The influence of website quality on consumer’s e-loyalty through the mediating role of e-trust and e-satisfaction: An evidence from online shopping in Viet Nam
Internet has been changing the traditional ways of purchasing goods and services. The users have no
longer been restricted by time and geographical factors. They could actively purchase the products and
goods regardless of any time and location factors. The Internet has brought about new methods of
communication and new ways of exchanging everyday information among peoples. The everincreasing number of Internet users would also coincide with the development of online purchasing
(Joines et al., 2003). The fast development of the Internet would be explained by the combination of
broadband technology and the change of customer behavior (Oppenheim, 2006). Online shopping, also
known as internet shopping or e-shopping, can be explained as electronic commerce when buyers and
sellers virtually meet others through a web browser (Kaur & Joshi, 2012). In other words, e-shopping
is a process when users decide to buy products or services on the Internet economy (Puranik & Bansal,
2014). Unlike traditional shops that require physical locations, physical security services, and specific
timeframes to operate, internet shops need none of those requirements. Customers can access to the
shop from anywhere (e.g., without worrying about geographical boundaries) and anytime (e.g., 24-hour
opening, 7 days a week, time zones) they like as long as they have internet connection and an
appropriate device like a computer, a tablet or a smartphone (Bidgoli, 2010; Karthika &
Manojanaranjani, 2018). Since people are more and more busy with their jobs and internet has been
widely and easily accessible, e-shopping has “redefined business and customer relationships, business
processes, even sometimes restructuring the whole industry by providing new distribution channel, new
delivery methods, new payment methods and new medium for communication” (Cosgun &
Dogerlioglu, 2012).

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4

Trang 5

Trang 6

Trang 7

Trang 8
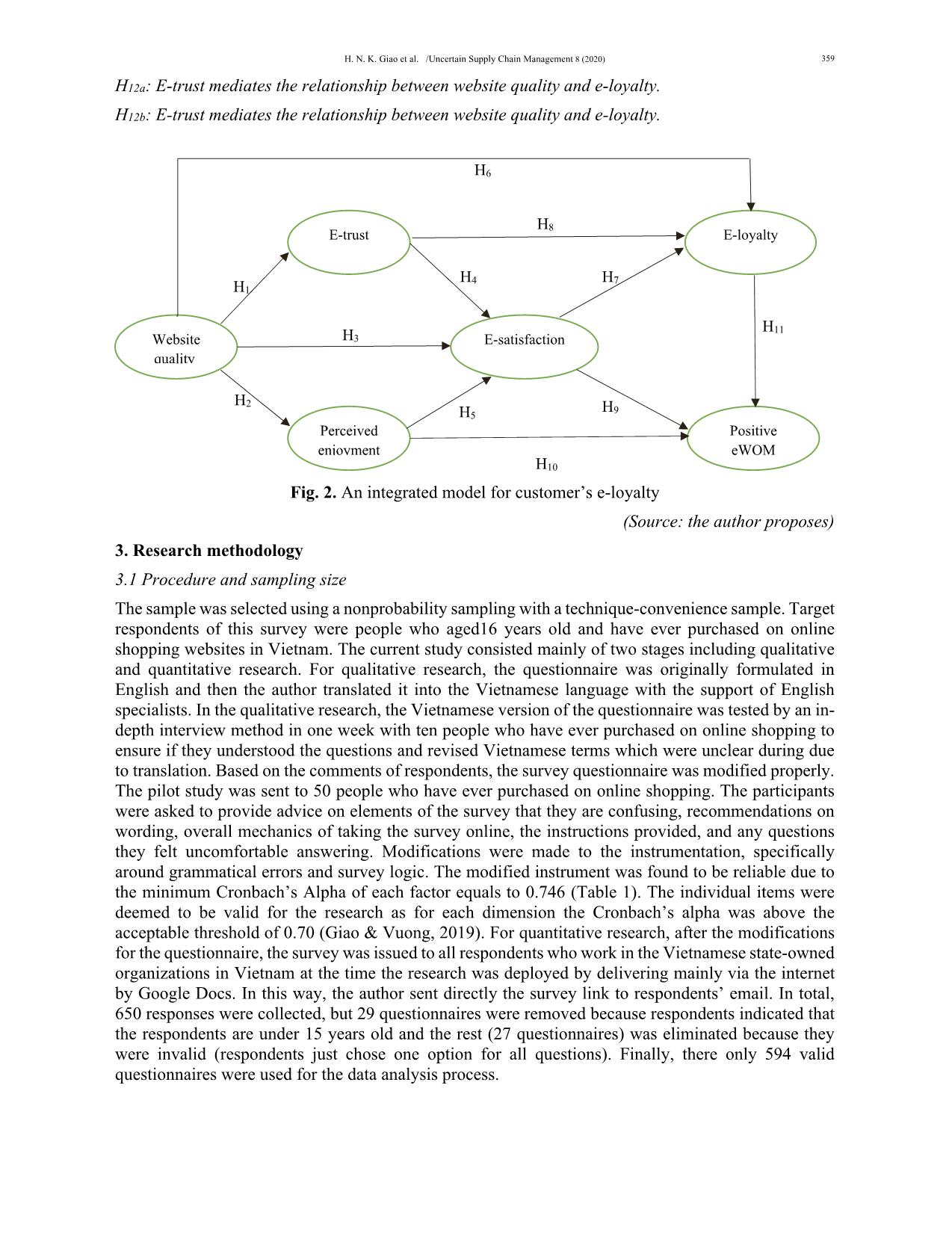
Trang 9
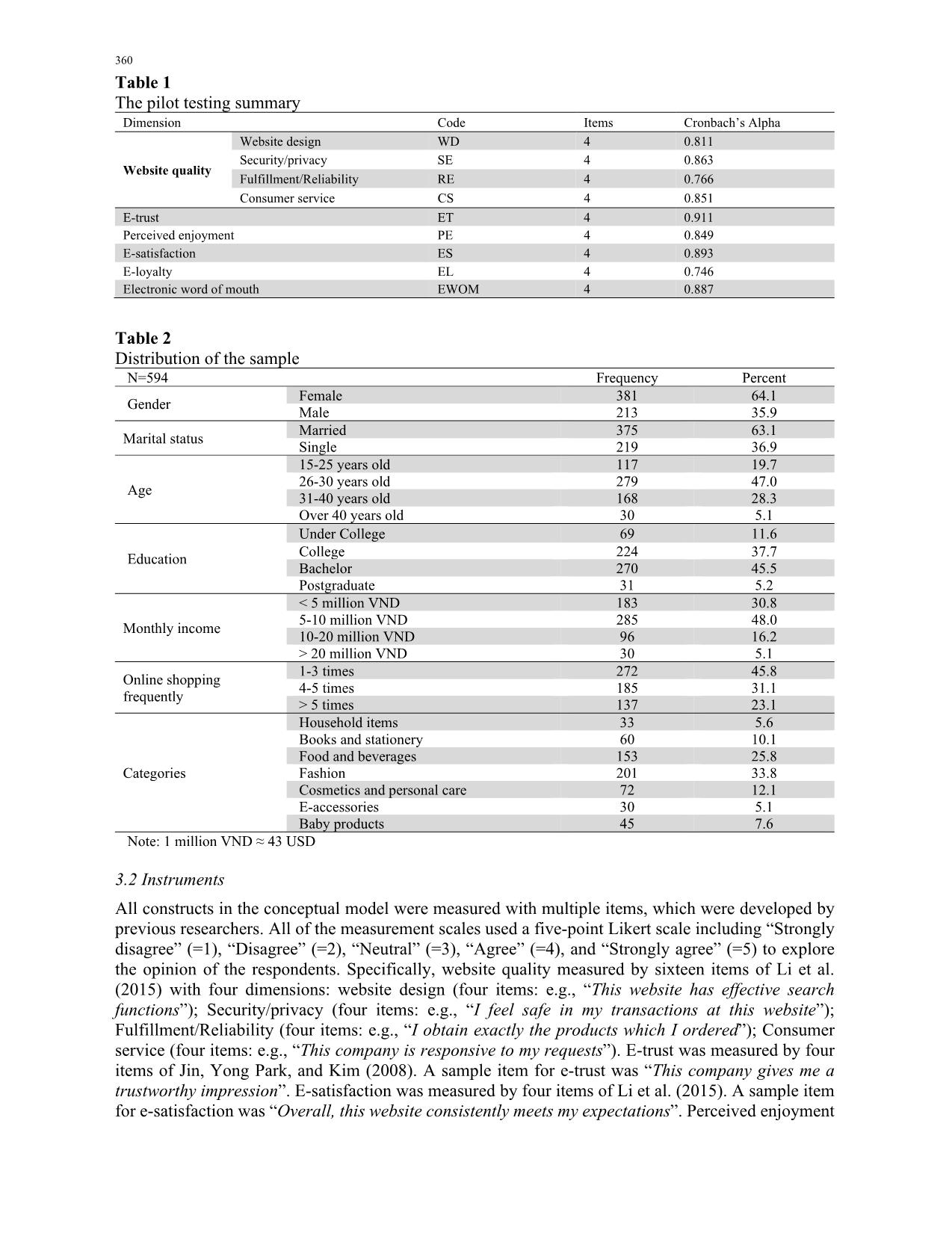
Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: The influence of website quality on consumer’s e-loyalty through the mediating role of e-trust and e-satisfaction: An evidence from online shopping in Viet Nam

* Corresponding author E-mail address: nhatvuonga1@gmail.com (B. N. Vuong) © 2020 by the authors; licensee Growing Science. doi: 10.5267/j.uscm.2019.11.004 Uncertain Supply Chain Management 8 (2020) 351–370 Contents lists available at GrowingScience Uncertain Supply Chain Management homepage: www.GrowingScience.com/uscm The influence of website quality on consumer’s e-loyalty through the mediating role of e-trust and e-satisfaction: An evidence from online shopping in Vietnam Ha Nam Khanh Giaoa, Bui Nhat Vuonga* and Tran Nhu Quana aFaculty of Air Transport, Vietnam Aviation Academy, Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam C H R O N I C L E A B S T R A C T Article history: Received October 20, 