From previous studies on usage IS, applying the successful IS model of DeLone & McLean and TAM model, the author has built a relationship model between quality of Accounting Infor- mation System, Perceived Usefullness and Usage Accounting Information System. The results show that the measurement scales of research concepts are highly reliable. The accepted hypothe- 1069 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE FOR YOUNG RESEARCHERS IN ECONOMICS & BUSINESS 2020 ICYREB 2020 ypothesis Relationship Std Beta Std Error t-value Decision f2 95% CI LL 95% CI UL H1 ASQ —> PU 0.684 0.08 8.770*** Supported 0.91 0.546 0.803 H3 PU —> ASU 0.22 0.147 1.522 Unsupported 0.033 -0.029 0.458 H2 ASQ —> ASU 0.277 0.12 2.18* Supported 0.045 0.073 0.473 Relationship Std Beta Std Error t-value Decision 95% CI LL 95% CI UL ASQ -> PU -> ASU 0.152 0.107 1.452 No -0.009 0.345 ses include hypotheses H1 and H2, whereby the quality AIS has an impact on the perceived use- fulness of AIS and quality AIS that affects the usage AIS. However, perceived usefulness AIS does not act as a mediating variable in the relationship between AIS quality and the usage AIS. 5.2. Research Implication With the research results shows that the need to improve the quality of AIS in enterprises. AIS is now a system with the support of IT, mainly in the application environment of accounting software and ERP, so improving the quality of AIS should focus on: - Continue to improve processes and procedures in the process of collecting, processing, storing data and providing information to different users, creating ease of access and use the sys- tem. These procedures should be specific in writing and stored in the system with system docu- mentation tools such as data flow diagrams and flowcharts for each of the different processing processes, but have full approval. - Increased AIS connectivity further with other systems in the enterprise through the help of processing software. Orientation and apply technology effectively in accounting and manage- ment, creating convenience and ease in using the system. - Control the ERP software evaluation and selection process in AIS, regularly update new software versions and suit business needs, to ensure flexibility, integration, and customization requirements and high control over software. According to the survey results on the use of ERP systems, there are 2 groups of ERP software used by enterprises, which are domestic and foreign software. For domestic software, although the cost is lower, it is necessary to pay attention to control and integration features to contribute to improving the quality of AIS. - Further improve the quality of data of enterprises and business operations of enterprises, create a diverse and scaled data warehouse to serve the needs of data mining and analysis to sup- port more useful information for administrators. - Improve the quality of IT infrastructure, regularly monitor and manage computer systems, peripheral devices, and communications to promptly detect problems and risks and take appro- priate corrective measures. Strengthening network security solutions, especially in the case of information transfer on computer networks. When the AIS on the computer platform has stable operation and effective management, the quality of AIS will be enhanced. - Improving the quality of AIS will contribute to improving the quality of accounting in- formation, currently most businesses have applied IT in accounting, although the level of IT ap- plication in accounting is not the same, but basically businesses are applying accounting software and ERP system in accounting work and enterprise management. The level of IT application will affect the way of collecting, processing data and providing accounting information, thus affecting risks as well as the management and control of AIS. The awareness and assessment of the possi- bility of errors and frauds for AIS in the computer environment, thereby having important control procedures, will contribute to improving the quality of AIS. In AIS control, it is necessary to focus on general control and application control, general control including control activities re- lated to the entire processing system and affecting all processing application systems in business. 1070 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE FOR YOUNG RESEARCHERS IN ECONOMICS & BUSINESS 2020 ICYREB 2020 Application control includes the implementation policies and procedures that affect a specific application system and performance in AIS. These two controls are established and coordinated will help ensure the entire AIS operates effectively and efficiently. 5.3. Limitations and future research Although the initial purpose of evaluating the mediating role of perceived usefulness AIS in the relationship between AIS quality and usage AIS has been achieved, this study also has some of the limitations First, the survey is mainly in Ho Chi Minh City and a neighboring province, so the gener- ality of the study is not high and may be certain limited. In addition, the study used convenient sampling by sending questionnaires directly or via email to survey subjects. Therefore, further studies should conduct additional surveys in different regions of the country and have a classifi- cation of survey subjects. Second, according to the TAM model, there may be many external factors influencing the perceived usefulness of IS. Further studies need to develop additional factors influencing the per- ceived usefulness of AIS such as individual characteristics, subjective standards and the organi- zation support in the operation of the AIS. Third, it is possible to learn and apply more relevant background theories in AIS to build research models and use some more moderating, mediating variables in relationships