An investigation into efl students’ perception of blended learning at university of foreign languages, Hue university
Abstract: A survey was conducted with 102 students from Hue University of Foreign Languages
(HUFL) English Department who had opportunity to take part in blended courses. In addition, a focus
group discussion was also administered with 10 voluntary students. The findings from this study
revealed the general perception of blended learning of EFL students and expressed their positive
attitudes towards blended learning. The study also indicated that the strengths of blended learning
outweighed its weaknesses. Some advantages can be listed as flexibility, usefulness, and increased
interaction. In addition, the limitations and problems of blended learning cannot be ignored, inluding
technical and Internet problems, time-consuming procedure, heavy workload and plagiarism. Those
challenges are followed by a number of practical suggestions for addressing the drawbacks, including
solving technical and Internet problems, providing proper training to students, increasing the number of
labs blended courses. Students’ acceptance of blended learning was also shown from their preference
to take another blended course in the future and their liking to recommend for their friends.
Keywords: Blended learning, EFL learners, benefits, challeng

Trang 1

Trang 2

Trang 3

Trang 4
Trang 5
Trang 6
Trang 7

Trang 8

Trang 9

Trang 10
Tải về để xem bản đầy đủ
Tóm tắt nội dung tài liệu: An investigation into efl students’ perception of blended learning at university of foreign languages, Hue university

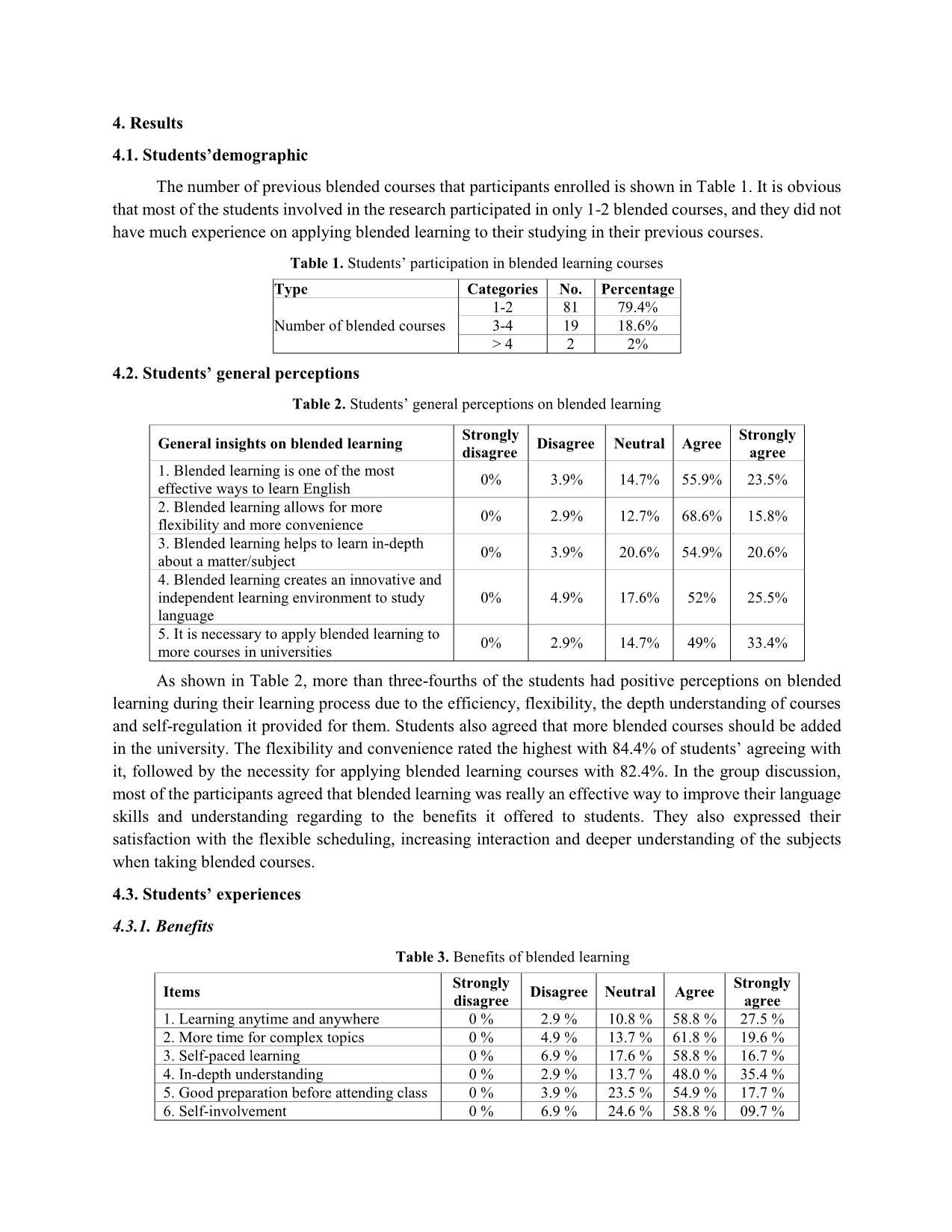
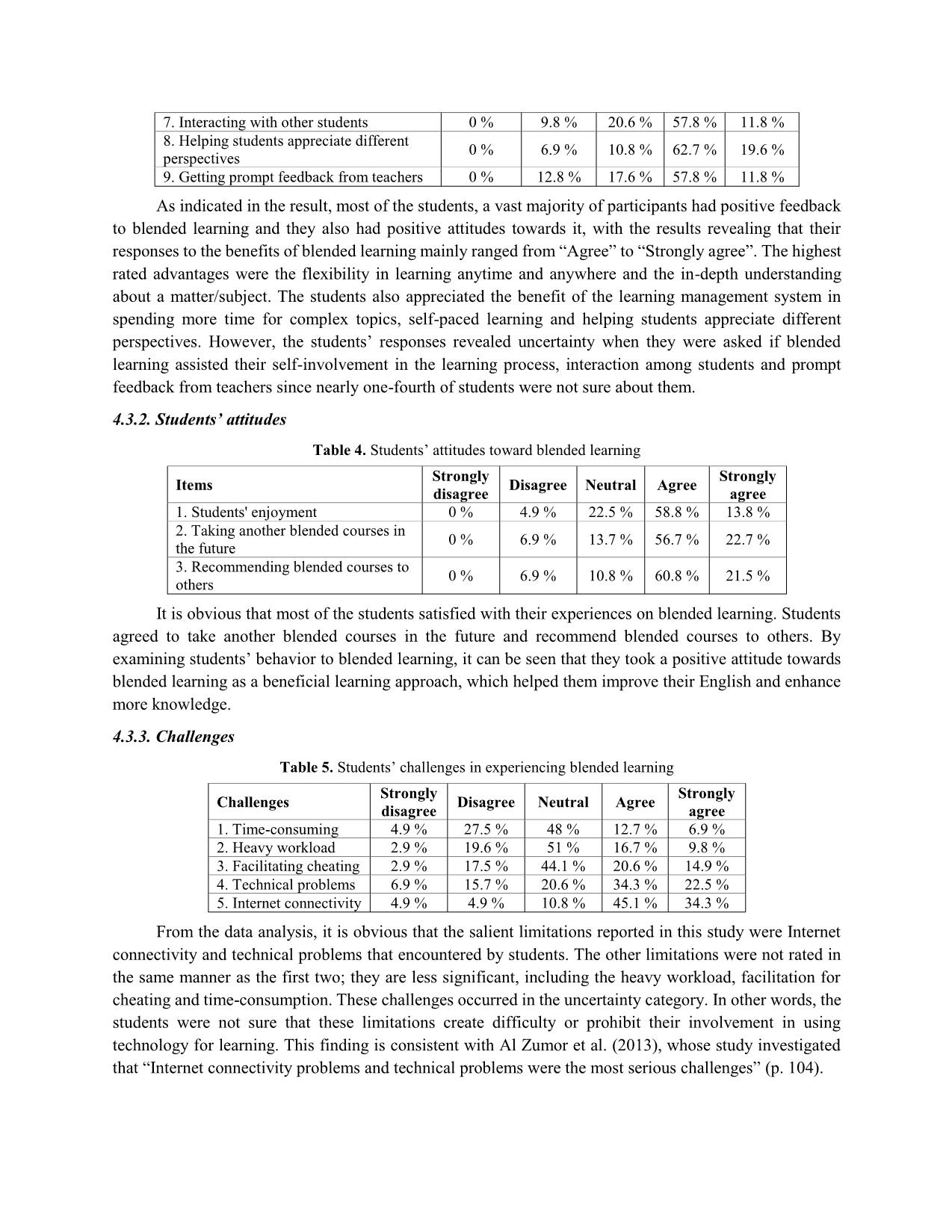
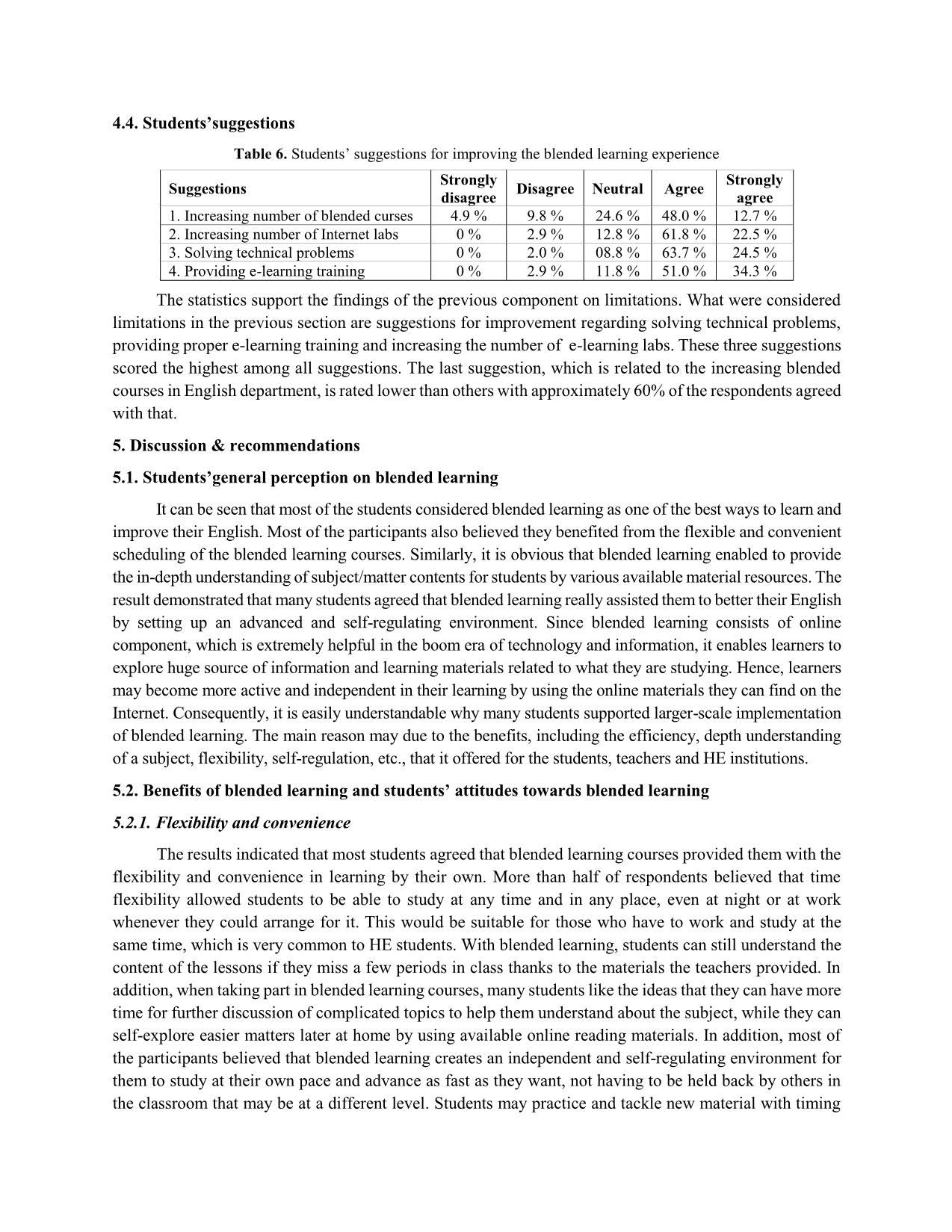
AN INVESTIGATION INTO EFL STUDENTS’ PERCEPTION OF BLENDED LEARNING AT UNIVERSITY OF FOREIGN LANGUAGES, HUE UNIVERSITY Nguyen Hoang Hanh An* Univerity of Foreign Languages, Hue Univerity Received: 02/03/2020; Revised: 10/04/2020; Accepted: 28/04/2020 Abstract: A survey was conducted with 102 students from Hue University of Foreign Languages (HUFL) English Department who had opportunity to take part in blended courses. In addition, a focus group discussion was also administered with 10 voluntary students. The findings from this study revealed the general perception of blended learning of EFL students and expressed their positive attitudes towards blended learning. The study also indicated that the strengths of blended learning outweighed its weaknesses. Some advantages can be listed as flexibility, usefulness, and increased interaction. In addition, the limitations and problems of blended learning cannot be ignored, inluding technical and Internet problems, time-consuming procedure, heavy workload and plagiarism. Those challenges are followed by a number of practical suggestions for addressing the drawbacks, including solving technical and Internet problems, providing proper training to students, increasing the number of labs blended courses. Students’ acceptance of blended learning was also shown from