Chiến thuật làm bài đọc Ielts được sử dụng bởi những thí sinh đạt điểm cao trong kỳ thi học thuật Ielts
Nghiên cứu này nhằm mục đích làm sáng tỏ những chiến thuật đọc
thường được áp dụng bởi những thí sinh đạt điểm cao kỹ năng đọc
trong bài thi IELTS học thuật. Hai câu hỏi nghiên cứu gồm: (1) Các thí
sinh Việt Nam thường sử dụng chiến lược làm bài nào trong các bài thi
đọc IELTS? (2) Các chiến lược làm bài thi đó có liên quan như thế nào
đến thành tích của thí sinh? Nghiên cứu sử dụng phương pháp khảo sát
đối với 100 người tham gia và phỏng vấn 06 người học tiếng Anh đã
tham gia kỳ thi IELTS và đạt ít nhất 7.0 cho kỹ năng đọc; từ đó, chỉ ra
các chiến lược đọc phổ biến được sử dụng bởi những thí sinh đạt điểm
cao và ảnh hưởng của những chiến lược này tới kết quả của thí sinh.
Các phát hiện từ nghiên cứu minh họa sự đa dạng trong việc áp dụng
các chiến lược làm bài thi đọc IELTS và tác động của các chiến lược
đến kết quả bài thi. Các phát hiện cũng khuyến khích người học tìm
hiểu và trau dồi phương pháp tiếp cận cơ bản khi làm bài thi đọc, đặc
biệt là trong bài thi đọc IELTS, nhằm nâng cao mức độ thành thạo đối
với kỹ năng đọc hiểu của bản thân.
Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3
Trang 4

Trang 5
Trang 6

Trang 7

Trang 8
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: Chiến thuật làm bài đọc Ielts được sử dụng bởi những thí sinh đạt điểm cao trong kỳ thi học thuật Ielts

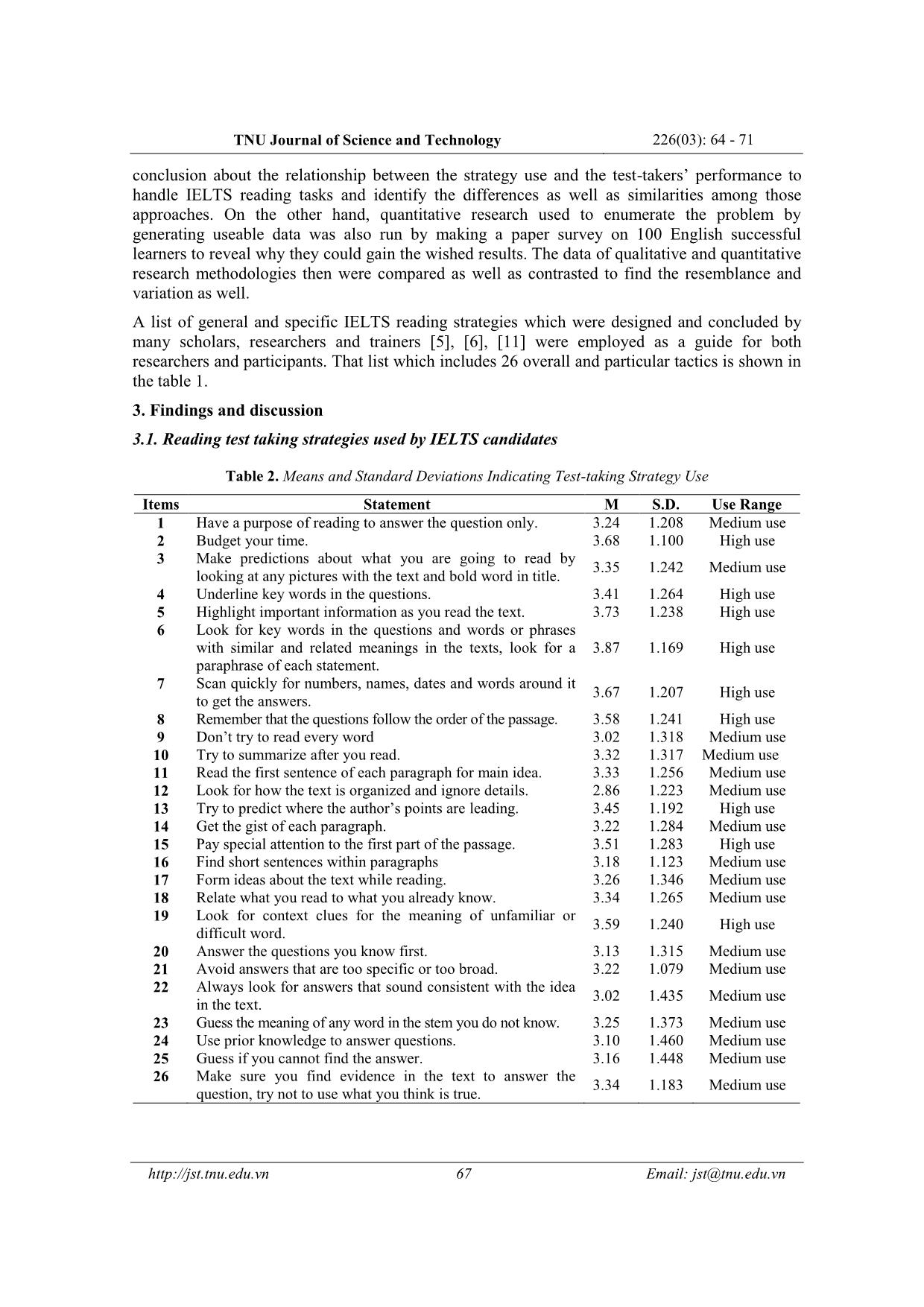
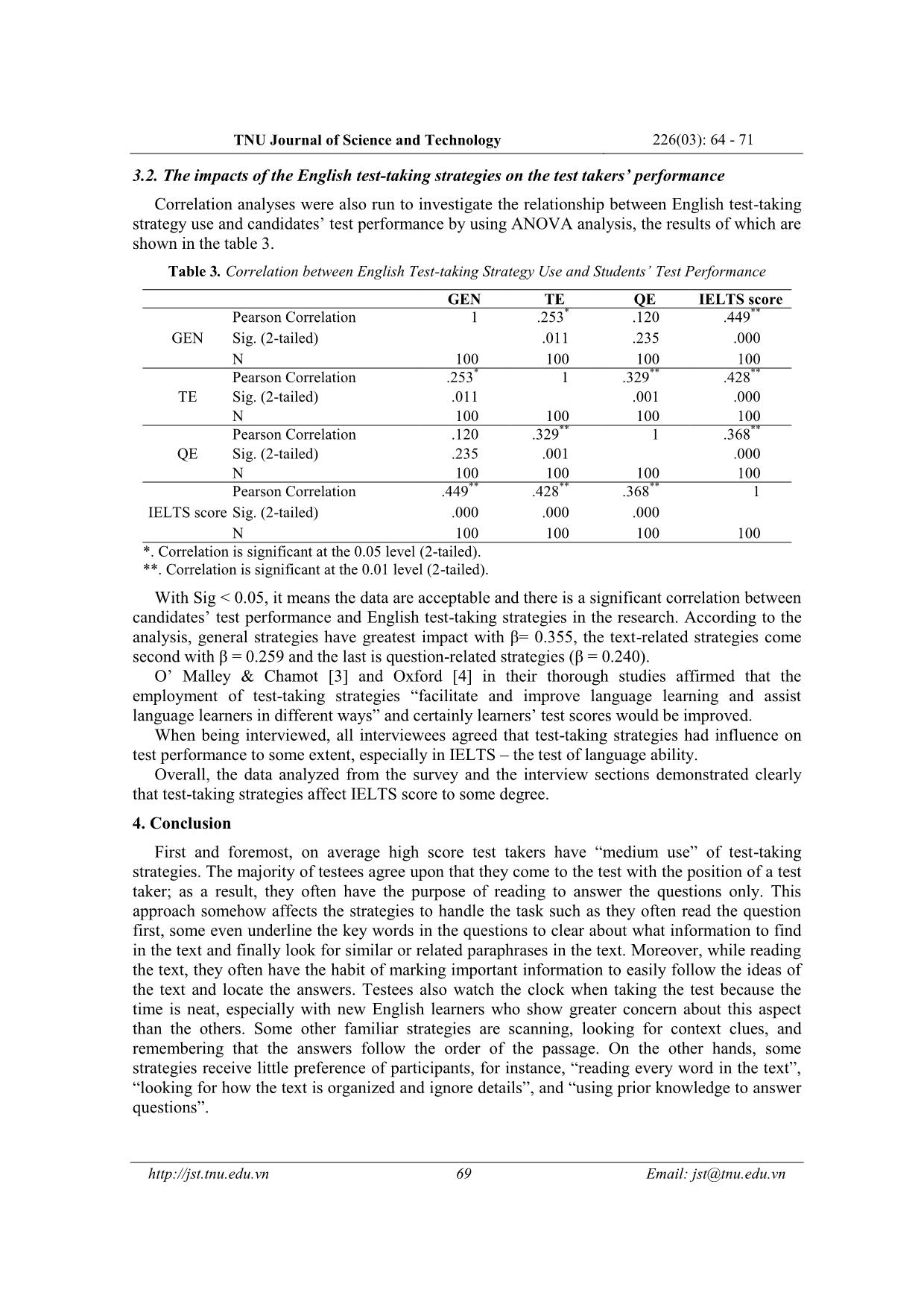
TNU Journal of Science and Technology 226(03): 64 - 71 64 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn IELTS READING TEST-TAKING STRATEGIES EMPLOYED BY HIGH SCORE CANDIDATES IN ACADEMIC TRAINING MODULE Phi Thi Mui, Vu Thi Quyen * TNU - School of Foreign Languages ARTICLE INFO ABSTRACT Received: 08/3/2021 This research aims to illuminate how the successful IELTS takers perform their IELTS reading test and provide a useful guidance for anyone concerning about IELTS reading test. This study is motivated by two research questions: (1) What test-taking strategies frequently used by Vietnam test takers in performing IELTS reading tasks? (2) How are those English test-taking strategies related to test takers’ performance? The research employed multiple methods including a broad survey questionnaire of 100 participants and a thorough interview of 06 English language learners who had taken the IELTS test and gained at least 7.0 for reading skill to point out the common reading strategies used by high score test takers and indicate the influence of them on the test takers’ performance. The findings from the research illustrate the variety in application of test-taking strategies and the impact of strategies on the results when taking the test. The findings also prompt an encouragement to learn and sharpen basic approach when learners take reading tests, especially in IELTS reading, so that they can improve their reading skill. Revised: 30/3/2021 Published: 31/3/2021 KEYWORDS IELTS reading test Strategy Test takers Performance