between research concepts and the usage AIS. REFERENCES Amoako-Gyampah, K. (2007),‘Perceived usefulness, user involvement and behavioral intention: an empirical study of ERP implementation’, Computers in Human Behavior, 23(3), 1232-1248. Amoako-Gyampah, K., & Salam, A. F. (2004), ‘An extension of the technology acceptance model in an ERP implementation environment’, Information & management, 41(6), 731-745. Bagozzi, R. P., Yi, Y., & Nassen, K. D. (1998). Representation of measurement error in marketing variables: Review of approaches and extension to three-facet designs. Journal of Econometrics, 89(1-2), 393-421. Calisir, F., Altin Gumussoy, C., & Bayram, A. (2009), ‘Predicting the behavioral intention to use enterprise resource planning systems: An exploratory extension of the technology accept- ance model’, Management research news, 32(7), 597-613. Cheng, Y. M. (2012). Effects of quality antecedents on e-learning acceptance. Internet Research. Davis, F. D. (1989), 'Perceived Usefulness, Perceived Ease of Use, and User Acceptance of Information Technology',MIS Quarterly, 13(3), 319-339. Delone, W. H., & McLean, E. R. (2003), 'The DeLone and McLean model of information systems success: a ten-year update', Journal of management information systems, 19(4), 9-30. 1071 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE FOR YOUNG RESEARCHERS IN ECONOMICS & BUSINESS 2020 ICYREB 2020 Delone, W. H. & Mclean, E. R. (2016). Information systems success measurement. Foundations and Trends® in Information Systems, 2(1),1-116. Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Structural equation models with unobservable v ariables and measurement error: Algebra and statistics. Gefen, D., Straub, D., & Boudreau, M. C. (2000). Structural equation modeling and regression: Guidelines for research practice. Communications of the association for information systems, 4(1), 7. Hair Jr, J. F., Sarstedt, M., Matthews, L. M., & Ringle, C. M. (2016). Identifying and treat- ing unobserved heterogeneity with FIMIX-PLS: part I–method. European Business Review. Hassanzadeh, A., Kanaani, F., & Elahi, S. (2012). A model for measuring e-learning systems success in universities. Expert Systems with Applications, 39(12), 10959-10966. Henseler, J., Hubona, G., & Ray, P. A. (2016). Using PLS path modeling in new technology research: updated guidelines. Industrial management & data systems. Hulland, J. (1999). Use of partial least squares (PLS) in strategic management research: A review of four recent studies. Strategic management journal, 20(2), 195-204. Lee, S., & Heo, C. Y. (2009). Corporate social responsibility and customer satisfaction among US publicly traded hotels and restaurants. International Journal of Hospitality Manage- ment, 28(4), 635-637. Liu, Y., Li, H., & Carlsson, C. (2010). Factors driving the adoption of m-learning: An em- pirical study. Computers & Education, 55(3), 1211-1219. Iivari, J. (2005). An empirical test of the DeLone-McLean model of information system success. ACM SIGMIS Database: the DATABASE for Advances in Information Systems, 36(2), 8-27. Mamić Sačer, I., Žager, K., & Tušek, B. (2006). Accounting information system’s quality as the ground for quality business reporting. In IADIS International conference, e-commerce 2006 (p. 59). Mohammadi, H. (2015). Social and individual antecedents of m-learning adoption in Iran. Computers in Human Behavior, 49, 191-207. Nunnally, J. C., & Bernstein, I. H. (1994), Psychological theory, MacGraw-Hill, New York. Nwankpa, J., & Roumani, Y. (2014), 'Understanding the link between organizational learn- ing capability and ERP system usage: An empirical examination', Computers in Human Behavior, 33, 224-234. Nwankpa, J. K. (2019). ERP systems benefit realization and the role of ERP-enabled ap- plication integration. In Advanced methodologies and technologies in business operations and management (pp. 802-815). IGI Global. Petter, S., DeLone, W., & McLean, E. (2008). Measuring information systems success: models, dimensions, measures, and interrelationships. European journal of information systems, 17(3), 236-263. 1072 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE FOR YOUNG RESEARCHERS IN ECONOMICS & BUSINESS 2020 ICYREB 2020 Rajan, C. A. & Baral, R. (2015), 'Adoption of ERP system: An empirical study of factors influencing the usage of ERP and its impact on end user', IIMB Management Review, 27(2), 105- 117. Reynolds, G. W., & Stair, R. M. (2018). Principles of information systems. Cengage Learning. Romney, M. B., & Steinbart, P. J. (2018). Accounting Information Systems. Fourteenth. Saadé, R., & Bahli, B. (2005), 'The impact of cognitive absorption on perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use in on-line learning: an extension of the technology acceptance model', Information & management, 42(2), 317-327. Seddon, P., & Kiew, M. Y. (1996). A partial test and development of DeLone and McLean's model of IS success. Australasian Journal of Information Systems, 4(1). Tilahun, M. (2019). A Review on Determinants of Accounting Information System Adop- tion. Science Journal of Business and Management, 7(1), 17-22. Uzoka, F. M. E., Abiola, R. O., & Nyangeresi, R. (2008). Influence of product and organi- zational constructs on ERP acquisition using an extended technology acceptance model. Interna- tional Journal of Enterprise Information Systems (IJEIS), 4(2), 67-83. Wixom, B. H., & Todd, P. A. (2005). A theoretical integration of user satisfaction and tech- nology acceptance. Information systems research, 16(1), 85-102. 1073 INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE FOR YOUNG RESEARCHERS IN ECONOMICS & BUSINESS 2020 ICYREB 2020
File đính kèm:
 vai_tro_trung_gian_cua_nhan_thuc_tinh_huu_ich_len_moi_quan_h.pdf
vai_tro_trung_gian_cua_nhan_thuc_tinh_huu_ich_len_moi_quan_h.pdf