their preference to take another blended course in the future and their liking to recommend for their friends. Keywords: Blended learning, EFL learners, benefits, challenges 1. Introduction 1.1. Background of study In the boom era of technology and information, computers and the Internet have had an essential effect on every aspect of human life, especially education. The advances in technology and developments in teaching and learning methodologies have presented new circumstances for more effective implementation of learning programs. Apart from the existence of the traditional face-to-face classroom, the technology development has led to the birth of a new learning environment that is called blended- learning. One of the areas where the application of blended learning takes place is in higher educational institutions, which include universities and colleges. Over the last decade, blended learning has been growing in demand and popularity in higher education and has become a widespread teaching phenomenon. However, while blended learning is well-received in western societies, levels of success vary in Asian countries because of a number of challenges relating to different cultural backgrounds, different attitudes, as well as issues around implementation (Tham & Tham, 2011). With the development of information technology, Vietnamese educators have identified the integration of ICT (Information and Communication Technology) in education as one of the vital ways to achieve its aim of developing a modern education system. The use of ICT in education and training has been encouraged to increase. Blended learning, a combination of face-to-face learning and online learning, Email: annguyen18997@gmail.com has been introduced to the country with the belief that it can easily broaden the spaces and opportunities available for learning to a large number of learners. Educational institutions in Vietnam are increasingly using blended delivery strategies to deliver course contents to diverse and dispersed student cohorts. Like many other universities, HUCFL has prioritized the development and application of blended- learning in education in order to up-scale and improve training quality. The material facilities and learning sources are being upgraded and supplemented to meet the students’ needs. Expectations and requirements on students in HUCFL are becoming more and more challenging, while they have more time to prepare for the lessons and self-study, which requires both students and teachers to have appropriate learning approach for students’ self-studying activities. Hence, the students need to be flexible in their process of learning by simultaneously using other sources of learning, especially online learning, to obtain information besides taking classes in traditional classroom. 1.2. Research questions 1. What are the students’ general perceptions of blended learning? 2. What are the students’ experiences of blended learning courses? 3. What are students’ suggestions to improve the implementation of blended learning in their language learning? 