Skill CHIẾN THUẬT LÀM BÀI ĐỌC IELTS ĐƯỢC SỬ DỤNG BỞI NHỮNG THÍ SINH ĐẠT ĐIỂM CAO TRONG KỲ THI HỌC THUẬT IELTS Phí Thị Mùi, Vũ Thị Quyên* Trường Ngoại ngữ - ĐH Thái Nguyên THÔNG TIN BÀI BÁO TÓM TẮT Ngày nhận bài: 08/3/2021 Nghiên cứu này nhằm mục đích làm sáng tỏ những chiến thuật đọc thường được áp dụng bởi những thí sinh đạt điểm cao kỹ năng đọc trong bài thi IELTS học thuật. Hai câu hỏi nghiên cứu gồm: (1) Các thí sinh Việt Nam thường sử dụng chiến lược làm bài nào trong các bài thi đọc IELTS? (2) Các chiến lược làm bài thi đó có liên quan như thế nào đến thành tích của thí sinh? Nghiên cứu sử dụng phương pháp khảo sát đối với 100 người tham gia và phỏng vấn 06 người học tiếng Anh đã tham gia kỳ thi IELTS và đạt ít nhất 7.0 cho kỹ năng đọc; từ đó, chỉ ra các chiến lược đọc phổ biến được sử dụng bởi những thí sinh đạt điểm cao và ảnh hưởng của những chiến lược này tới kết quả của thí sinh. Các phát hiện từ nghiên cứu minh họa sự đa dạng trong việc áp dụng các chiến lược làm bài thi đọc IELTS và tác động của các chiến lược đến kết quả bài thi. Các phát hiện cũng khuyến khích người học tìm hiểu và trau dồi phương pháp tiếp cận cơ bản khi làm bài thi đọc, đặc biệt là trong bài thi đọc IELTS, nhằm nâng cao mức độ thành thạo đối với kỹ năng đọc hiểu của bản thân. Ngày hoàn thiện: 30/3/2021 Ngày đăng: 31/3/2021 TỪ KHÓA Bài đọc IELTS Chiến thuật Thí sinh Thành tích Kỹ năng DOI: https://doi.org/10.34238/tnu-jst.4107 * Corresponding author. Email: vuquyen.sfl@tnu.edu.vn TNU Journal of Science and Technology 226(03): 64 - 71 65 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn 1. Introduction Test-taking strategies have been playing a crucial role for language learners as nowadays test is used as a reliable way of checking and evaluating learners’ knowledge. The International English Language Testing System (IELTS), which is the world’s leading English language proficiency test, has been recognized as one of the most secure, valid and reliable means in assessing English language proficiency for education, immigration and professional accreditation. IELTS test, which is a high stake test, success or failure, can have a life changing impact on candidates. As a result, smart and critical reading and thinking strategies need to be used sufficiently in order to be successful or to achieve the best possible score in the test [1], [2]. There are numerous factors affecting the candidates’ results except for knowledge and ability. One of the most important factors is learning and test-taking strategies [1], [3]. Test- taking strategies are simply defined as specific actions or techniques taken by users to aid them overcome the test easier, faster and more accurate. As Oxford [4] defines, learning strategies are “specific actions taken by the learner to make learning easier, faster, more enjoyable, more self- directed and more transferrable to new situations”. Test-taking strategies have been the focus of many studies [1], [5] – [7], [8] – [10]. In spite of many attempts made towards learning and test-taking strategies, few were devoted to test-taking strategies used in reading modules of IELTS while for many Vietnamese candidates, reading is regarded as the most challenging one. All of these reasons stated have become the motivations that stimulate the researchers to carry out the study named “ ... h use 6 Look for key words in the questions and words or phrases with similar and related meanings in the texts, look for a paraphrase of each statement. 