2019 Received in revised format November 10, 2019 Accepted November 20 2019 Available online November 20 2016 The aim of the present study is to examine the influence of website quality on consumer’s e- loyalty, noting the mediating role of e-trust, e-satisfaction, and perceived enjoyment. Besides, this study examines the consequence of consumer’s e-loyalty. Survey data collected from 594 respondents aged at least 16 years and performed some online shopping through websites in Vietnam. Based on the theoretical framework, PLS-SEM using SmartPLS 3.0 software was deployed to discover links between the constructs. The results showed a positive effect of website quality on e-loyalty, which was mediated partially through consumer e-trust and e- satisfaction. Moreover, e-loyalty had a positive association with electronic word of mouth (eWOM) as well. The main findings of this research provide some empirical implications for Internet marketers and online retailers in Vietnam. E-vendors should understand the customers’ expectations and e-loyalty regarding online shopping to attract new customers as well as to retain their existing customers. .license Growing Science, Canada2020 by the authors; © Keywords: Website quality E-trust E-satisfaction Perceived enjoyment E-loyalty Electronic word of mouth 1. Introduction Internet has been changing the traditional ways of purchasing goods and services. The users have no longer been restricted by time and geographical factors. They could actively purchase the products and goods regardless of any time and location factors. The Internet has brought about new methods of communication and new ways of exchanging everyday information among peoples. The ever- increasing number of Internet users would also coincide with the development of online purchasing (Joines et al., 2003). The fast development of the Internet would be explained by the combination of broadband technology and the change of customer behavior (Oppenheim, 2006). Online shopping, also known as internet shopping or e-shopping, can be explained as electronic commerce when buyers and sellers virtually meet others through a web browser (Kaur & Joshi, 2012). In other words, e-shopping is a process when users decide to buy products or services on the Internet economy (Puranik & Bansal, 2014). Unlike traditional shops that require physical locations, physical security services, and specific timeframes to operate, internet shops need none of those requirements. Customers can access to the shop from anywhere (e.g., without worrying about geographical boundaries) and anytime (e.g., 24-hour opening, 7 days a week, time zones) they like as long as they have internet connection and an appropriate device like a computer, a tablet or a smartphone (Bidgoli, 2010; Karthika & 352 Manojanaranjani, 2018). Since people are more and more busy with their jobs and internet has been widely and easily accessible, e-shopping has “redefined business and customer relationships, business processes, even sometimes restructuring the whole industry by providing new distribution channel, new delivery methods, new payment methods and new