1.3. Significance The study focuses on examining EFL students’ perception of blended learning at HUFL. This will help in understanding the students’ perception and experience on blended course delivery process and exploring students’ views regarding the advantages and limitations of merging the features of face-to-face language instruction and online language learning in a new pedagogical approach called blended learning. The findings of this study may promote e ... they can find on the Internet. Consequently, it is easily understandable why many students supported larger-scale implementation of blended learning. The main reason may due to the benefits, including the efficiency, depth understanding of a subject, flexibility, self-regulation, etc., that it offered for the students, teachers and HE institutions. 5.2. Benefits of blended learning and students’ attitudes towards blended learning 5.2.1. Flexibility and convenience The results indicated that most students agreed that blended learning courses provided them with the flexibility and convenience in learning by their own. More than half of respondents believed that time flexibility allowed students to be able to study at any time and in any place, even at night or at work whenever they could arrange for it. This would be suitable for those who have to work and study at the same time, which is very common to HE students. With blended learning, students can still understand the content of the lessons if they miss a few periods in class thanks to the materials the teachers provided. In addition, when taking part in blended learning courses, many students like the ideas that they can have more time for further discussion of complicated topics to help them understand about the subject, while they can self-explore easier matters later at home by using available online reading materials. In addition, most of the participants believed that blended learning creates an independent and self-regulating environment for them to study at their own pace and advance as fast as they want, not having to be held back by others in the classroom that may be at a different level. Students may practice and tackle new material with timing that is perfect just for them, which means they can control the pace of their learning. It can promote deeper learning, reduce stress, and increase student satisfaction. 5.2.2. Usefulness As indicated in the result, 68.5% - 83.4% of students agreed blended contents, including available online and offline materials, helped in providing documents for learning, creating understanding of each lecture before attending them and self-involvement in class. This is quite reasonable as in face-to-face classroom, the knowledge is only provided in the textbooks and some reference books, which was not so sufficient for students’ learning. Compared to traditional approach, by using blended learning, the knowledge now can be provided by various sources of materials and by the teachers based on their experiences. Thus, students will be more active in approaching the problems in different ways thanks to those information resources. Moreover, they will be encouraged to involve in the learning process with the knowledge and ideas they prepared before attending the lectures. 