3.87 1.169 High use 7 Scan quickly for numbers, names, dates and words around it to get the answers. 3.67 1.207 High use 8 Remember that the questions follow the order of the passage. 3.58 1.241 High use 9 Don’t try to read every word 3.02 1.318 Medium use 10 Try to summarize after you read. 3.32 1.317 Medium use 11 Read the first sentence of each paragraph for main idea. 3.33 1.256 Medium use 12 Look for how the text is organized and ignore details. 2.86 1.223 Medium use 13 Try to predict where the author’s points are leading. 3.45 1.192 High use 14 Get the gist of each paragraph. 3.22 1.284 Medium use 15 Pay special attention to the first part of the passage. 3.51 1.283 High use 16 Find short sentences within paragraphs 3.18 1.123 Medium use 17 Form ideas about the text while reading. 3.26 1.346 Medium use 18 Relate what you read to what you already know. 3.34 1.265 Medium use 19 Look for context clues for the meaning of unfamiliar or difficult word. 3.59 1.240 High use 20 Answer the questions you know first. 3.13 1.315 Medium use 21 Avoid answers that are too specific or too broad. 3.22 1.079 Medium use 22 Always look for answers that sound consistent with the idea in the text. 3.02 1.435 Medium use 23 Guess the meaning of any word in the stem you do not know. 3.25 1.373 Medium use 24 Use prior knowledge to answer questions. 3.10 1.460 Medium use 25 Guess if you cannot find the answer. 3.16 1.448 Medium use 26 Make sure you find evidence in the text to answer the question, try not to use what you think is true. 3.34 1.183 Medium use TNU Journal of Science and Technology 226(03): 64 - 71 68 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn Oxford’s key to understanding mean scores on SILL-based instruments [12] was employed to report the frequency of English test-taking strategy use: High use = 4.5 to 5.0 (always or almost always used and 3.5 to 4.4 (usually used) Medium use = 2.5 to 3.4 (sometimes used) Low use = 1.5 to 2.4 (usually not used) or 1.0-1.4 (never or almost never used) As shown in table 2, in general, the mean overall strategy use was 3.00 on the 5-point Likert scale, which suggested “medium” use of strategy. There were 09 “high” use strategies, in which strategy 06 (Look for key words in the questions and words or phrases with similar and related meanings in the texts, look for a paraphrase of each statement) stood at the highest position with 3.87 mean and strategy 05 (Highlight important information as you read the text ) ranked second with 3.73 mean, the third was strategy 02 (Budget your time.). Strategies 07, 08, and 19 (Scan quickly for numbers, names, dates and words around it to get the answers; Remember that the questions follow the order of the passage and Look for context clues for the meaning of unfamiliar or difficult word) also received lots of preference of IELTS test-takers. 