medium for communication” (Cosgun & Dogerlioglu, 2012). With the tremendous opportunity to grow and a very promising market to exploit, e-shopping has been attracting many scholars and experts to make researches in order to become successful in this new method of selling products. As a result of that, many factors have been explored to contribute to a successful online business. Chu and Zhang (2016) showed that one of the most significant factors that lead to the customers’ satisfaction is their attitude towards e-retailing. In that research, the authors also highlighted the easiness, usefulness and effortless when customers interact with the web pages can create favorable shopping intentions. Besides the attitude towards e-shopping, Chu and Zhang (2016) added that customers’ trust played an important role in increasing customers’ satisfaction to shop online. They also proved that trust in e-vendor can be gained when people know that shop owners earn nothing more by cheating, a shop is safe to make a trans ... s conducted only in Viet Nam. Thus, data results mainly reflected in customer behaviors in Vietnam. The author recommended replicating the study in different nations to get an international sample. Second, the different shoppers may have different online shopping intentions, but this research did not perform an analysis of variance on demographic variables of buyers. Future research should perform a comparison of demographic variables such as gender, income, age, education, marital status on behavioral intention. Finally, respondents answered the questionnaire based on various websites rather than responding to questions about a specific website. So, the type of distinctive websites may influence customers’ perceptions and experience of online shopping. References Abdullah, F., & Ward, R. (2016). Developing a general extended technology acceptance model for e-learning (GETAMEL) by analysing commonly used external factors. Computers in Human Behavior, 56, 238-256. Abubakar, A. M., Ilkan, M., & Sahin, P. (2016). eWOM, eReferral and gender in the virtual community. 368 Marketing Intelligence & Planning, 34(5), 692–710. Aladwani, A. M., & Palvia, P. C. (2002). Developing and validating an instrument for measuring user-perceived web quality. Inf. Manage., 39(6), 467-476. Alshibly, H., & Chiong, R. (2015). Customer empowerment: Does it influence electronic government success? A citizen-centric perspective. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 14(6), 393-404. Anderson, R. E., & Srinivasan, S. S. (2003). E-satisfaction and e-loyalty: A contingency framework. Psychology & Marketing, 20(2), 123-138. Arndt, J. (1967). Role of product-related conversationsin the diffusion of a newproduct. JournalofMarketingResearch, 4, 291-295. Bansal, H. S., McDougall, G. H. G., Dikolli, S. S., et al. (2004). Relating e‐satisfaction to behavioral outcomes: an empirical study. Journal of Services Marketing, 18(4), 290–302. Bidgoli, H. (2010). The Handbook of Technology Management, Supply Chain Management, Marketing and Advertising, and Global Management. Chichester, United Kingdom: John Wiley and Sons