5.2.3. Interaction The result showed that most of the students could get benefits from the interaction with their peers and teachers. In face-to-face class, because of the limitation of time, students did not have opportunities to listen to all of their friends’ opinions; similarly, teachers could not give every student feedback in a timely manner. But with blended learning, the interaction between students with their teachers and peers can be significantly increased by means of communication tools. Students may also feel free to express their ideas at any time to get involved in online class discussions. Additionally, a large number of students agreed that different opinions from other peers could help them approach the problem from different angles, which was very helpful for the development of their lateral thinking. 5.2.4. Attitude From the result, it is obvious that most of the students satisfied with their experiences on blended learning course. Thanks to the benefits that blended learning provided during the course delivery, many students might choose to take more blended courses in the future. Additionally, there was a strong agreement that blended learning should be recommended to students who had no experience of it before. It seemed students were very enthusiastic about introducing blended learning to their friends. This is understandable since blended learning was a very efficient learning approach that is pretty new to students, especially those who have been studying in HUCFL. By examining students’ behavior to blended learning, it can be seen that they took a positive attitude towards blended learning as a beneficial learning approach, which helped them improve their English and enhance more knowledge. 5.2.5. Students’ challenges in experiencing blended learning Five statements were presented in the survey in this category, and the students were requested to express their opinions using the five-point Likert Scale as explained in the methodology section. Of those statements, Internet connectivity problems and technical problems rated the highest and were the most serious challenges. This finding is quite significant and must be seriously considered by institutions before and during introduction of technology to EFL students if students are to accept technology in their learning. Moreover, in the students' answers to the open-ended question regarding the problems and limitations of the e-learning mode, most of the students mentioned technical and the Internet problems as the major challenge to their learning process. The remaining limitations and problems as shown in table 5 are less significant, including the heavy workload, facilitation for cheating and waste of time. However, the other limitations cannot be underestimated, since there were about 20.5% - 32.5% of students who still agreed to the undesirable aspects of blended learning, which comprise “Blended learning is time-consuming”, “Blended learning can lead students to cheating and other unethical practices” and “The workload of online component of blended learning is too heavy”. The reason for a few of these disagreements could be the free and uncontrolled access to the online contents and lack of time management skill. 