17 strategies were categorized into “medium” use; however, strategies 12 (Look for how the text is organized and ignore details) stood at the bottom of the overall mean. Almost all the readers advise IELTS test-takers to take a look at the questions first instead of reading the text immediately in order to know what they are being asked about, and then direct their attention to the piece of information containing the answers. Sometimes they can paraphrase the questions and then find the similar information in the text. All of interviewees when being asked to describe the step to do the tasks, reported they often looked at the questions first, then paraphrase it to know what they were being asked about, finally found the similar information in the text. Pour Mohammadi & Abidin [7] demonstrated that questions previewing supported examinees know where to look for needed information. However, some participants when being asked why they did not preview questions first expressed that if they looked at the questions without skimming the whole text, it was very difficult to answer the questions without knowing the main ideas of the text and sometimes they would miss some key information that might help figure out something. Some interviewees also agreed that it was essential to highlight important information in the text because this step would help them find the key easier and formalize the main ideas about the text while reading. That is the reason why “highlight important information as you read the text” ranks second in terms of frequency. “Scanning”; “Remembering the answers follow the order of the text” and “Looking for context clues for the meaning of unfamiliar or difficult word” are familiar tips with high score IELTS test takers. Most of the previous studies on reading strategies also revealed the significance of scanning strategies [1], [8], [9], [13]. On the contrary, some strategies prove not to be efficient with the majority of participants. One of the typical tactics is “Look for how the text is organized and ignore details”. It is quite comprehensible when it is the test, the more answer test takers get, the higher score they have. As a result, they do not need to read everything in the passage or pay attention to the text’s organization. This is in agreement with Phatiki’s and Cohen’s findings [8], [9] which revealed that scanning technique enabled the readers to “cover a vast amount of material very rapidly” without reading and understanding every word of a text. The analysis of the data collected from the survey also point out that IELTS takers employed varieties of strategies when reading including general strategies, text-related strategies and question-related strategies. By utilizing a wide range of strategies, the participants are able