Ltd. Bone, P. F. (1992). Determinants of word-of-mouth communications during product consumption. Advances in Consumer Research, 19(1), 579-583. Bulut, Z. A., & Karabulut, A. N. (2018). Examining the role of two aspects of eWOM in online repurchase intention: An integrated trust–loyalty perspective. Journal of Consumer Behaviour, 17(4), 407-417. Chang, H. H., & Chen, S. W. (2008). The impact of customer interface quality, satisfaction and switching costs on e-loyalty: Internet experience as a moderator. Computers in Human Behavior, 24(6), 2927-2944. Cheung, C. M. K., & Thadani, D. R. (2012). The impact of electronic word-of-mouth communication: A literature analysis and integrative model. Decision Support Systems, 54, 461-470. Chu, F., & Zhang, X. (2016, 24-27 July). Satisfaction, trust and online purchase intention: A study of consumer perceptions. Paper presented at the 2016 International Conference on Logistics, Informatics and Service Sciences (LISS). Churchill, G. A., & Surprenant, C. (1982). An investigation into the determinants of customer satisfaction. Journal of Marketing Research, 19(4), 491-504. Cimigo. (2019). Vietnam online shopping hits 60% penetration. Retrieved from https://blog.cimigo.com/vietnam-online-shopping/ Corbitt, B. J., Thanasankit, T., & Yi, H. (2003). Trust and e-commerce: a study of consumer perceptions. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications, 2(3), 203-215. Cosgun, V., & Dogerlioglu, O. (2012). Critical success factors affecting e-commerce activities of small and medium enterprises. Information Technology Journal, 11, 1664-1676. Curran, J. M., & Lennon, R. (2011). Participating in the conversation: Exploring usage of social media networking sites. Academy of Marketing Studies Journal, 15(1), 21-38. Cyr, D., Kindra, G. S., & Dash, S. (2008). Web site design, trust, satisfaction and e-loyalty: The Indian experience. Online Information Review, 32(6), 773–790. Davis, F. D., Bagozzi, R. P., & Warshaw, P. R. (1992). Extrinsic and intrinsic motivation to use computers in the workplace. Journal of Applied Social Psychology, 22(14), 1111-1132. Dolnicar, S., Coltman, T., & Sharma, R. (2015). Do satisfied tourists really intend to come back? Threeconcerns with empirical studies linking satisfaction to behavioural intentions. Journal of Travel Research, 54(2), 152- 178. Featherman, M. S., & Pavlou, P. A. (2003). Predicting e-services adoption: A perceived risk facets perspective. International Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 59(4), 451-474. Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39-50. Gefen, D., Karahanna, E., & Straub, D. W. (2003). Trust and TAM in online shopping: An integrated model. MIS Quarterly, 27(1), 51-90. Ghalandari, K. (2012). The effect of e-service quality on e-trust and e-satisfaction as key factors influencing creation of e-loyalty in e-business context: The moderating role of situational factors. Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research, 2(12), 12847-12855. Giao, H. N. K., & Vuong, B. N. (2019). Giáo Trình Cao Học Phương Pháp Nghiên Cứu Trong Kinh Doanh Cập Nhật SmartPLS. TP. Hồ Chí Minh, Việt Nam: Nhà Xuất Bản Tài Chính. Goles, T., Rao, S. V., Lee, S., et al. (2009). Trust violation in electronic commerce: Customer concerns and reactions. Journal Of Computer Information Systems, 49(4), 1-9. Gommans, M., Krishman, K. S., & Scheffold, K. B. (2001). From brand loyalty to e-loyalty: A conceptual framework. Journal of Economic & Social Research, 3(1), 43. Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., et al. (2014). A primer on partial least squares structural equation H. N. K. Giao et al. /Uncertain Supply Chain Management 8 (2020) 369 modeling (PLS-SEM). Thousand Oaks: Sage Publication, Inc. Hernandez, B., Jimenez, J., & Jose Martin, M. (2009). The impact of self-efficacy, ease of use and usefulness on e-purchasing: An analysis of experienced e-shoppers. Interacting with Computers, 21(1), 146-156. Iprice. (2019). The map of e-commerce in Vietnam. Retrieved from https://iprice.vn/insights/mapofecommerce/en/ Ittner, C. D., & Larcker, D. F. (1998). Are nonfinancial measures leading indicators of financial performance? An analysis of customer satisfaction. Journal of Accounting Research, 36, 1-35. Jin, B., Yong Park, J., & Kim, J. (2008). Cross‐cultural examination of the relationships among firm reputation, e‐satisfaction, e‐trust, and e‐loyalty. International Marketing Review, 25(3), 324–337. Joines, J., Scherer, C., & Scheufele, D. (2003). Exploring motivations for consumer Web use and their implications for e‐commerce. Journal of Consumer Marketing, 20(2), 90-108. Karthika, I., & Manojanaranjani, A. (2018). A Study on the various food ordering apps based on consumer preference. World Wide Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Development, 4(11), 88-89. Kaur, P., & Joshi, M. M. (2012). E-commerce in india: A review. InternatIonal Journal of Computer SCIenCe and teChnology, 3(1), 802-804. Kim, D., & Benbasat, I. (2003). Trust-related arguments in internet stores: A framework for evaluation. Journal of Electronic Commerce Research, 4(2), 49-64. Kim, J., Ahn, K., & Chung, N. (2013). Examining the factors affecting perceived enjoyment and usage intention of ubiquitous tour information services: A service quality perspective. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 18(6), 598-617. Kim, J., & Lennon, S. J. (2013). Effects of reputation and website quality on online consumers'emotion, perceived risk and purchase intention. Journal of Research in Interactive Marketing, 7(1), 33 - 56. Li, H., Aham-Anyanwu, N., Tevrizci, C., et al. (2015). The interplay between value and service quality experience: e-loyalty development process through the eTailQ scale and value perception. Electronic Commerce Research, 15(4), 585-615. Liao, C., Palvia, P., & Lin, H.-N. (2006). The roles of habit and web site quality in e-commerce. International Journal of Information Management, 26(6), 469-483. Lii, Y., & Lee, M. (2012). The joint effects of compensation frames and price levels on service recovery of online pricing error. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal, 22(1), 4-20. Lim, W., & Ting, D. H. (2012). E-shopping: An analysis of the uses and gratifications theory. Modern Applied Science, 6, 48-63. Litvin, S. W., Goldsmith, R. E., & Pan, B. (2018). A retrospective view of electronic word-of-mouth in hospitality and tourism management. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 30(1), 313-325. Mayer, R. C., Davis, J. H., & Schoorman, F. D. (1995). An integrative model of organizational trust. The Academy of Management Review, 20(3), 709-734. Mihić, M., & Kursan Milaković, I. (2017). Examining shopping enjoyment: personal factors, word of mouth and moderating effects of demographics. Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, 30(1), 1300-1317. Mohan, G., Sivakumaran, B., & Sharma, P. (2013). Impact of store environment on impulse buying behavior. European Journal of Marketing, 47(10), 1711–1732. Nusair, K. K., & Kandampully, J. (2008). The antecedents of customer satisfaction with online travel services: A conceptual model. European Business Review, 20(1), 4-19. Oliver, R. L. (2010). Satisfaction: A Behavioral Perspective on the Consumer (2nd Ed.). New York: Routledge. Oliver, R. L., & DeSarbo, W. S. (1988). Response determinants in satisfaction judgments. Journal of Consumer Research, 14(4), 495-507. Oppenheim, C. (2006). Evaluation of web sites for B2C e‐commerce. Aslib Proceedings, 58(3), 237-260. Pavlou, P. A. (2003). Consumer acceptance of electronic commerce: Integrating trust and risk with the technology acceptance model. International Journal of Electronic Commerce, 7, 101-134. Polites, G. L., Williams, C. K., Karahanna, E., et al. (2012). A theoretical framework for consumer e-satisfaction and site stickiness: An evaluation in the context of online hotel reservations. Journal of Organizational Computing and Electronic Commerce, 22(1), 1-37. Prayag, G., Hosany, S., Muskat, B., et al. (2017). Understanding the relationships between tourists’ emotional experiences, perceived overall image, satisfaction, and intention to recommend. Journal of Travel Research, 56(1), 41-54. Puranik, R., & Bansal, A. (2014). A study of internet users' perception towards e-shopping. Pacific Business Review International, 6(9), 37-44. 370 Ribbink, D., Van Riel, A. C., Liljander, V., et al. (2004). Comfort your online customer: Quality, trust and loyalty on the internet. Managing Service Quality: An International Journal, 14, 446-456. Richins, M. L. (1983). Negative word-of-mouth by dissatisfied consumers: A pilot study. Journal of Marketing, 47(1), 68-78. Rodgers, W., Negash, S., & Suk, K. (2005). The moderating effect of on-line experience on the antecedents and consequences of on-line satisfaction. Psychology & Marketing, 22(4), 313-331. Safa, N. S., & Solms, R. V. (2016). Customers repurchase intenton formaton in e-commerce. South African Journal of Informaton Management, 18(1), 1-9. Salehnia, N., Saki, M., Eshaghi, A., et al. (2014). A model of e-loyalty and word-of-mouth based on e-trust in e- banking services (case study: Mellat bank). New Marketing Research Journal(Special Issue), 101-114. Serra-Cantallops, A., Ramon-Cardona, J., & Salvi, F. (2018). The impact of positive emotional experiences on eWOM generation and loyalty. Spanish