5.3. Students’suggestions The centrality of students in the instructional process has become integral in academic institutions of higher education today. Surveying students’ suggestions for improving their learning environment is expected to be crucial in enhancing students’ satisfaction. Table 5 shows the students' suggested priorities for a better blended learning environment. Solving the students' technical problems, providing them with proper training, and increasing the number of labs are believed to be key suggestions for creating an environment conducive to successful blended learning. The fact that students agreed with these suggestions indicates their dissatisfaction with the manner in which the current infrastructure serves their desired purposes. Recognition of students' distinguished performance is effective in contributing to their increased use of technological systems for learning. The last suggestion, which is related to the increasing blended courses in the English Department, is rated lower than others with approximately 60% of the respondents agreed with that. However, there were nearly one-fourth of the participants who neither supported nor rejected the increasing number of blended courses in learning process. Those students might think that it may lead to aggravating students’ suffering as they could spend too much time only finishing the online tasks so that they would not have enough time for other subjects. There were some interesting ideas appearing in the qualitative data. Some participants proposed that teachers should balance the classwork and online homework to reduce stress for students. They suggested that the online work should be split into small task and be given clear deadline. A few of them gave the idea that teachers should instruct them carefully how to apply blended learning to their learning. It is understandable as there was lack of e-learning training for students in the university, hence the teachers had to play the role of technical trainers to instruct students how to apply technology in their learning. 5.4. Recommendations For teachers in higher education, they should develop a clearer course delivery standard to balance the online and face-to-face course time. Additionally, teachers should equip themselves with sufficient knowledge about the online tools or software before applying them to the blended course to teach students. They should also be aware of their students' needs and abilities and choose the suitable software for them. Finally, teachers can employ communication tools online to create more opportunities for students’ collaborative learning. For university leaders, the ICT directorate should give an emphasis by installing and maintaining wired and wireless Internet access. Similarly, lack of ICT infrastructure that could affect students’ course commitment should be solved by providing more Internet labs with sufficient devices. Lastly, institutions should provide - and actively promote - training for students in the use of technologies that students will use in their courses. 