to comprehend the passages better. In other words, they may get more success in the IELTS reading module. TNU Journal of Science and Technology 226(03): 64 - 71 69 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn 3.2. The impacts of the English test-taking strategies on the test takers’ performance Correlation analyses were also run to investigate the relationship between English test-taking strategy use and candidates’ test performance by using ANOVA analysis, the results of which are shown in the table 3. Table 3. Correlation between English Test-taking Strategy Use and Students’ Test Performance GEN TE QE IELTS score GEN Pearson Correlation 1 .253 * .120 .449 ** Sig. (2-tailed) .011 .235 .000 N 100 100 100 100 TE Pearson Correlation .253 * 1 .329 ** .428 ** Sig. (2-tailed) .011 .001 .000 N 100 100 100 100 QE Pearson Correlation .120 .329 ** 1 .368 ** Sig. (2-tailed) .235 .001 .000 N 100 100 100 100 IELTS score Pearson Correlation .449 ** .428 ** .368 ** 1 Sig. (2-tailed) .000 .000 .000 N 100 100 100 100 *. Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed). **. Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed). With Sig < 0.05, it means the data are acceptable and there is a significant correlation between candidates’ test performance and English test-taking strategies in the research. According to the analysis, general strategies have greatest impact with β= 0.355, the text-related strategies come second with β = 0.259 and the last is question-related strategies (β = 0.240). O’ Malley & Chamot [3] and Oxford [4] in their thorough studies affirmed that the employment of test-taking strategies “facilitate and improve language learning and assist language learners in different ways” and certainly learners’ test scores would be improved. When being interviewed, all interviewees agreed that test-taking strategies had influence on test performance to some extent, especially in IELTS – the test of language ability. Overall, the data analyzed from the survey and the interview sections demonstrated clearly that test-taking strategies affect IELTS score to some degree. 4. Conclusion First and foremost, on average high score test takers have “medium use” of test-taking strategies. The majority of testees agree upon that they come to the test with the position of a test taker; as a result, they often have the purpose of reading to answer the questions only. This approach somehow affects the strategies to handle the task such as they often read the question first, some even underline the key words in the questions to clear about what information to find in the text and finally look for similar or related paraphrases in the text. Moreover, while reading the text, they often have the habit of marking important information to easily follow the ideas of the text and locate the answers. Testees also watch the clock when taking the test because the time is neat, especially with new English learners who show greater concern about this aspect than the others. Some other familiar strategies are