Journal of Marketing. Shin, J. I., Chung, K. H., Oh, J. S., et al. (2013). The effect of site quality on repurchase intention in Internet shopping through mediating variables: The case of university students in South Korea. International Journal of Information Management, 33(3), 453-463. Silverman, G. (2011). The secrets of word-of-mouth marketing: How to trigger exponential sales through runaway word of mouth. New York AMACOM. Taheri, F., & Akbari, N. (2016). Moderating effects of online shopping experience on customer satisfaction and repurchase intentions. International Academic Institute for Science and Technology, 3(4), 21-27. Tandon, U., Kiran, R., & Sah, A. N. (2017). Customer satisfaction as mediator between website service quality and repurchase intention: An emerging economy case. Service Science, 9(2), 106-120. Tirtayani, I. G. A., & Sukaatmadja, I. P. G. (2018). The effect of perceived website quality, e-satisfaction, and e -trust towards online repurchase intention. International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management, 6(10), 262-287. Tsao, W.-C., & Hsieh, M.-T. (2012). Exploring how relationship quality influences positive eWOM: the importance of customer commitment. Total Quality Management & Business Excellence, 23(7-8), 821-835. VECITA. (2018). E-commerce industry in Vietnam. Retrieved from www.ukabc.org.uk/wp- content/uploads/2018/09/EVBN-Report-E-commerce-Final-Update-180622.pdf Vuong, B. N., & Giao, H. N. K. (2019). The impact of perceived brand globalness on consumers’ purchase intention and the moderating role of consumer ethnocentrism: An evidence from vietnam. Journal of International Consumer Marketing, 1-22. doi:10.1080/08961530.2019.1619115 Wangenheim, F. V. (2005). Postswitching negative word of mouth. Journal of Service Research, 8(1), 67-78. Warrington, T. B., Abgrab, N. j., & Caldwell, H. M. (2000). Building trust to develop competitive advantage in e‐business relationships. Competitiveness Review, 10(2), 160–168. Wen, C. (2012). The impact of quality on customer behavioral intentions based on the consumer decision making process as applied in e-commerce. (Doctor of Philosophy), University of North Texas, Texas. Wen, C., Prybutok, V. R., & Xu, C. (2011). An integrated model for customer online repurchase intention. Journal Of Computer Information Systems, 52(1), 14-23. Westbrook, R. A. (1987). Product/consumption-based affective responses and postpurchase processes. Journal of Marketing Research, 24(3), 258-270. Wolfinbarger, M., & Gilly, M. C. (2003). eTailQ: Dimensionalizing, measuring and predicting etail quality. Journal of Retailing, 79(3), 183-198. Yang, F. X. (2017). Effects of restaurant satisfaction and knowledge sharing motivation on eWOM intentions: The moderating role of technology acceptance factors. Journal of Hospitality & Tourism Research, 41(1), 93-127. © 2020 by the authors; licensee Growing Science, Canada. This is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (
File đính kèm:
 the_influence_of_website_quality_on_consumers_e_loyalty_thro.pdf
the_influence_of_website_quality_on_consumers_e_loyalty_thro.pdf