6. Conclusion Blended learning remains a relatively new concept at many academic institutions; however, recent research appears to indicate that when "appropriately" implemented, blended learning can significantly improve the learning experience (Marsh, 2012). The present study has contributed to investigating students’ perceptions on blended learning and proving the strengths of blended language learning for EFL learners. The component on advantages clearly demonstrates how blended learning provides an environment for more effective employment of language learning. Additionally, a vast majority of participants had a positive attitude towards blended learning because of its benefits they experienced on blended courses. Despite of its positive perception, a few students in this study indicated some challenges hindering the effectiveness of the blended learning environment. Technical problems, especially problems with the Internet transmission, were reported as the main obstacle to students’ learning experiences. The other limitations were less significant, including waste of time, heavy workload and cheating problems. These challenges occurred in the uncertainty category since many students answered that they were not sure whether those limitations could create difficulty for their involvement in blended learning environment. The institution leaders must take such obstacles quite seriously. To address these problems, students' suggestions for solving their technical problems, providing proper training to students, increasing the number of labs, etc... should be translated into an action plan and a road map to enhance the effectiveness of using blended learning to create supportive learning opportunities for language learners. References Al Zumor, A.L.W.Q., Al Refaai, I.K., Eddin, E.A.B., & Al-Rahman, F.H.A. (2013). EFL students’ perceptions of a blended learning environment: Advantages, limitations and suggestions for improvement. English Language Teaching, 6(10), 95-110. Badawi, M.F. (2009). Using blended learning for enhancing EFL prospective teachers' pedagogical knowledge and performance. Conference paper: Learning & language - The spirit of the age. Cairo: Ain Shams University. Graham, C.R. (2006). Blended learning systems: Definitions, current trends and future directions. In C.J. Bonk & C.R. Graham (Eds.), The handbook of blended learning: Global perspective, local designs (pp. 3-21). San Francisco, CA: Pfeiffer. Graham, C.R. (2013). Emerging practice and research in blended learning. In M.G. Moore (Ed.), Handbook of distance education (3rd edition) (pp. 333-350). New York: Routledge. Grgurovic, M. (2010). Technology-enhanced blended learning in an ESL class: A description of a model and an application of the diffusion of innovation theories. Doctoral dissertation. Iowa State University. Marsh, D. (2012). Blended learning creating learning opportunities for language learners. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Partridge, H., Ponting, D., & McCay, M. (2011). Good practice report: Blended learning. Australian learning and teaching council. Retrieved from: Sharma, P., & Barrett, B. (2007). Blended learning: Using technology in and beyond the language classroom. Oxford: Macmillan Education. Stacey, E., & Gerbic, P. (2008). Success factors for blended learning. In Hello! Where are you in the landscape of educational technology? Proceedings ASCILITE Melbourne 2008. Retrieved from: Stodel, E.J., Thompson, T.L., & MacDonald, C.J. (2006). Learners' perspectives on what is missing from online learning: Interpretations through the community of inquiry framework. The International Review of Research in Open and Distance Learning, 7(3), 1-24. Tham, K., & Tham, C. (2011). Blended learning - A focus study on Asia. International Journal of Computer Science Issues, 8(2), 1694-0814. Retrieved from: Vaughan, N.D. (2007). Perspectives on blended learning in higher education. International Journal on E-learning, 6(1), 81-94. NGHIÊN CỨU VỀ NHẬN THỨC CỦA SINH VIÊN TIẾNG ANH ĐỐI VỚI VIỆC HỌC KẾT HỢP TẠI TRƯỜNG ĐẠI HỌC NGOẠI NGỮ, ĐẠI HỌC HUẾ Tóm tắt: Một cuộc khảo sát được tiến hành trên 102 sinh viên Khoa Tiếng Anh, Trường Đại học Ngoại ngữ, Đại học Huế đã có cơ hội tham gia vào các khoá học kết hợp. Bên cạnh đó, một buổi thảo luận nhóm tập trung cũng được tổ chức với 10 sinh viên tự nguyện tham gia. Những phát hiện từ nghiên cứu này cho thấy nhận thức chung của sinh viên học tiếng Anh với việc học kết hợp cũng như biểu đạt thái độ tích cực với cách học này. Nghiên cứu cũng chỉ ra những điểm mạnh của việc học kết hợp vượt xa những khó khăn mà nó mang lại. Một số ưu điểm có thể liệt kê ra bao gồm tính linh hoạt, hữu dụng và tương tác. Bên cạnh đó, chúng ta cũng không thể bỏ qua một số vấn đề và hạn chế của việc học kết hợp, bao gồm vấn đề về kĩ thuật và kết nối Internet, quá trình thực hiện tốt thời gian, khối lượng công việc nặng và vấn nạn đạo văn. Những thách thức này có thể được giải quyết bởi một số kiến nghị thiết thực, trong đó có các giải pháp như giải quyết các vấn đề về kỹ thuật và kết nối Internet, cung cấp cho sinh viên chương trình đào tạo phù hợp, tăng số lượng phòng máy cũng như số lượng các khoá học kết hợp. Sự hoan nghênh của sinh viên đối với phương pháp học kết hợp cũng đã được thể hiện qua sự yêu thích và mong muốn có thể tham gia các khoá học kết hợp khác trong tương lai cũng như mong muốn có thể giới thiệu chúng đến với bạn bè xung quanh. Từ khoá: Học kết hợp, sinh viên học tiếng Anh, thuận lợi, thách thức
File đính kèm:
 an_investigation_into_efl_students_perception_of_blended_lea.pdf
an_investigation_into_efl_students_perception_of_blended_lea.pdf