scanning, looking for context clues, and remembering that the answers follow the order of the passage. On the other hands, some strategies receive little preference of participants, for instance, “reading every word in the text”, “looking for how the text is organized and ignore details”, and “using prior knowledge to answer questions”. TNU Journal of Science and Technology 226(03): 64 - 71 70 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn In terms of how reading strategies affect the test takers’ performance, the findings demonstrate a close correlation between those variables. Of three examined strategies, general tactics have greatest influence, the second is text-related strategies and the third is question- related ones. The findings of the study have lots of common with previous famous research [3], [4], [14]. Moreover, the collected data from the interview section also strongly support this conclusion, 100% of interviewees agreed that test-taking strategies played a crucial role in helping test takers improve their IELTS scores. It can be concluded that test-taking strategies improve test performance in one or another way. Accordingly, being familiar even having clear steps to deal with different task types needs to be prepared in advance, especially IELTS takers. IELTS trainers and English teachers should integrate test-taking strategies into teaching curriculum. An awareness of strategy instruction, even being presented or modeled will certainly help learners to benefit from test taking strategies and employ them effectively [14]. Anyone having tension to take the IELTS test can consult the findings of the study to apply into practice. One of the obvious drawbacks of the study is the number of participants. The study’s results would be more reliable if the number of the participants was increased. Therefore, the standard deviation in the data analysis process is somehow higher than expected. Moreover, the number of male and female participants in the study are not equal so it is hard to generalize the results representing for the whole group of people. The study only focuses on IELTS high scorers so the results are not diverse. Any researchers’ attempts to investigate in this field can conduct a study about the strategies employed by low scorers and high scorers to compare the similarities and the differences in test-taking employment of these two groups. Besides, an approach to examine the test taking strategies of singular task type such as Multiple Choice, Yes/ No/ Not Given or True/ False/ Not Given, Matching Headings or Cloze Test, Chart or Graph Filling can be considered as a new necessary topic for further study. REFERENCES [1] L. F. Bachman and A. Palmer, Language Testing in Practice. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1996. [2] W. Rogers and D. Harley, “An empirical comparison of three-and four-choice items and tests: Susceptibility to testwiseness and internal consistency reliability,” Educational and Psychological Measurement, vol. 50, no. 2, pp. 234-247, April 1999. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1177/00131649921969820. [Accessed January 02, 2021]. [3] J. M. O’ Malley and A.U. Chamot, Learning strategies in second language acquisition. Cambridge, England: Cambridge University Press, 1990. [4] R. L. Oxford, Language Learning Strategies: What every teacher should know. New York: Newbury House, 1990. [5] A. A. Rupp, T. Ferne, and H. Choi, “How assessing reading comprehension with multiple-choice questions shapes the construct: a cognitive processing perspective,” Language Testing, vol. 23, pp. 441-474, October 2006. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1191/0265532206lt337oa. [Accessed December 10, 2020]. [6] A. D. Cohen and T. A. Upton, “I want to go back to the text: Response strategies on the reading subtest of the new TOEFL,” Language Testing, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 209-250, April 2007. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1177/0265532207076364. [Accessed December 10, 2020]. [7] M. Pour-Mohammadi and M. J. Z. Abidin, “Does instructing test-taking strategies significantly enhance reading comprehension test performance? The case of Iranian EFL learners,” International Journal of Linguistics, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 293–297, August 2012. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.5296/ijl.v4i3.1964. [Accessed December 12, 2020]. [8] A. D. Cohen. Strategies in learning and using a second language. London: Longman, 1998. [9] A. Phakiti, “A closer look at the relationship of cognitive and metacognitive strategy use to EFL reading achievement test performance,” Language Testing, vol. 20, no.1, pp. 26-56, January 2003. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1191/0265532203lt243oa. [Accessed December 14, 2020]. TNU Journal of Science and Technology 226(03): 64 - 71 71 Email: jst@tnu.edu.vn [10] N. Nevo, “Test-taking strategies on a multiple-choice test of reading comprehension,” Language Testing, vol. 6, no. 2, pp. 199-215, December 1989. [Online]. Available: https://doi.org/10.1177/026553228900600206. [Accessed December 17, 2020]. [11] R. Farr, R. Pritchard, and B. Smitten, “A Description of What Happens When an Examinee Takes a Multiple-Choice Reading Comprehension Test,” Journal of Educational Measurement, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 209-226, National Council on Measurement in Education, 1990. [12] R. L. Oxford, Language Learning Strategies: What every teacher should know. New York: Newbury House, 1990. [13] D.H. Brown, First Language Acquisition. Principles of Languages Learning and Teaching, 5 th Ed. Pearson ESL, 2007. [14] R. C. Anderson, “Role of the reader’s schema in comprehension, learning, and memory” in Theoretical models and processes of reading, H. Singer and R. B. Ruddell, 3 rd ed. Newark, DE: International Reading Association, 1985, pp. 372–384.
File đính kèm:
 chien_thuat_lam_bai_doc_ielts_duoc_su_dung_boi_nhung_thi_sin.pdf
chien_thuat_lam_bai_doc_ielts_duoc_su_dung_boi_nhung_thi_sin.pdf

